It was therefore shortly after the discovery of g that Spearman’s contemporary, Godfrey Thomson, proposed that the general factor represents a global network phenomenon 11, 12, 13. Thomson held that g emerges from the interaction among the many elements of the brain, which he referred to as neural arcs or bonds 14, 15. According to Thomson’s Sampling Theory of Mental Ability, each item on an achievement test samples a number of these bonds 11, 12, 13. He proposed that the degree of overlap among bonds accounted for the correlation between tests and the resulting positive manifold. Thus, Thomson’s theory was the first to show that Spearman’s discovery of the general factor of intelligence is consistent with a network perspective.
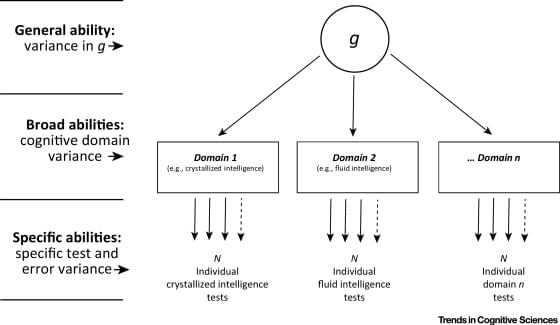
Thomson’s legacy can be found in modern psychological theories which posit that g originates from the mutual interactions among cognitive processes [16]. Individual differences in g are known to be influenced, for example, by language abilities 10, 17, which facilitate a wealth of cognitive, social, and affective processes through mutual interactions (i.e., reciprocal causation) [18]. The central idea of the Mutualism Model is that change or growth in one aspect of mental ability is (i) partially autonomous (owing to developmental maturation), and is also (ii) based on growth in other areas (owing to the mutual interaction between cognitive processes). By accounting for both the autonomous and interactive nature of cognitive processes, this model is able to explain individual differences in the general factor of intelligence – accounting for the positive manifold and the hierarchical pattern of correlations among tests [16].
Advances in network neuroscience have further sharpened Thomson’s notion of neural bonds, revealing principles of brain organization that support (i) the modularity of cognitive processes (enabling the autonomy of mental processes), and (ii) the dynamic reorganization of this modular architecture in the service of system-wide flexibility and adaptation (enabling mutual interactions between cognitive processes). The following sections review these principles of brain organization and introduce a Network Neuroscience Theory for understanding individual differences in the general factor of intelligence based on the small-world topology and network dynamics of the human brain. This framework relies upon formal concepts from network neuroscience and their application to understanding the neurobiological foundations of g.