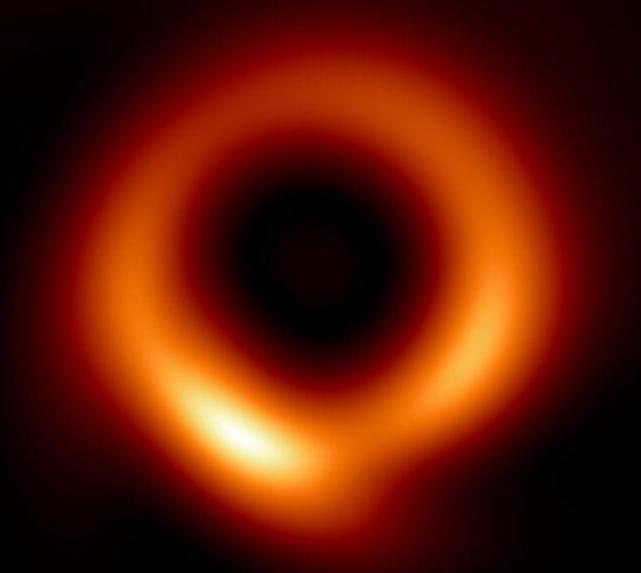
Astronomers have used machine learning to sharpen the 2019 Event Horizon Telescope image of the black hole M87*, the first direct image of a black hole ever taken.
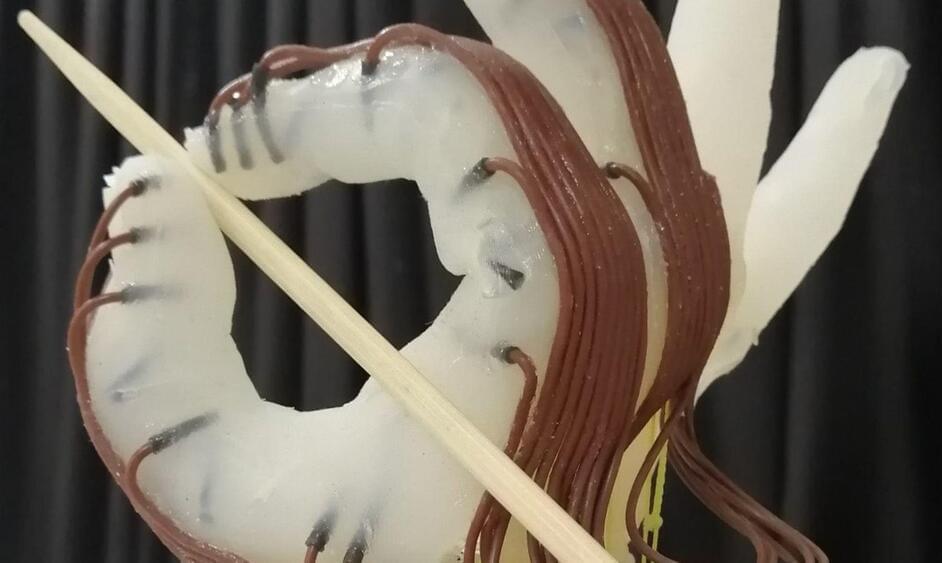



The 3D-printed appendage is designed to be low-cost and energy-efficient, capable of carrying out complex movements despite not being able to use each finger independently.
Professor Fumiya Iida, of the University of Cambridge’s Bio-Inspired Robotics Laboratory, said the goal was to “simplify the hand as much as possible”.

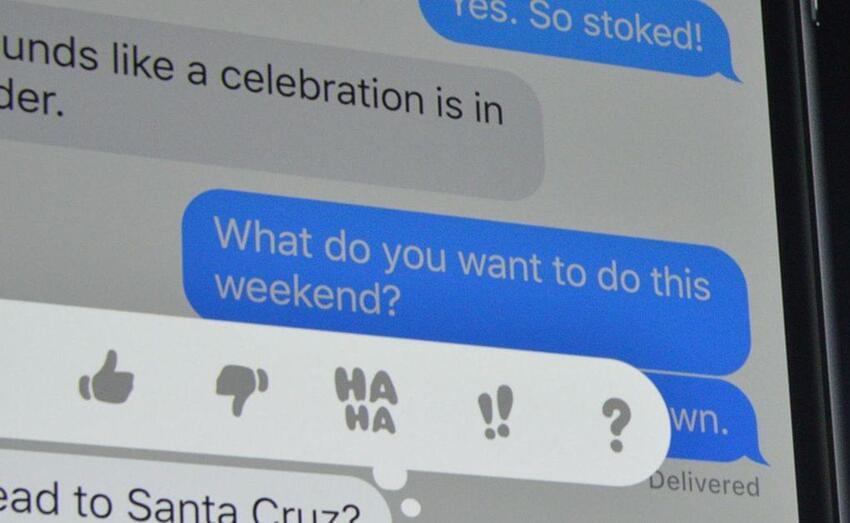
As data scientist Izzy Miller puts it, the group chat is “a hallowed thing” in today’s society. Whether located on iMessage, WhatsApp, or Discord, it’s the place where you and your best friends hang out, shoot the shit, and share updates about life, both trivial and momentous. In a world where we are increasingly bowling alone, we can, at least, complain to the group chat about how much bowling these days sucks ass.
“My group chat is a lifeline and a comfort and a point of connection,” Miller tells The Verge. “And I just thought it would be hilarious and sort of sinister to replace it.”
So he did.

Amazon is throwing its hat into the generative AI ring. But rather than build AI models entirely by itself, it’s recruiting third parties to host models on AWS today unveiled Amazon Bedrock, which provides a way to build generative AI-powered apps via pretrained models from startups including AI21 Labs, Anthropic and Stability AI. Available in a “limited preview,” Bedrock also offers access to Titan FMs (foundation models), a family of models trained in-house by AWS.
AWS today unveiled Amazon Bedrock, which provides a way to build generative AI-powered apps via pretrained models from startups including AI21 Labs, Anthropic and Stability AI. Available in a “limited preview,” Bedrock also offers access to Titan FMs (foundation models), a family of models trained in-house by AWS.
“Applying machine learning to the real world — solving real business problems at scale — is what we do best,” Vasi Philomin, VP of generative AI at AWS, told TechCrunch in a phone interview. “We think every application out there can be reimagined with generative AI.”

Italy’s data protection watchdog has laid out what OpenAI needs to do for it to lift an order against ChatGPT issued at the end of last month — when it said it suspected the AI chatbot service was in breach of the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and ordered the U.S.-based company to stop processing locals’ data.
The EU’s GDPR applies whenever personal data is processed, and there’s no doubt large language models such as OpenAI’s GPT have hoovered up vast amounts of the stuff off the public internet in order to train their generative AI models to be able to respond in a human-like way to natural language prompts.
OpenAI responded to the Italian data protection authority’s order by swiftly geoblocking access to ChatGPT. In a brief public statement, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman also tweeted confirmation it had ceased offering the service in Italy — doing so alongside the usual Big Tech boilerplate caveat that it “think[s] we are following all privacy laws.”

The court claimed that after posing a number of inquiries to the AI chatbot, it was pleased with the responses received.
A municipal court in Pakistan has announced its judgment using artificial intelligence technology, a first for the Asian country.
The case was processed by ChatGPT-4, OpenAI’s cutting-edge AI chatbot, before the local judge announced the decision, Samaa reported on Wednesday.

The company is offering rewards ‘for exceptional discoveries’.
OpenAI, the creator of conversational chatbot ChatGPT, has announced a Bug Bounty program where users can report “vulnerabilities, bugs, or security flaws” and be financially rewarded for finding them. The company has announced rewards ranging from $200 to $20,000 depending on the severity of the flaw and teamed up with a popular bug-finding platform to streamline the process.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT has ushered in a race for artificial intelligence (AI) models that provide comprehensive solutions to user queries and can even simulate intriguing imagery with the help of a few text prompts.
Sestovic/iStock.
While the technology is advancing at a breathtaking pace and producing some mind-boggling results, there are also concerns about these products’ safety. AI researchers like Stuart Russell have warned that unchecked, the rise of AI could result in a Chernobyl-like incident for the tech industry.
It’s not unusual for a company to try and innovate on an existing products or technology, but robotics firm Flexiv promises that its massaging robot won’t be like the mechanical massagers of the past.
Robotic or mechanical messagers are hardly a new idea, but a robotics firm called Flexiv is hoping that its new robot masseuse will succeed where others have succeeded at becoming a novelty at best and an embarrassing disaster at worst.
Announced earlier this week on its website, Flexiv is debuting its Rizon 4 robot which has been developed to enable a fully automatic massage experience.
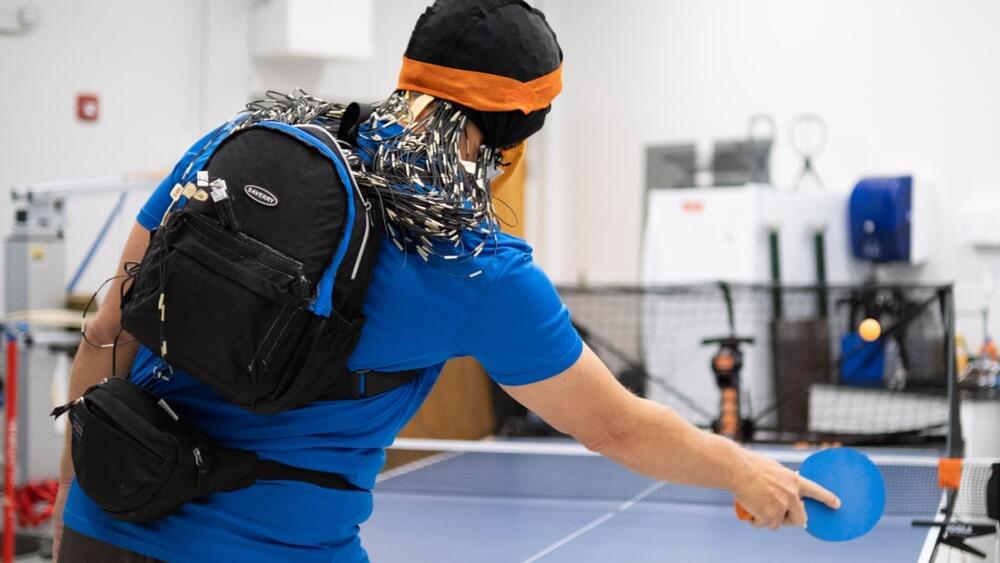

To analyze the human player’s brain, the team designed a cap with over 100 electrodes mounted on a backpack-sized device.
A one-of-a-kind study documents how a human brain reacts when playing table tennis against a robotic opponent.
Scanning the brain activity with electrodes.
Frazier Springfield.
This study by the University of Florida scientists provides intriguing insights into human brain activity. The findings revealed that human players’ brains reacted differently to opponents (other humans and ball machines). And playing against a robotic opponent was much more difficult for the human brain.