Jan Leike explains OpenAI’s effort to protect humanity from superintelligent AI.




Please see my new FORBES article:
Thanks and please follow me on Linkedin for more tech and cybersecurity insights.
More remarkably, the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning-based computers in the next century may alter how we relate to ourselves.
The digital ecosystem’s networked computer components, which are made possible by machine learning and artificial intelligence, will have a significant impact on practically every sector of the economy. These integrated AI and computing capabilities could pave the way for new frontiers in fields as diverse as genetic engineering, augmented reality, robotics, renewable energy, big data, and more.
Three important verticals in this digital transformation are already being impacted by AI: 1) Healthcare, 2) Cybersecurity, and 3) Communications.
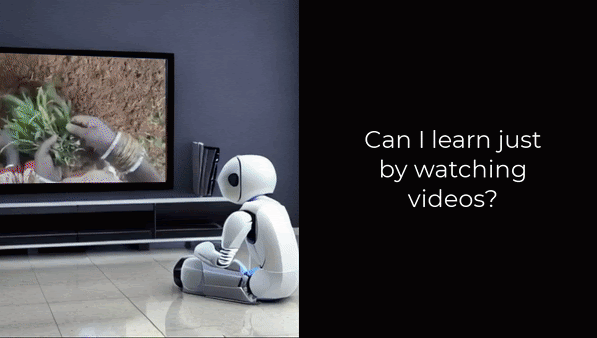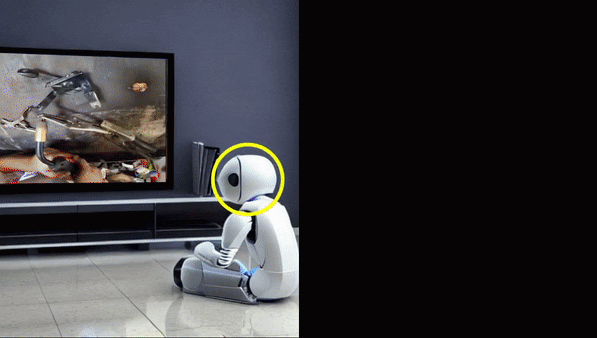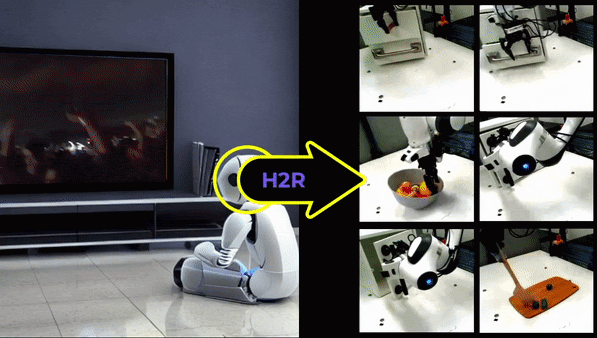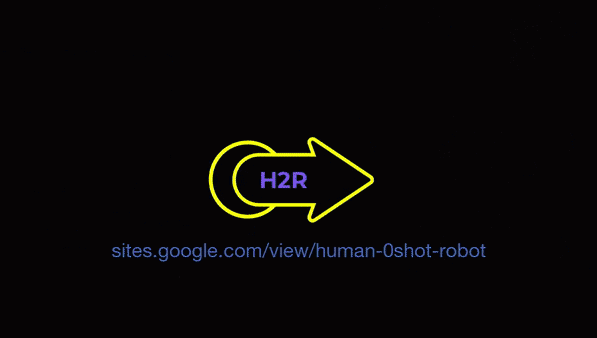
Can we learn robot manipulation for everyday tasks, only by watching videos of humans doing arbitrary tasks in different unstructured settings? Unlike widely adopted strategies of learning task-specific behaviors or direct imitation of a human video, we develop a a framework for extracting agent-agnostic action representations from human videos, and then map it to the agent’s embodiment during deployment. Our framework is based on predicting plausible human hand trajectories given an initial image of a scene. After training this prediction model on a diverse set of human videos from the internet, we deploy the trained model zero-shot for physical robot manipulation tasks, after appropriate transformations to the robot’s embodiment. This simple strategy lets us solve coarse manipulation tasks like opening and closing drawers, pushing, and tool use, without access to any in-domain robot manipulation trajectories. Our real-world deployment results establish a strong baseline for action prediction information that can be acquired from diverse arbitrary videos of human activities, and be useful for zero-shot robotic manipulation in unseen scenes.

With careful development and thoughtful approaches, Kazi believes the changes AI will bring to healthcare will be some of the most exciting technological advances of our lifetime.
Learn more about building a modern data foundation to deliver the next generation of personalized healthcare with AI, ML, and generative AI.
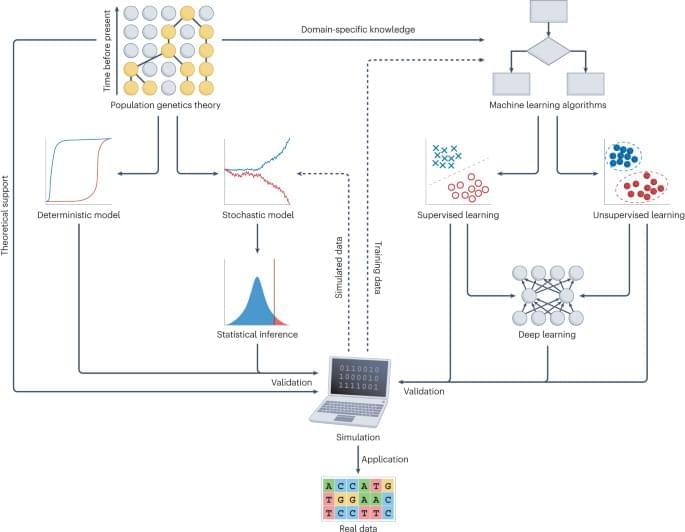
Applying deep learning to large-scale genomic data of species or populations is providing new opportunities to understand the evolutionary forces that drive genetic diversity. This Review introduces common deep learning architectures and provides comprehensive guidelines to implement deep learning models for population genetic inference. The authors also discuss current opportunities and challenges for deep learning in population genetics.
A molecular assembler, as defined by K. Eric Drexler, is a “proposed device able to guide chemical reactions by positioning reactive molecules with atomic precision”. A molecular assembler is a kind of molecular machine. Some biological molecules such as ribosomes fit this definition. This is because they receive instructions from messenger RNA and then assemble specific sequences of amino acids to construct protein molecules. However, the term “molecular assembler” usually refers to theoretical human-made devices.
Beginning in 2007, the British Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council has funded development of ribosome-like molecular assemblers. Clearly, molecular assemblers are possible in this limited sense. A technology roadmap project, led by the Battelle Memorial Institute and hosted by several U.S. National Laboratories has explored a range of atomically precise fabrication technologies, including both early-generation and longer-term prospects for programmable molecular assembly; the report was released in December, 2007. In 2008 the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council provided funding of 1.5 million pounds over six years for research working towards mechanized mechanosynthesis, in partnership with the Institute for Molecular Manufacturing, amongst others. Likewise, the term “molecular assembler” has been used in science fiction and popular culture to refer to a wide range of fantastic atom-manipulating nanomachines, many of which may be physically impossible in reality. Much of the controversy regarding “molecular assemblers” results from the confusion in the use of the name for both technical concepts and popular fantasies. In 1992, Drexler introduced the related but better-understood term “molecular manufacturing”, which he defined as the programmed “chemical synthesis of complex structures by mechanically positioning reactive molecules, not by manipulating individual atoms”.This article mostly discusses “molecular assemblers” in the popular sense. These include hypothetical machines that manipulate individual atoms and machines with organism-like self-replicating abilities, mobility, ability to consume food, and so forth. These are quite different from devices that merely (as defined above) “guide chemical reactions by positioning reactive molecules with atomic precision”.
Because synthetic molecular assemblers have never been constructed and because of the confusion regarding the meaning of the term, there has been much controversy as to whether “molecular assemblers” are possible or simply science fiction. Confusion and controversy also stem from their classification as nanotechnology, which is an active area of laboratory research which has already been applied to the production of real products; however, there had been, until recently, no research efforts into the actual construction of “molecular assemblers”.
Nonetheless, a 2013 paper by David Leigh’s group, published in the journal Science, details a new method of synthesizing a peptide in a sequence-specific manner by using an artificial molecular machine that is guided by a molecular strand. This functions in the same way as a ribosome building proteins by assembling amino acids according to a messenger RNA blueprint. The structure of the machine is based on a rotaxane, which is a molecular ring sliding along a molecular axle. The ring carries a thiolate group which removes amino acids in sequence from the axle, transferring them to a peptide assembly site. In 2018, the same group published a more advanced version of this concept in which the molecular ring shuttles along a polymeric track to assemble an oligopeptide that can fold into a α-helix that can perform the enantioselective epoxidation of a chalcone derivative (in a way reminiscent to the ribosome assembling an enzyme). In another paper published in Science in March 2015, chemists at the University of Illinois report a platform that automates the synthesis of 14 classes of small molecules, with thousands of compatible building blocks. In 2017 David Leigh’s group reported a molecular robot that could be programmed to construct any one of four different stereoisomers of a molecular product by using a nanomechanical robotic arm to move a molecular substrate between different reactive sites of an artificial molecular machine. An accompanying News and Views article, titled ‘A molecular assembler’, outlined the operation of the molecular robot as effectively a prototypical molecular assembler.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Molecular_assembler.
Created with WikipediaReaderReborn © WikipediaReader.
The long-sought finding challenges scientists’ understanding of the strong nuclear force, and the AI that can beat human champions at drone racing.

Italian robotics co…
The qb SoftHand2 Research is the stronger, smarter and more versatile evolution of qb SoftHand Research: an anthropomorphic robotic hand with 19 disclosable self-healing finger joints. It is always adaptable and robust, easy-to-use and flexible.
The qb SoftHand2 Research represents a compromise between complexity and dexterity. This new hand is capable of performing both precision and power grips, as well as manipulating objects while maintaining a stable grip.
The introduction of second synergy hallows the qb SoftHand2 Research to manipulate objects intended for interaction with the human hand, without changing the wrist orientation.

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch a humanoid robot into space as part of its Gaganyaan mission, its first human spaceflight mission.
The much-delayed mission is back on track after ISRO successfully landed its probe on the moon’s South Pole, a world first.
According to the ISRO, the Gaganyaan project was established to demonstrate human spaceflight capability by launching a three-person crew to an orbit of 248 miles for a three-day mission and then bring them back to Earth safely, landing in Indian sea waters.