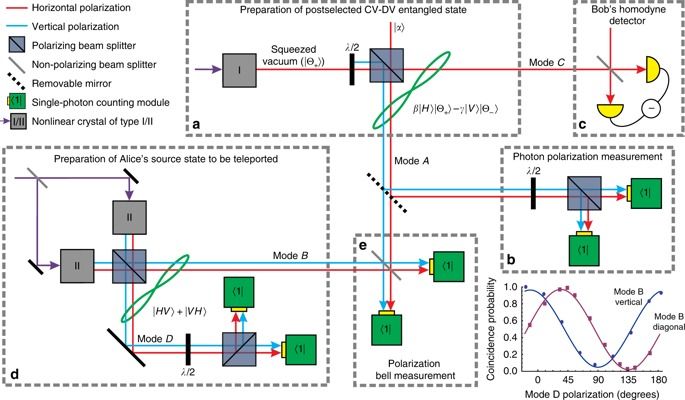
Scientists have developed a topological photonic chip to process quantum information, promising a more robust option for scalable quantum computers.
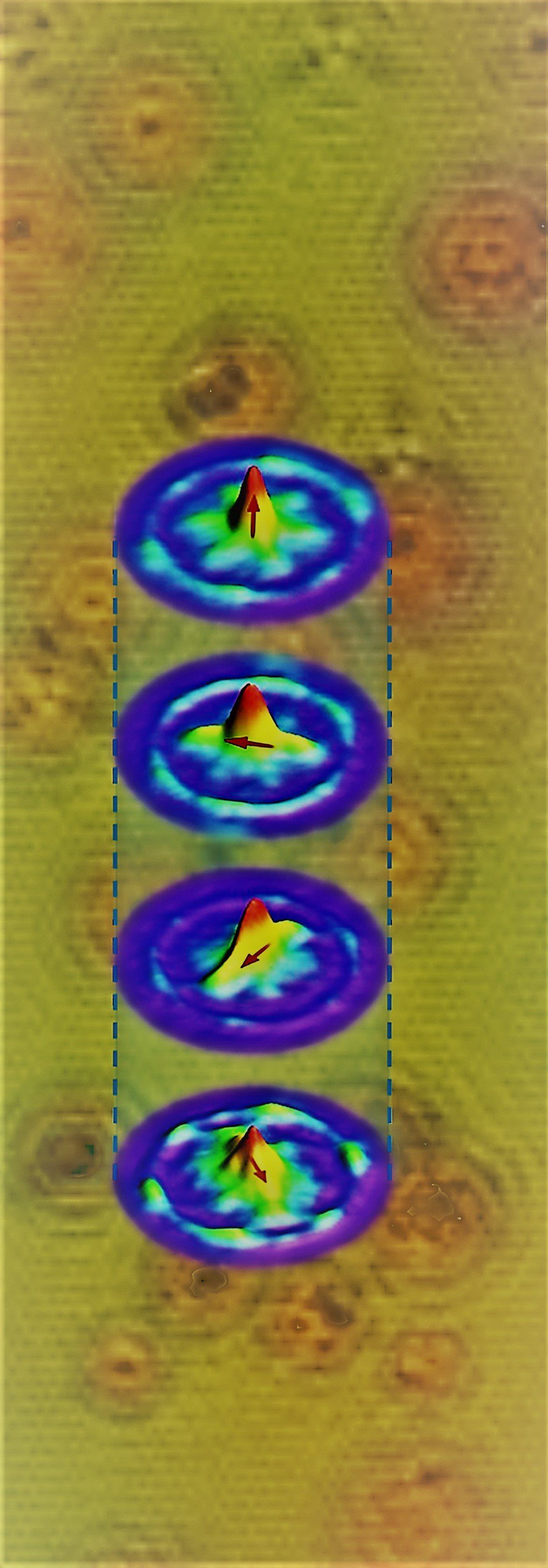
The research team, led by RMIT University’s Dr. Alberto Peruzzo, has for the first time demonstrated that quantum information can be encoded, processed and transferred at a distance with topological circuits on the chip. The research is published in Science Advances.
The breakthrough could lead to the development of new materials, new generation computers and deeper understandings of fundamental science.