Alice controls Bob via quantum measurements. Bob can’t reciprocate.


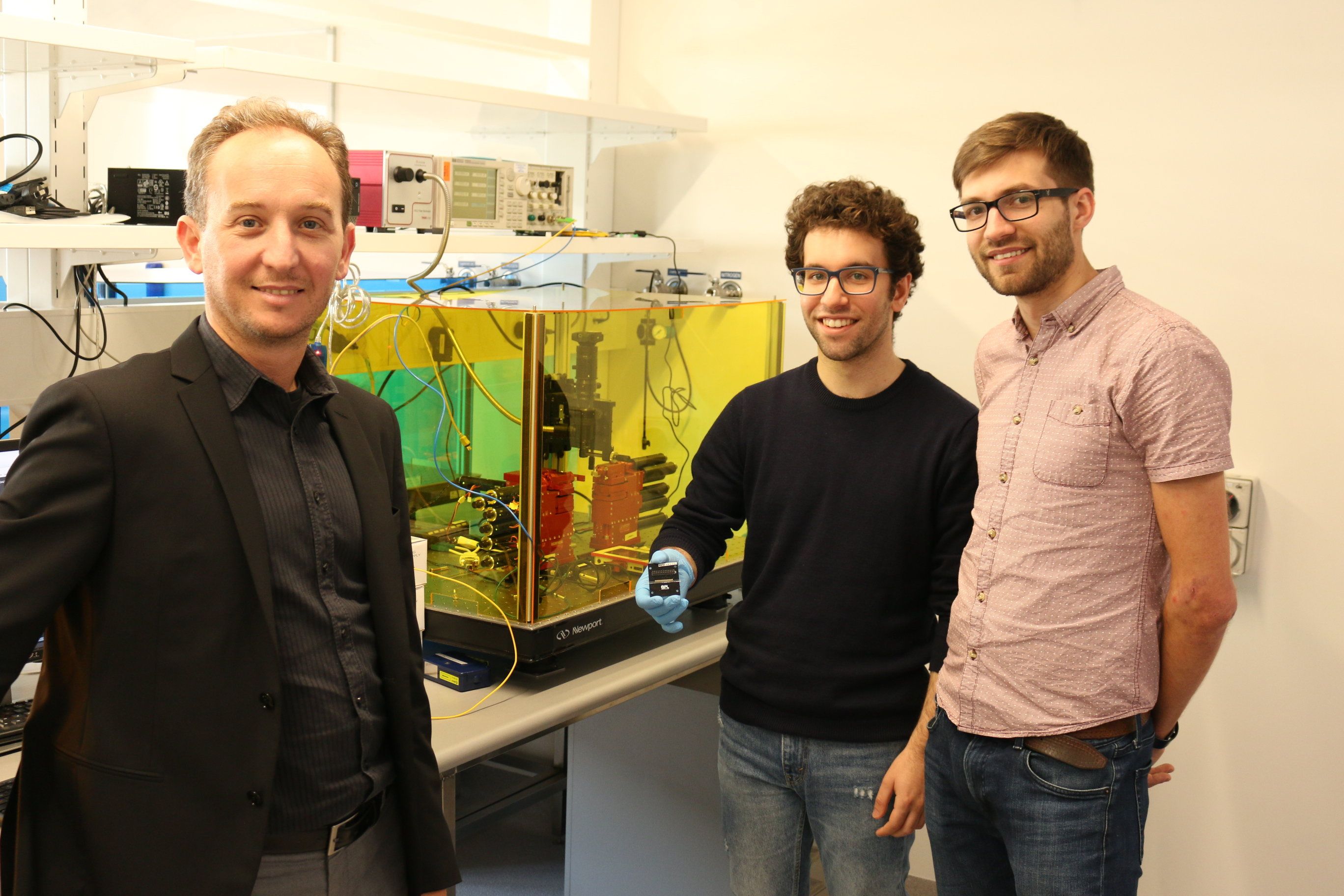
Scientists have developed a topological photonic chip to process quantum information, promising a more robust option for scalable quantum computers.
The research team, led by RMIT University’s Dr. Alberto Peruzzo, has for the first time demonstrated that quantum information can be encoded, processed and transferred at a distance with topological circuits on the chip. The research is published in Science Advances.
The breakthrough could lead to the development of new materials, new generation computers and deeper understandings of fundamental science.
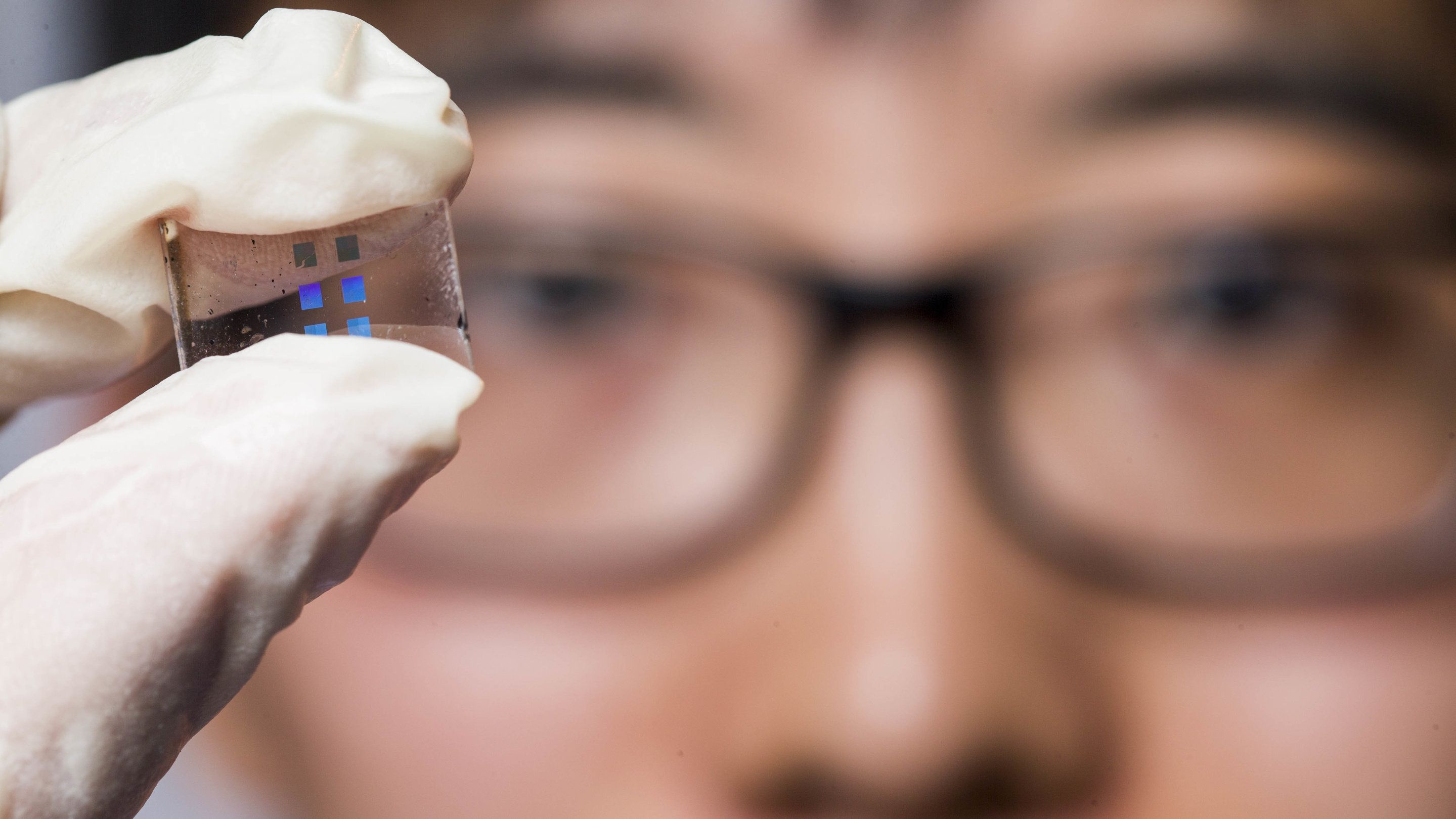
An international team of researchers led by The Australian National University (ANU) has invented a tiny camera lens, which may lead to a device that links quantum computers to an optical fibre network.
Quantum computers promise a new era in ultra-secure networks, artificial intelligence and therapeutic drugs, and will be able to solve certain problems much faster than today’s computers.
The unconventional lens, which is 100 times thinner than a human hair, could enable a fast and reliable transfer of quantum information from the new-age computers to a network, once these technologies are fully realised.
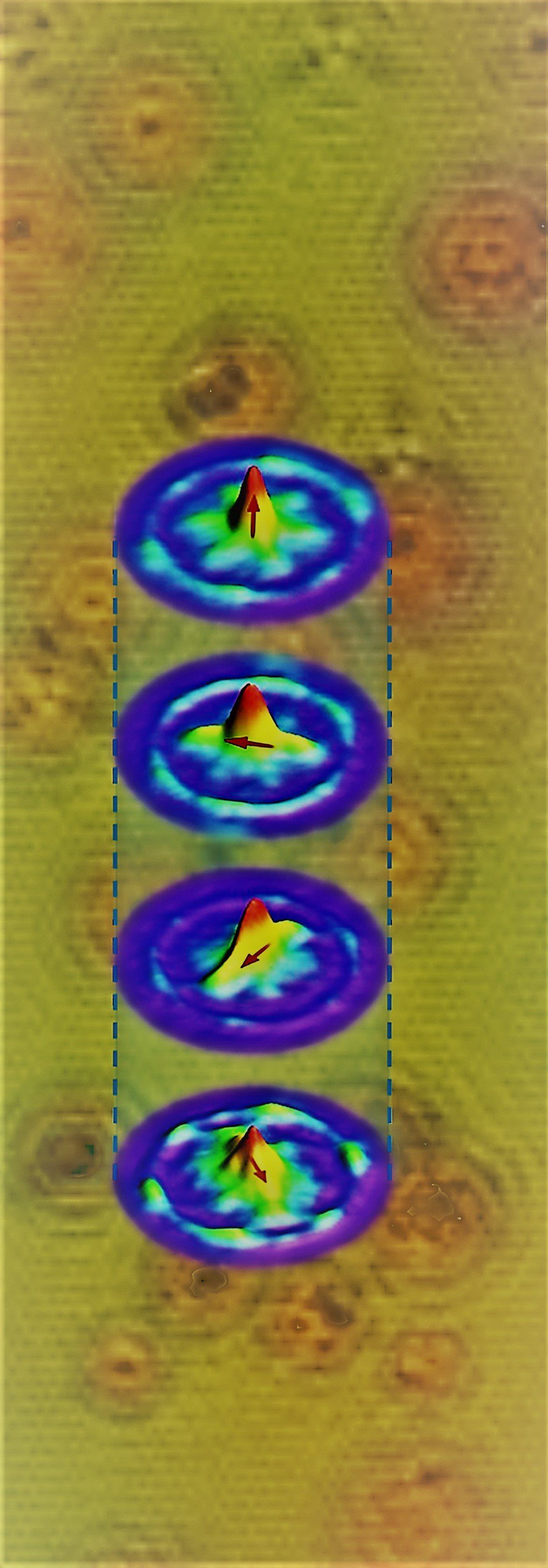
Quantum particles can be difficult to characterize, and almost impossible to control if they strongly interact with each other—until now.
An international team of researchers led by Princeton physicist Zahid Hasan has discovered a quantum state of matter that can be “tuned” at will—and it’s 10 times more tuneable than existing theories can explain. This level of manipulability opens enormous possibilities for next-generation nanotechnologies and quantum computing.
“We found a new control knob for the quantum topological world,” said Hasan, the Eugene Higgins Professor of Physics. “We expect this is tip of the iceberg. There will be a new subfield of materials or physics grown out of this. … This would be a fantastic playground for nanoscale engineering.”
A recent discovery by William & Mary and University of Michigan researchers transforms our understanding of one of the most important laws of modern physics. The discovery, published in the journal Nature, has broad implications for science, impacting everything from nanotechnology to our understanding of the solar system.
“This changes everything, even our ideas about planetary formation,” said Mumtaz Qazilbash, associate professor of physics at William & Mary and co-author on the paper. “The full extent of what this means is an important question and, frankly, one I will be continuing to think about.”
Qazilbash and two W&M graduate students, Zhen Xing and Patrick McArdle, were asked by a team of engineers from the University of Michigan to help them test whether Planck’s radiation law, a foundational scientific principle grounded in quantum mechanics, applies at the smallest length scales.
A system made of just a handful of particles acts just like larger systems, allowing scientists to study quantum behaviour more easily.
Most substances physicists study are made up of huge numbers of particles—so large that there is essentially no difference between the behavioural properties of a drop or a swimming pool’s worth of pure water. Even a single drop can contain more than a quadrillion particles.
This makes understanding their collective behaviour relatively easy. For example, both the water in the drop and in the pool will freeze at 0C and boil at 100C.

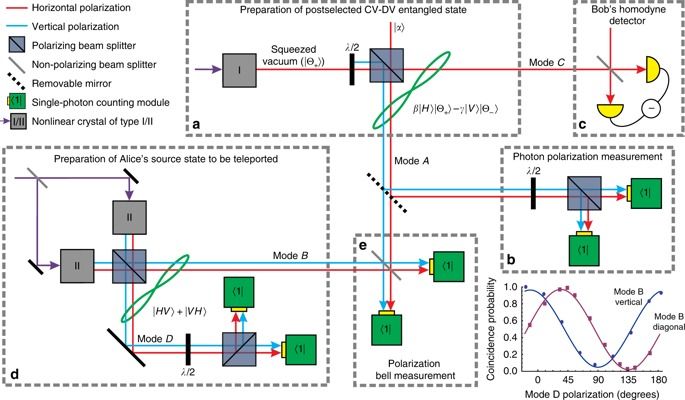
Interfacing quantum information between discrete and continuous would allow exploiting the best of both worlds, but it has been shown only for single-rail encoding. Here, the authors extend this to the more practical dual-rail encoding, realizing teleportation between a polarization qubit and a CV qubit.
Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger (1887−1961), one of the giants of contemporary science, considered entanglement the most interesting property in quantum mechanics. In his view, it was this phenomenon that truly distinguished the quantum world from the classical world. Entanglement occurs when groups of particles or waves are created or interact in such a way that the quantum state of each particle or wave cannot be described independently of the others, however far apart they are. Experiments performed at the University of São Paulo’s Physics Institute (IF-USP) in Brazil have succeeded in entangling six light waves generated by a simple laser light source known as an optical parametric oscillator.
Articles about these experiments have been published in Physical Review Letters and Physical Review A. The experiments are highlighted in a special news feature posted online.
“Our platform is capable of generating a massive entanglement of many optical modes with different but well-defined frequencies, as if connecting the nodes of a large network. The quantum states thus produced can be controlled by a single parameter: the power of the external laser that pumps the system,” said Marcelo Martinelli, one of the coordinators of the experiments. Martinelli is a professor at IF-USP and the principal investigator for the project.
