Researchers at the University of Chicago (UChicago) have recently reported an experimental observation of a matter field with thermal fluctuations that is in accordance with Unruh’s radiation predictions. Their paper, published in Nature Physics, could open up new possibilities for research exploring the dynamics of quantum systems in a curved spacetime.
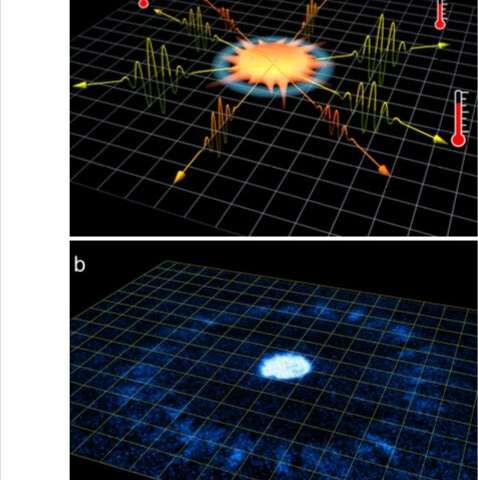
“Our team at UChicago has been investigating a new quantum phenomena called Bose fireworks that we discovered two years ago,” Cheng Chin, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “Our paper reports its hidden connection to a gravitational phenomenon called Unruh radiation.”
The Unruh effect, or Unruh radiation, is closely connected to Hawking radiation. In 1974, theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking predicted that the strong gravitational force near black holes leads to the emission of a thermal radiation of particles, which resembles the heat wave emitted by an oven. This phenomenon remains speculative with no direct experimental confirmation.
Read more