This thorough review focuses on the impact of AI, 5G, and edge computing on the healthcare sector in the 2020s as well as a look at quantum computing’s potential impact on AI, healthcare, and financial services.
Category: quantum physics – Page 888
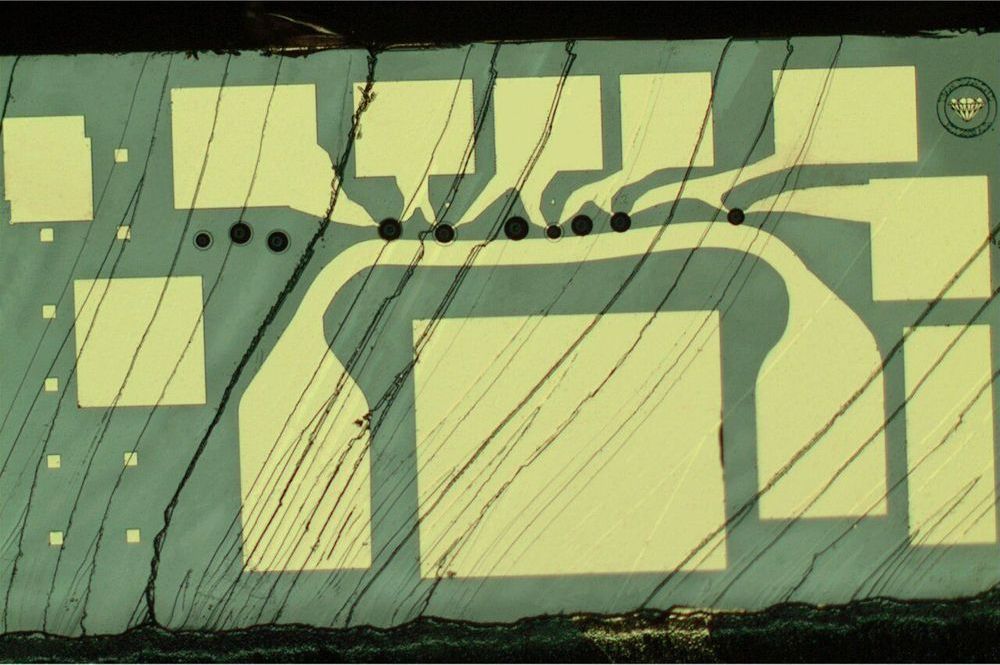

A ten-qubit solid-state spin register with remarkable quantum memory
In years to come, quantum computers and quantum networks might be able to tackle tasks that are inaccessible to traditional computer systems. For instance, they could be used to simulate complex matter or enable fundamentally secure communications.
The elementary building blocks of quantum information systems are known as qubits. For quantum technology to become a tangible reality, researchers will need to identify strategies to control many qubits with very high precision rates.
Spins of individual particles in solids, such as electrons and nuclei have recently shown great promise for the development of quantum networks. While some researchers were able to demonstrate an elementary control of these qubits, so far, no one has reported entangled quantum states containing more than three spins.

This New Chip Could Bridge The Gap Between Classical And Quantum Computing
Quantum computers exist today, although they’re limited, cut-down versions of what we hope fully blown quantum computers are going to be able to do in the future.
But now, researchers have developed hardware for a ‘probabilistic computer’ – a device that might be able to bridge the gap between genuine quantum computers and the standard PCs and Macs we have today.
The special trick that a probabilistic computer can do is to solve quantum problems without actually going quantum, as it were. It does this using a p-bit, which the team behind this research describes as a “poor man’s qubit”.
Quantum Internet Is One Step Closer to Reality With U.S. Army Research Breakthrough
Research Triangle Park, N.C. — A U.S. Army research result brings the quantum internet a step closer. Such an internet could offer the military security, sensing, and timekeeping capabilities not possible with traditional networking approaches.
The U.S. Army’s Combat Capability Development’s Army Research Laboratory’s Center for Distributed Quantum Information, funded and managed by the lab’s Army Research Office, saw researchers at the University of Innsbruck achieve a record for the transfer of quantum entanglement between matter and light — a distance of 50 kilometers using fiber optic cables.
Entanglement is a correlation that can be created between quantum entities such as qubits. When two qubits are entangled and a measurement is made on one, it will affect the outcome of a measurement made on the other, even if that second qubit is physically far away.
Leonard Susskind: Quantum Mechanics, String Theory and Black Holes
Leonard Susskind is a professor of theoretical physics at Stanford University, and founding director of the Stanford Institute for Theoretical Physics. He is widely regarded as one of the fathers of string theory and in general as one of the greatest physicists of our time both as a researcher and an educator. This conversation is part of the Artificial Intelligence podcast.
INFO:
Podcast website:
https://lexfridman.com/ai
iTunes:
https://apple.co/2lwqZIr
Spotify:
https://spoti.fi/2nEwCF8
RSS:
https://lexfridman.com/category/ai/feed/
Full episodes playlist:
Clips playlist:
OUTLINE:
00:00 — Introduction
01:02 — Richard Feynman
02:09 — Visualization and intuition
06:45 — Ego in Science
09:27 — Academia
11:18 — Developing ideas
12:12 — Quantum computers
21:37 — Universe as an information processing system.
26:35 — Machine learning
29:47 — Predicting the future
30:48 — String theory
37:03 — Free will
39:26 — Arrow of time
46:39 — Universe as a computer
49:45 — Big bang
50:50 — Infinity
51:35 — First image of a black hole
54:08 — Questions within the reach of science.
55:55 — Questions out of reach of science.
CONNECT:
- Subscribe to this YouTube channel
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/lexfridman
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/lexfridman
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/lexfridman
- Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/lexfridman
- Medium: https://medium.com/@lexfridman
- Support on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/lexfridman

Project brings quantum internet closer to reality
A U.S. Army research result brings the quantum internet a step closer. Such an internet could offer the military security, sensing and timekeeping capabilities not possible with traditional networking approaches.
The U.S. Army’s Combat Capability Development’s Army Research Laboratory’s Center for Distributed Quantum Information, funded and managed by the lab’s Army Research Office, saw researchers at the University of Innsbruck achieve a record for the transfer of quantum entanglement between matter and light—a distance of 50 kilometers using fiber optic cables.
Entanglement is a correlation that can be created between quantum entities such as qubits. When two qubits are entangled and a measurement is made on one, it will affect the outcome of a measurement made on the other, even if that second qubit is physically far away.
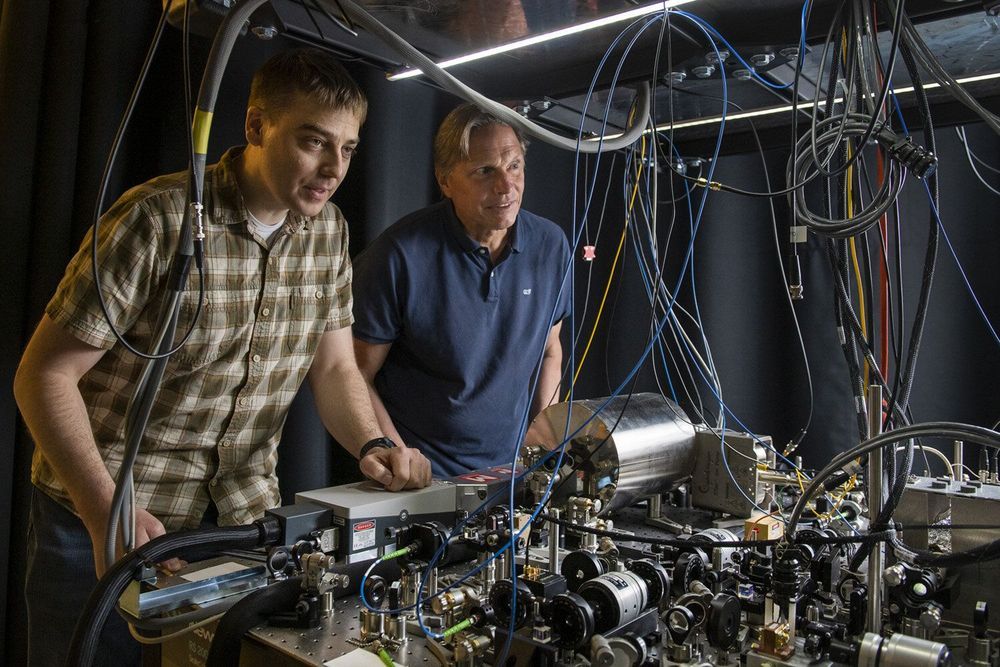
A different kind of gravitational wave detector
Hidden deep in a basement at Stanford stands a 10-meter-tall tube, wrapped in a metal cage and draped in wires. A barrier separates it from the main room, beyond which the cylinder spans three stories to an apparatus holding ultra-cold atoms ready to shoot upward. Tables stocked with lasers to fire at the atoms—and analyze how they respond to forces such as gravity—fill the rest of the laboratory.
The tube is an atom interferometer, a custom-built device designed to study the wave nature of atoms. According to quantum mechanics, atoms exist simultaneously as particles and waves. The Stanford instrument represents a model for an ambitious new instrument ten times its size that could be deployed to detect gravitational waves—minute ripples in spacetime created by energy dissipating from moving astronomical objects. The instrument also could shed light on another mystery of the universe: dark matter.
Stanford experimental physicists Jason Hogan and Mark Kasevich never intended for their device to be implemented this way. When Hogan began his graduate studies in Kasevich’s lab, he focused instead on testing gravity’s effects on atoms. But conversations with theoretical physicist Savas Dimopoulos, a professor of physics, and his graduate students—often lured downstairs by an espresso machine housed directly across the hall from Kasevich’s office—led them to start thinking about its utility as a highly sensitive detector.
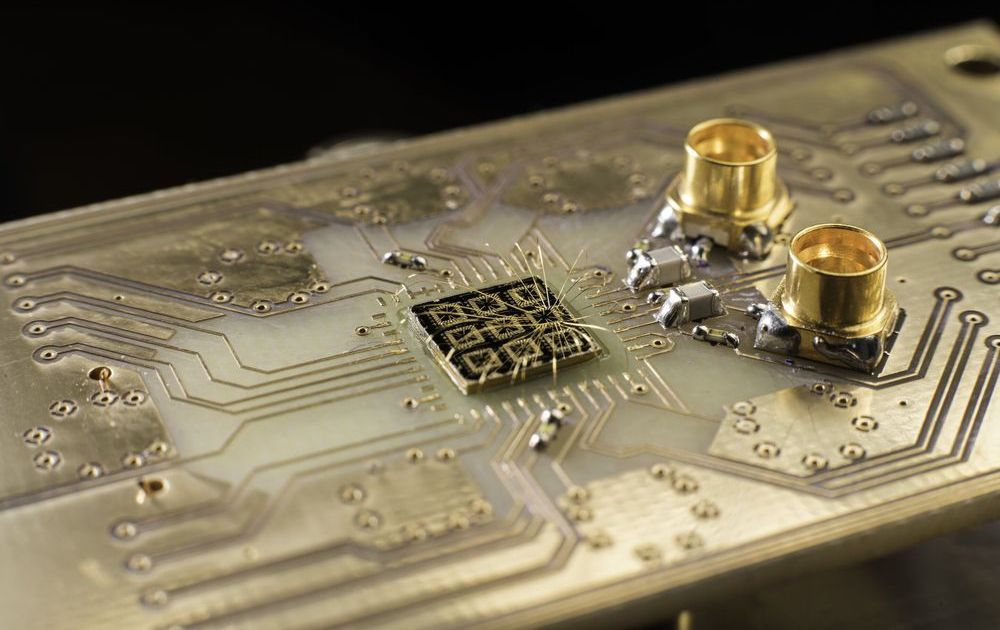
New research brings scientists one step closer to a fully functioning quantum computer
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize technology, medicine, and science by providing faster and more efficient processors, sensors, and communication devices.
But transferring information and correcting errors within a quantum system remains a challenge to making effective quantum computers.
In a paper in the journal Nature, researchers from Purdue University and the University of Rochester, including John Nichol, an assistant professor of physics, and Rochester Ph.D. students Yadav P. Kandel and Haifeng Qiao, demonstrate their method of relaying information by transferring the state of electrons. The research brings scientists one step closer to creating fully functional quantum computers and is the latest example of Rochester’s initiative to better understand quantum behavior and develop novel quantum systems. The University recently received a $4 million grant from the Department of Energy to explore quantum materials.
Big Blue’s Big Leap: Quantum center takes on 53 qubit system
IBM has a fleet of quantum computers. That much is fairly well known since IBM has been actively promoting quantum computing for several years. But IBM’s quantum story will get all the more interesting next month, when a 53 qubit computer joins the line, making it the most powerful quantum computer available for use outside IBM.
“Next month, IBM will make a 53-qubit quantum computer available to clients via its Q Network quantum cloud computing service,” said Bits&Chips. That network, said Asian Scientist Magazine, and grew into an “ecosystem of Fortune 500 companies, start-ups, universities and national research labs.”
IBM’s new machine will be part of the company’s quantum computation center in Poughkeepsie, New York State, marking an unveiling of its 14th quantum computer. The center “is essentially a data center for IBM’s quantum machines,” said Frederic Lardinois in TechCrunch.