Scientists suggest a desktop quantum computer based on nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) could soon be on its way to a classroom near you. Although the device might not be suited to handle large quantum applications, the makers say it could help students learn about quantum computing.
SpinQ Chief Scientist Prof. Bei Zeng from University of Guelph, announced the SpinQ Gemini, a two-qubit desktop quantum computer, at the industry session of the Quantum Information Processing (QIP2020) conference, which is held recently in Shenzhen, China. It is the first time that a desktop quantum computer is commercially available, according to the researchers.
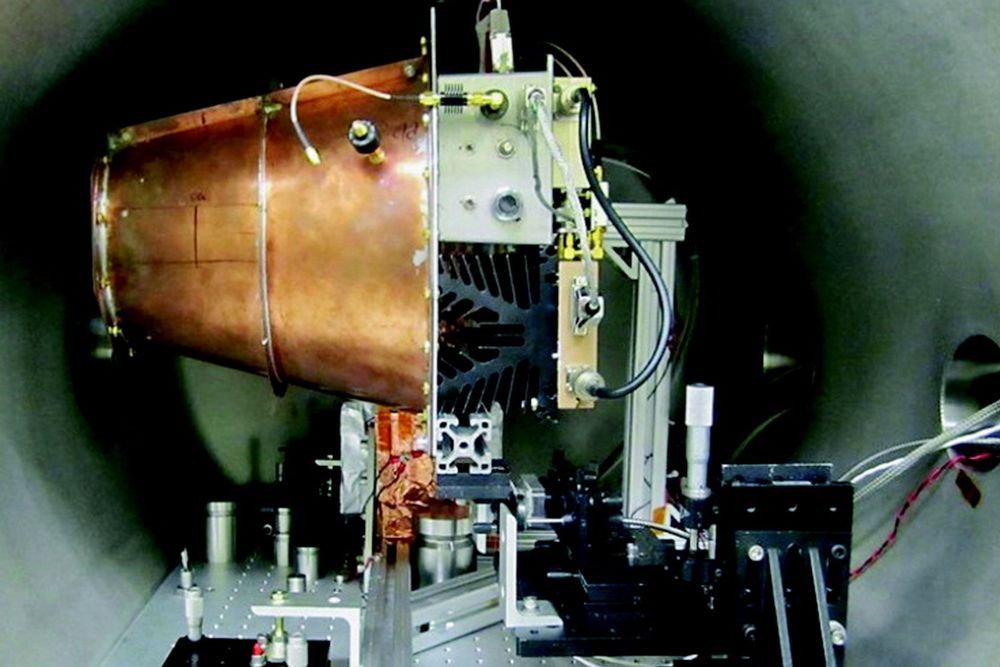
SpinQ Gemini is built by the state-of-the-art technology of permanent magnets, providing 1T magnetic field, running at room temperature, and maintenance free. It demonstrates quantum algorithms such as Deutsch’s algorithm and Grover’s algorithm for teaching quantum computing to university and high school students, also provides advanced models for quantum circuit design and control sequence design for researchers.