A new theory explains the seemingly irreversible arrow of time while yielding insights into entropy, quantum computers, black holes, and the past-future divide.


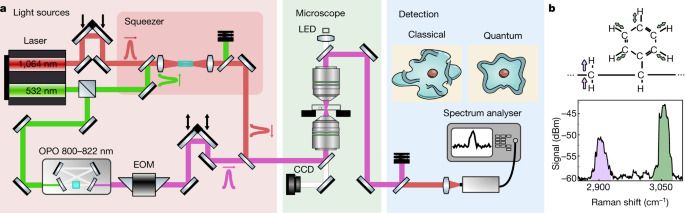
Technology advance could enable space-based atomic clocks, improving communications and GPS navigation.
Although quantum technology has proven valuable for highly precise timekeeping, making these technologies practical for use in a variety of environments is still a key challenge. In an important step toward portable quantum devices, researchers have developed a new high-flux and compact cold-atom source with low power consumption that can be a key component of many quantum technologies.
“The use of quantum technologies based on laser-cooled atoms has already led to the development of atomic clocks that are used for timekeeping on a national level,” said research team leader Christopher Foot from Oxford University in the U.K. “Precise clocks have many applications in the synchronization of electronic communications and navigation systems such as GPS. Compact atomic clocks that can be deployed more widely, including in space, provide resilience in communications networks because local clocks can maintain accurate timekeeping even if there is a network disruption.”
Not everything that is true can be proven. This discovery transformed infinity, changed the course of a world war and led to the modern computer. This video is sponsored by Brilliant. The first 200 people to sign up via https://brilliant.org/veritasium get 20% off a yearly subscription.
Special thanks to Prof. Asaf Karagila for consultation on set theory and specific rewrites, to Prof. Alex Kontorovich for reviews of earlier drafts, Prof. Toby ‘Qubit’ Cubitt for the help with the spectral gap, to Henry Reich for the helpful feedback and comments on the video.
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
References:
Dunham, W. (2013, July). A Note on the Origin of the Twin Prime Conjecture. In Notices of the International Congress of Chinese Mathematicians (Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 63–65). International Press of Boston. — https://ve42.co/Dunham2013
Conway, J. (1970). The game of life. Scientific American, 223, 4. — https://ve42.co/Conway1970
Churchill, A., Biderman, S., Herrick, A. (2019). Magic: The Gathering is Turing Complete. ArXiv. — https://ve42.co/Churchill2019

The ability to precisely control the various properties of laser light is critical to much of the technology that we use today, from commercial virtual reality (VR) headsets to microscopic imaging for biomedical research. Many of today’s laser systems rely on separate, rotating components to control the wavelength, shape and power of a laser beam, making these devices bulky and difficult to maintain.
Now, researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences have developed a single metasurface that can effectively tune the different properties of laser light, including wavelength, without the need of additional optical components. The metasurface can split light into multiple beams and control their shape and intensity in an independent, precise and power-efficient way.
The research opens the door for lightweight and efficient optical systems for a range of applications, from quantum sensing to VR/AR headsets.
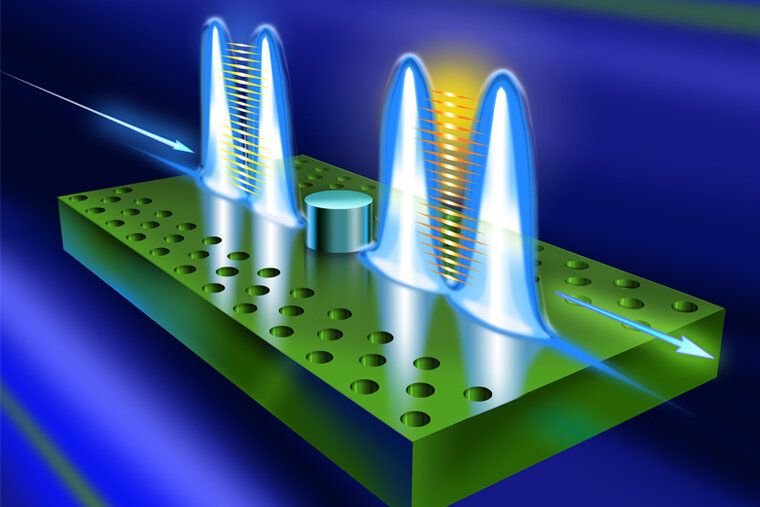
Research from the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis has found a missing piece in the puzzle of optical quantum computing.
Jung-Tsung Shen, associate professor in the Department of Electrical & Systems Engineering, has developed a deterministic, high-fidelity two-bit quantum logic gate that takes advantage of a new form of light. This new logic gate is orders of magnitude more efficient than the current technology.
“In the ideal case, the fidelity can be as high as 97%,” Shen said.

Russian scientists have experimentally proved the existence of a new type of quasiparticle—previously unknown excitations of coupled pairs of photons in qubit chains. This discovery could be a step towards disorder-robust quantum metamaterials. The study was published in Physical Review B.
Superconducting qubits are a leading qubit modality today that is currently being pursued by industry and academia for quantum computing applications. However, the performance of quantum computers is largely affected by decoherence that contributes to a qubit’s extremely short lifespan and causes computational errors. Another major challenge is low controllability of large qubit arrays.
Metamaterial quantum simulators provide an alternative approach to quantum computing, as they do not require a large amount of control electronics. The idea behind this approach is to create artificial matter out of qubits, the physics of which will obey the same equations as for some real matter. Conversely, you can program the simulator in such a way as to embody matter with properties that have not yet been discovered in nature.

A quantum-computing startup announced Tuesday that its future quantum processor designs will differ significantly from its current offerings. Rather than building a monolithic processor as everyone else has, Rigetti Computing will build smaller collections of qubits on chips that can be physically linked together into a single functional processor. This isn’t multiprocessing so much as modular chip design.
The move is consequential for both Rigetti processors and quantum computing more generally.

Imagine you sit down and pick up your favourite book. You look at the image on the front cover, run your fingers across the smooth book sleeve, and smell that familiar book smell as you flick through the pages. To you, the book is made up of a range of sensory appearances.
But you also expect the book has its own independent existence behind those appearances. So when you put the book down on the coffee table and walk into the kitchen, or leave your house to go to work, you expect the book still looks, feels, and smells just as it did when you were holding it.
Expecting objects to have their own independent existence – independent of us, and any other objects – is actually a deep-seated assumption we make about the world. This assumption has its origin in the scientific revolution of the 17th century, and is part of what we call the mechanistic worldview. According to this view, the world is like a giant clockwork machine whose parts are governed by set laws of motion.
