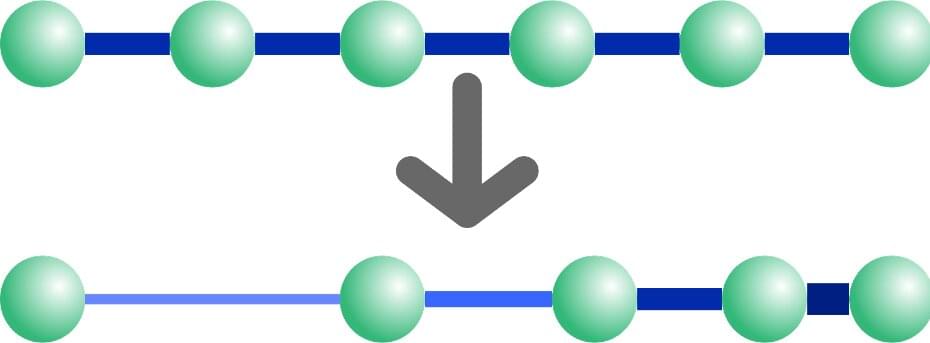
Research led by the University of Amsterdam has demonstrated that elusive radiation coming from black holes can be studied by mimicking it in the lab.
Black holes are the most extreme objects in the universe, packing so much mass into so little space that nothing—not even light—can escape their gravitational pull once it gets close enough.
Understanding black holes is key to unraveling the most fundamental laws governing the cosmos, because they represent the limits of two of the best-tested theories of physics: the theory of general relativity, which describes gravity as resulting from the (large-scale) warping of spacetime by massive objects, and the theory of quantum mechanics, which describes physics at the smallest length scales. To fully describe black holes, we would need to stitch these two theories together and form a theory of quantum gravity.