An unusual teleportation experiment uses ordinary quantum physics, but was inspired by tunnels in an exotic ‘toy universe’.


Professor leonard sussking on quantum gravity.

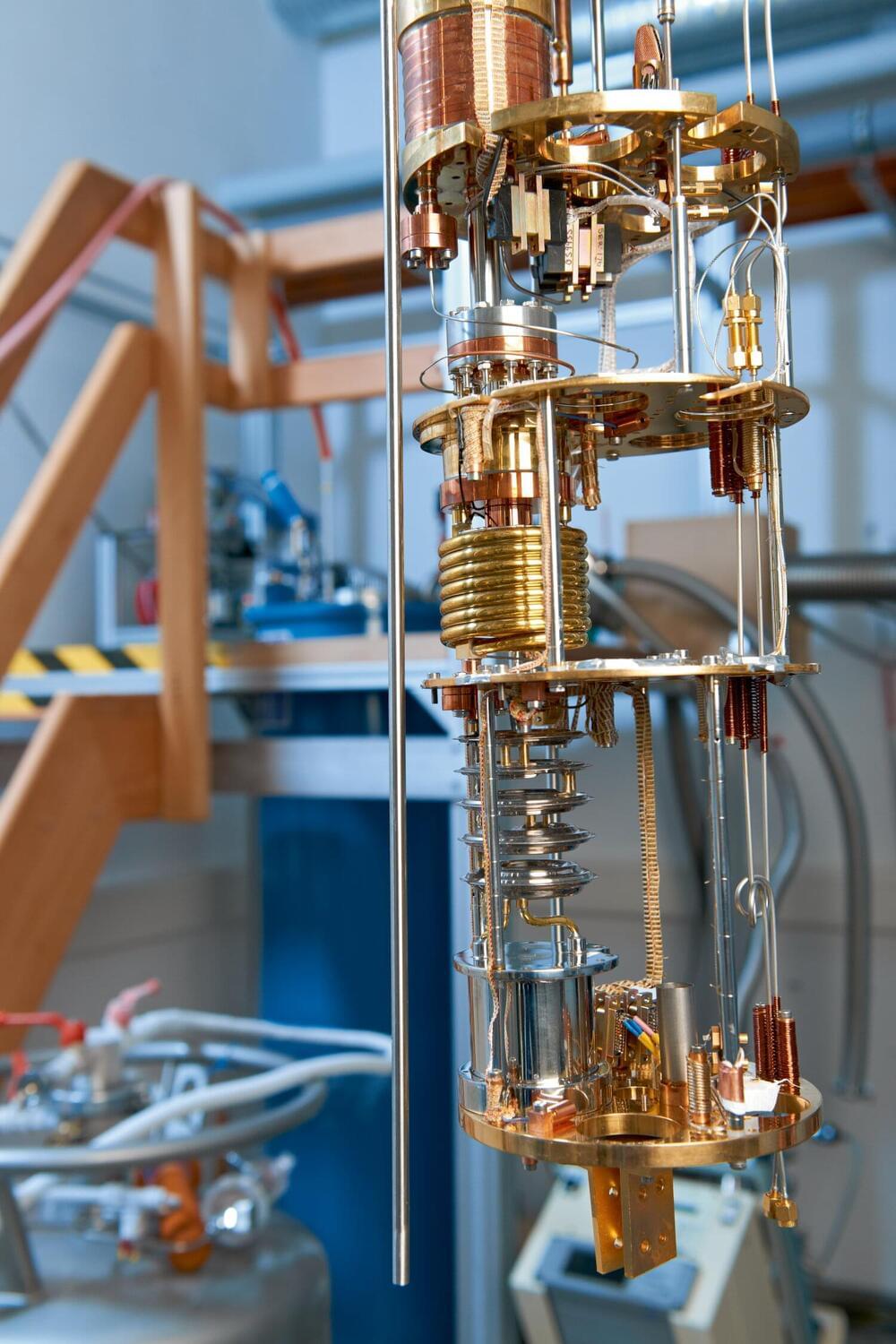
Water that simply will not freeze, no matter how cold it gets—a research group involving the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) has discovered a quantum state that could be described in this way.
Experts from the Institute of Solid State Physics at the University of Tokyo in Japan, Johns Hopkins University in the United States, and the Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems (MPI-PKS) in Dresden, Germany, managed to cool a special material to near absolute zero temperature.
They found that a central property of atoms—their alignment—did not “freeze,” as usual, but remained in a “liquid” state. The new quantum material could serve as a model system to develop novel, highly sensitive quantum sensors. The team has presented its findings in the journal Nature Physics.

Sign up for CNN’s Wonder Theory science newsletter. Explore the universe with news on fascinating discoveries, scientific advancements and more.
In science fiction – think films and TV like “Interstellar” and “Star Trek” – wormholes in the cosmos serve as portals through space and time for spacecraft to traverse unimaginable distances with ease. If only it were that simple.
Scientists have long pursued a deeper understanding of wormholes and now appear to be making progress. Researchers announced on Wednesday that they forged two minuscule simulated black holes – those extraordinarily dense celestial objects with gravity so powerful that not even light can escape – in a quantum computer and transmitted a message between them through what amounted to a tunnel in space-time.

IT WAS March 2018. The atmosphere at the annual meeting of the American Physical Society at the Los Angeles Convention Center was highly charged. The session had been moved to the atrium to accommodate the crowds, but people still had to cram onto the balconies to get a view of the action.
Rumours had it that Pablo Jarillo-Herrero, a physicist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, had something momentous to report. He and his colleagues had been experimenting with graphene, sheets of carbon just a single atom thick that are peeled from the graphite found in pencil lead. Graphene was already celebrated for its various promising electronic properties, and much more besides.
Here, Jarillo-Herrero showed that if you stacked two graphene sheets and twisted, or rotated, one relative to the other at certain “magic angles”, you could make the material an insulator, where electric current barely flows, or a superconductor, where current flows with zero resistance. It was a staggering trick, and potentially hugely significant because superconductivity holds promise for applications ranging from quantum computing to nuclear fusion.

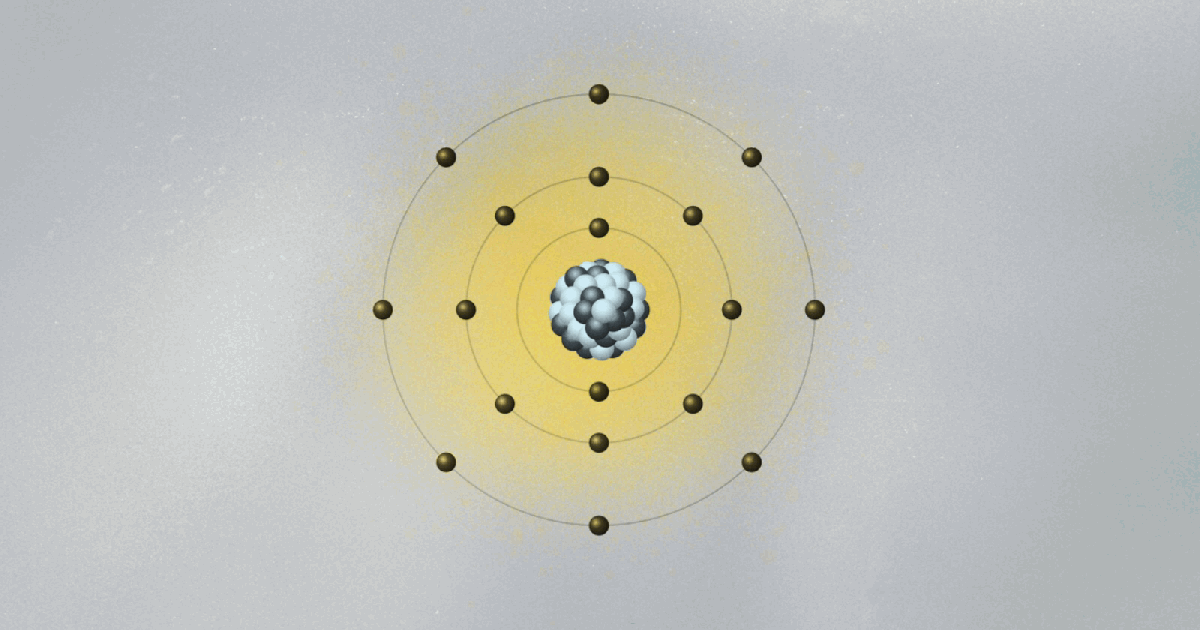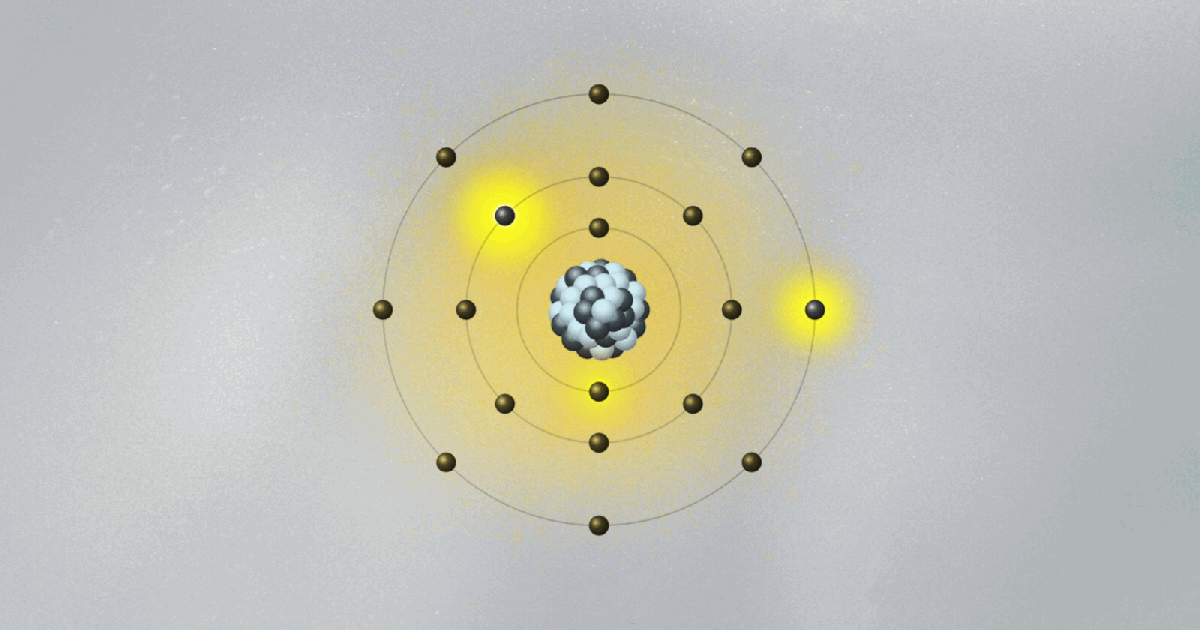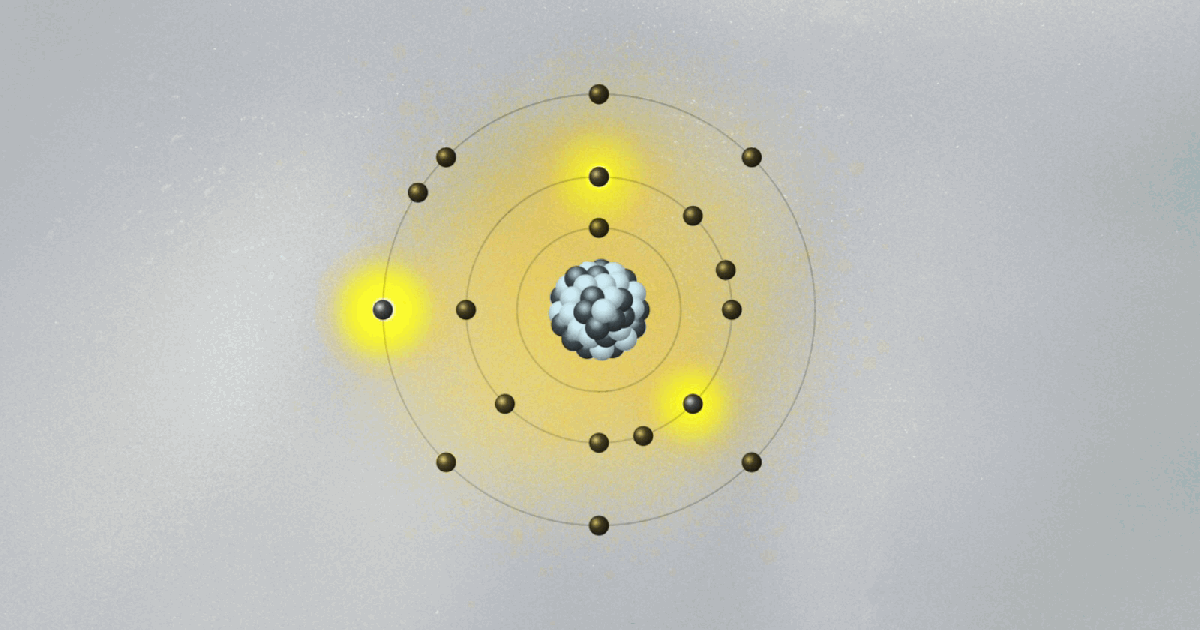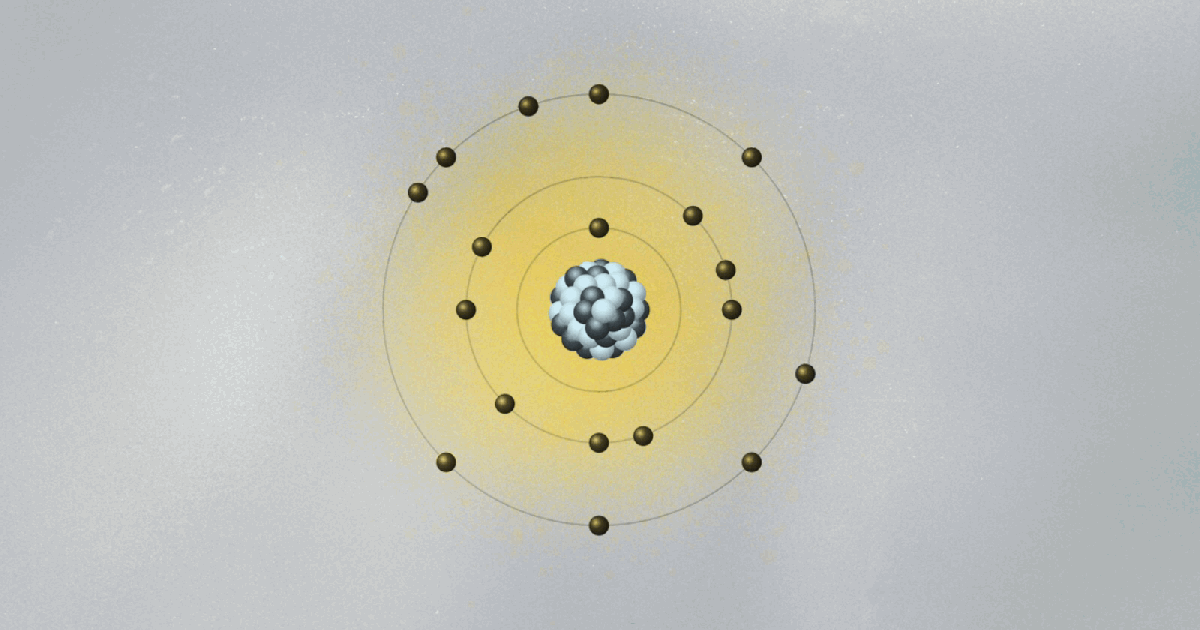
Bohr’s model of the atom is kind of crazy. His collage of ideas mixing old and new concepts was the fruit of Bohr’s amazing intuition. Looking only at hydrogen, the simplest of all atoms, Bohr formed the image of a miniature solar system, with a proton in the center and the electron circling around it.
Following the physicist’s way of doing things, he wanted to explain some of his observed data with the simplest possible model. But there was a problem. The electron, being negatively charged, is attracted to the proton, which is positive. According to classical electromagnetism, the theory that describes how charged particles attract and repel one another, an electron would spiral down to the nucleus. As it circled the proton, it would radiate away its energy and fall in. No orbit would be stable, and atoms could not exist. Clearly, something new and revolutionary was needed. The solar system could only go so far as an analogy.
To salvage the atom, Bohr had to invent new rules that clashed with classical physics. He bravely suggested the implausible: What if the electron could only circle the nucleus in certain orbits, separated from each other in space like the steps of a ladder or the layers of an onion? Just like you can’t stand between steps, the electron can’t stay anywhere between two orbits. It can only jump from one orbit to another, the same way we can jump between steps. Bohr had just described quantum jumps.

Physicists at Google Quantum AI have used their quantum computer to study a type of effective particle that is more resilient to environmental disturbances that can degrade quantum calculations. These effective particles, known as Majorana edge modes, form as a result of a collective excitation of multiple individual particles, like ocean waves form from the collective motions of water molecules. Majorana edge modes are of particular interest in quantum computing applications because they exhibit special symmetries that can protect the otherwise fragile quantum states from noise in the environment.
The condensed matter physicist Philip Anderson once wrote, “It is only slightly overstating the case to say that physics is the study of symmetry.” Indeed, studying physical phenomena and their relationship to underlying symmetries has been the main thrust of physics for centuries. Symmetries are simply statements about what transformations a system can undergo—such as a translation, rotation, or inversion through a mirror—and remain unchanged. They can simplify problems and elucidate underlying physical laws. And, as shown in the new research, symmetries can even prevent the seemingly inexorable quantum process of decoherence.
When running a calculation on a quantum computer, we typically want the quantum bits, or “qubits,” in the computer to be in a single, pure quantum state. But decoherence occurs when external electric fields or other environmental noise disturb these states by jumbling them up with other states to create undesirable states. If a state has a certain symmetry, then it could be possible to isolate it, effectively creating an island of stability that is impossible to mix with the other states that don’t also have the special symmetry. In this way, since the noise can no longer connect the symmetric state to the others, it could preserve the coherence of the state.

Scientists have, for the first time, developed a quantum experiment that allows them to study the dynamics, or behavior, of a special kind of theoretical wormhole. The experiment has not created an actual wormhole (a rupture in space and time), rather it allows researchers to probe connections between theoretical wormholes and quantum physics, a prediction of so-called quantum gravity. Quantum gravity refers to a set of theories that seek to connect gravity with quantum physics, two fundamental and well-studied descriptions of nature that appear inherently incompatible with each other.
“We found a quantum system that exhibits key properties of a gravitational wormhole yet is sufficiently small to implement on today’s quantum hardware,” says Maria Spiropulu, the principal investigator of the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science research program Quantum Communication Channels for Fundamental Physics (QCCFP) and the Shang-Yi Ch’en Professor of Physics at Caltech. “This work constitutes a step toward a larger program of testing quantum gravity physics using a quantum computer. It does not substitute for direct probes of quantum gravity in the same way as other planned experiments that might probe quantum gravity effects in the future using quantum sensing, but it does offer a powerful testbed to exercise ideas of quantum gravity.”
The research will be published December 1 in the journal Nature. The study’s first authors are Daniel Jafferis of Harvard University and Alexander Zlokapa (BS ‘21), a former undergraduate student at Caltech who started on this project for his bachelor’s thesis with Spiropulu and has since moved on to graduate school at MIT.