Quantum gravity seeks to unify the theory of general relativity with quantum physics to describe how gravity works at very small scales. But there’s a big puzzle surrounding the idea.


Electrons can freeze into strange geometric crystals and then melt back into liquid-like motion under the right quantum conditions. Researchers identified how to tune these transitions and even discovered a bizarre “pinball” state where some electrons stay locked in place while others dart around freely. Their simulations help explain how these phases form and how they might be harnessed for advanced quantum technologies.

Over the past several decades, researchers have been making rapid progress in harnessing light to enable all sorts of scientific and industrial applications. From creating stupendously accurate clocks to processing the petabytes of information zipping through data centers, the demand for turnkey technologies that can reliably generate and manipulate light has become a global market worth hundreds of billions of dollars.
One challenge that has stymied scientists is the creation of a compact source of light that fits onto a chip, which makes it much easier to integrate with existing hardware. In particular, researchers have long sought to design chips that can convert one color of laser light into a rainbow of additional colors—a necessary ingredient for building certain kinds of quantum computers and making precision measurements of frequency or time.
Now, researchers at JQI have designed and tested new chips that reliably convert one color of light into a trio of hues. Remarkably, the chips all work without any active inputs or painstaking optimization—a major improvement over previous methods. The team described their results in the journal Science on Nov. 6, 2025.

Elon Musk just made a bold announcement that could completely redefine Tesla’s future — but almost no one noticed. At the 2025 Tesla Shareholder Meeting, Elon revealed a deeper vision that goes far beyond cars. From AI and humanoid robots to clean energy and automation, Tesla is positioning itself as the driving force behind humanity’s next great leap.
In this video, Chris Smedley and the Ideal Wealth Grower team break down the hidden message behind Elon’s words, why the singularity may already be unfolding, and how Tesla’s shift toward artificial intelligence could reshape the global economy — and your investment strategy. Stay tuned till the end to discover why this could be the most important turning point in Tesla’s history.
Know what Type of Business suits you first at https://quiz.franchisewithbob.com/rg — and COPY THE RIGHT BUSINESS FOR YOU!
Thanks, Franchise with Bob, for sponsoring this episode!
Watch on Social media profiles:
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/posts/ameier…
https://twitter.com/IdealGrower/status/1986
… Welcome to Ideal Wealth Grower, the channel that helps you build real wealth, create passive income, and achieve true time freedom. I’m Axel Meierhoefer — former US Air Force officer, real estate investor, and lifelong learner inspired by visionaries like Elon Musk. After more than 20 years of successful real estate investing, I reached my own financial freedom point, and now I’m here to help you do the same. If you’re ready to stop trading time for money, take control of your financial future, and live life on your terms — you’re in the right place. Stay connected with us! ✅ X: twitter.com/idealgrower ✅ Our community: cutt.ly/0rDZ1fNI ✅ Linked In: / ameierhoefer ✨ ✨
/ @idealwealthgrower Top Data Scientist Exposes Quantum AI Disruption, Digital AI Twins | Anthony Scriffignano
• Top Data Scientist Exposes Quantum AI Disr… Is INFINITE BANKING the Future of Sustainable Wealth? with Chris Naugle | Age of Abundance
• Is INFINITE BANKING the Future of Sustaina… Elon Musk Just Changed Everything at Tesla — And No One’s Talking About It #elonmusk #tesla #chrissmedley #idealwealthgrower #teslanews #teslastock #teslainvestors #teslashareholdermeeting #teslaupdate #teslafuture #teslabot #teslaai #artificialintelligence #teslainnovation #futuretech #robotics #teslainvesting #wealthbuilding #financialfreedom #stockmarket #investing #technologynews #innovation #elonmusknews #teslamasterplan #ai what elon musk said at tesla 2025 meeting tesla AI day 2025 full presentation tesla master plan 4 explained tesla robot update 2025 elon musk latest tesla news elon musk tesla 2025 updates tesla shareholder meeting highlights.
X: https://twitter.com/IdealGrower/status/1986…
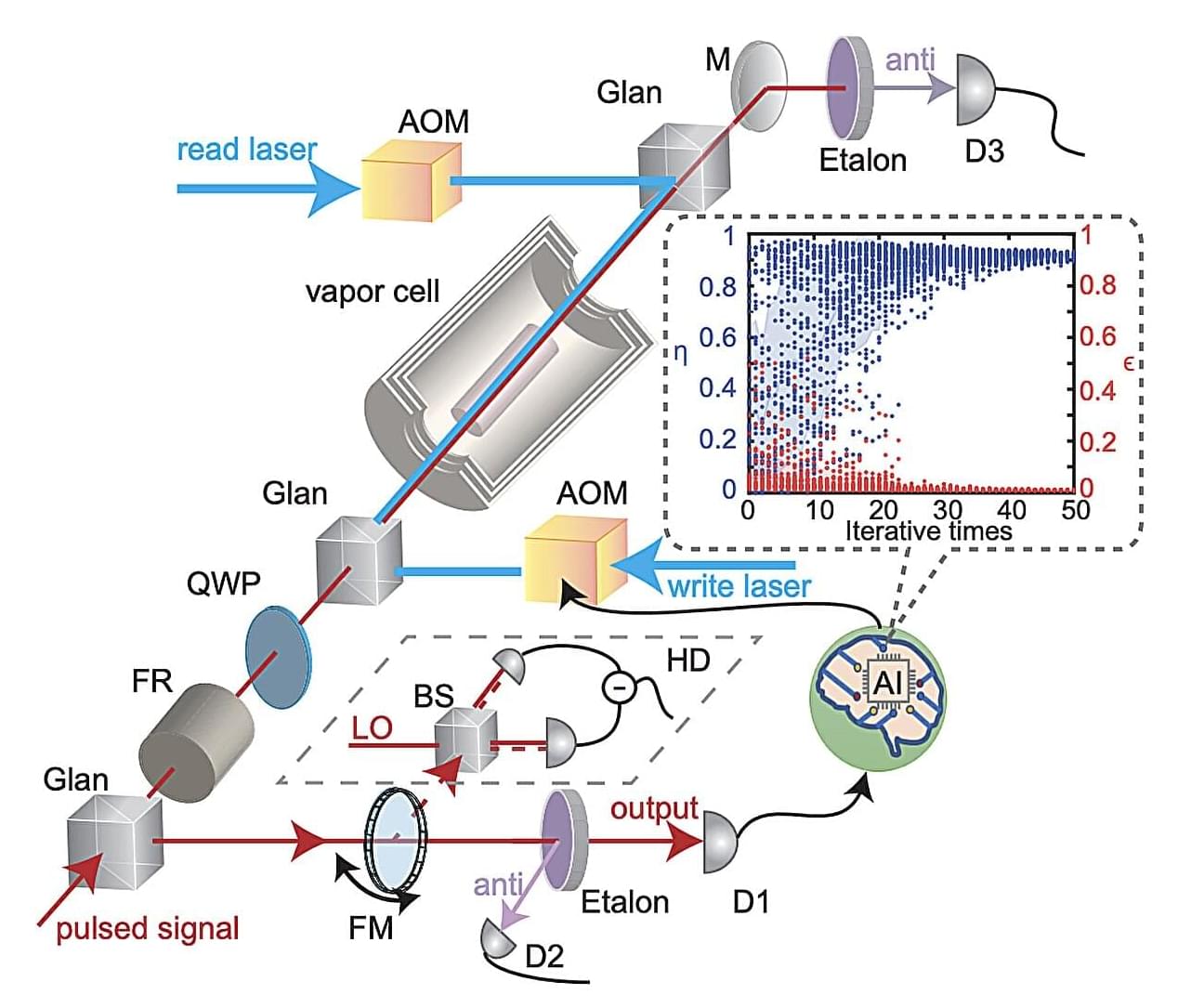
Over the past decades, quantum physicists and engineers have developed numerous technologies that harness the principles of quantum mechanics to push the boundaries of classical information science. Among these advances, quantum memories stand out as promising devices for storing and retrieving quantum information encoded in light or other physical carriers.
To be viable for real-world applications, quantum memory must deliver both high efficiency and high fidelity. In other words, they should be able to store and retrieve most of the input quantum information —typically over 90%—and ensure that a recovered state closely matches the original one.
Notably, most previously proposed strategies to develop efficient quantum memories were found to produce undesired random fluctuations (i.e., noise). These fluctuations could in turn degrade quantum information, reducing the system’s fidelity.
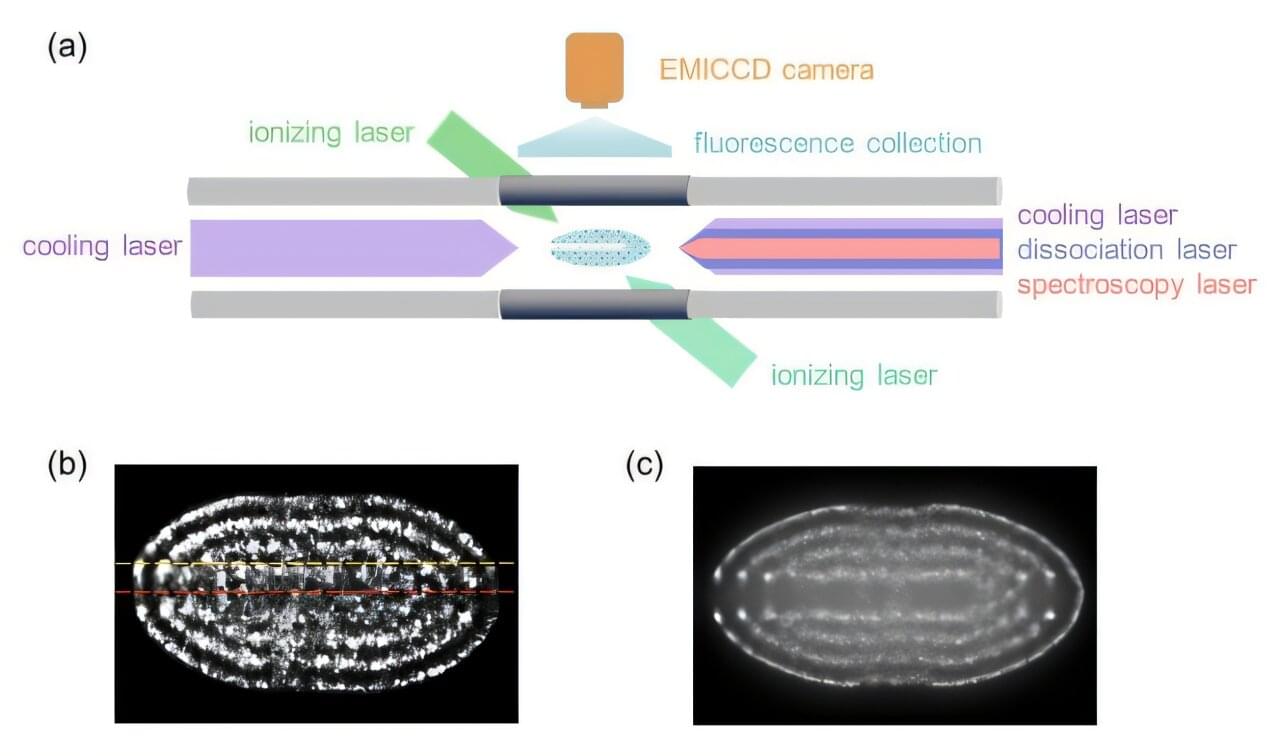
A research team from the Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology (APM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has made significant progress in precisely measuring the vibrational-rotational spectra of hydrogen molecular ions (HD⁺).
The researchers prepared a Be⁺-HD⁺ two-component ion Coulomb crystal at millikelvin temperatures in a linear ion trap. They developed an innovative quantum state preparation and spatially resolved fluorescence detection techniques and used these to measure the high-resolution vibrational-rotational transition spectra of HD⁺ molecular ions. Their findings were published in Physical Review A.
HD⁺ is the simplest heteronuclear molecular ion, composed of one proton, one deuteron, and one electron. Its vibrational-rotational transition energies can be precisely calculated, making it an ideal system for testing quantum electrodynamics (QED) theory and determining fundamental physical constants, such as the proton-electron mass ratio.