Wang, H., Xue, Y., Qu, Y. et al. Multidimensional Bose quantum error correction based on neural network decoder. npj Quantum Inf 8, 134 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-022-00650-z.
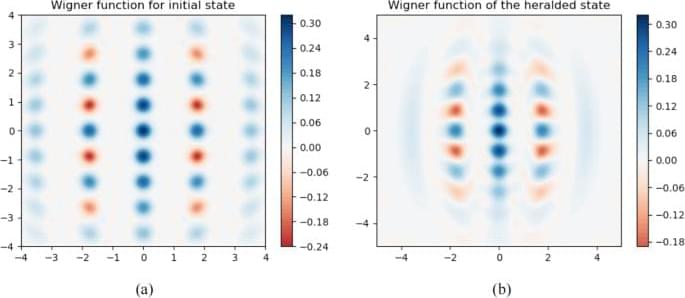

Wang, H., Xue, Y., Qu, Y. et al. Multidimensional Bose quantum error correction based on neural network decoder. npj Quantum Inf 8, 134 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-022-00650-z.

A research team led by the Paul Scherrer Institute has spectroscopically observed the fractionalization of electronic charge in an iron-based metallic ferromagnet. Experimental observation of the phenomenon is not only of fundamental importance. Since it appears in an alloy of common metals at accessible temperatures, it holds potential for future exploitation in electronic devices. The discovery is published in the journal Nature.
Basic quantum mechanics tells us that the fundamental unit of charge is unbreakable: the electron charge is quantized. Yet, we have come to understand that exceptions exist. In some situations, electrons arrange themselves collectively as if they were split into independent entities, each possessing a fraction of the charge.
The fact that charge can be fractionalized is not new: it has been observed experimentally since the early 1980s with the Fractional Quantum Hall Effect. In this, the conductance of a system in which electrons are confined to a two-dimensional plane is observed to be quantized in fractional—rather than integer—units of charge.
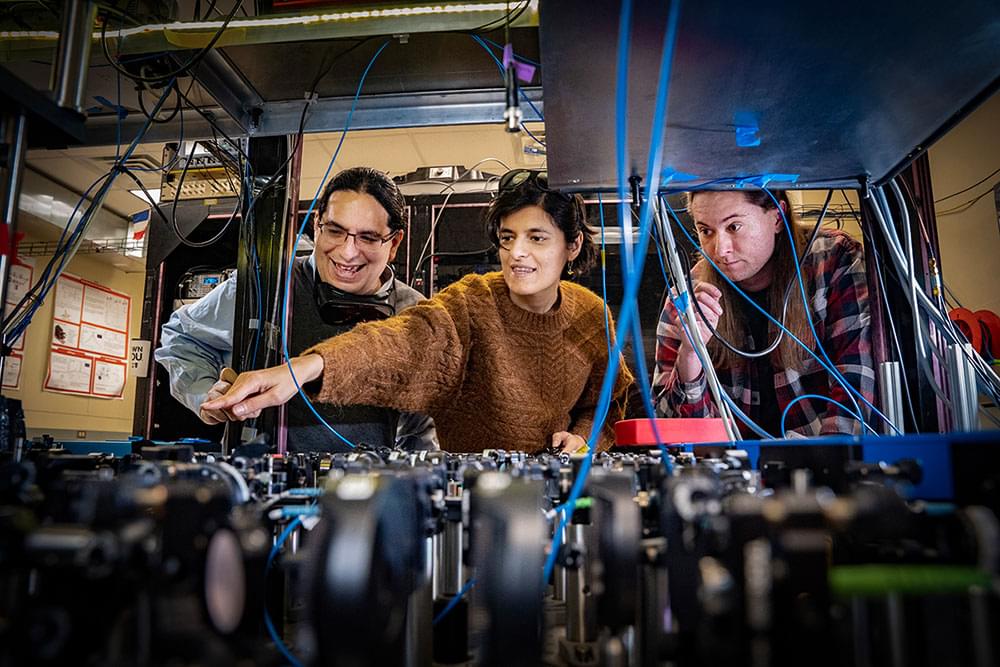
A team of Stony Brook University physicists and their collaborators have taken a significant step toward the building of a quantum internet testbed by demonstrating a foundational quantum network measurement that employs room-temperature quantum memories. Their findings are described in a paper published in the Nature journal Quantum Information.
Research with quantum computing and quantum networks is taking place around the world in the hopes of developing a quantum internet, a network of quantum computers, sensors, and communication devices that will create, process, and transmit quantum states and entanglement. It is anticipated to enhance society’s internet system and provide certain services and securities that the current internet does not have.
The field of quantum information combines aspects of physics, mathematics, and classical computing to use quantum mechanics to solve complex problems much faster than classical computing and to transmit information in an unhackable manner. While the vision of a quantum internet system is growing and the field has seen a surge in interest from researchers and the public at large, accompanied by a steep increase in the capital invested, an actual quantum internet prototype has not been built.

Quantum computers, which can solve several complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers, are expected to improve artificial intelligence (AI) applications deployed in devices like autonomous vehicles; however, just like their predecessors, quantum computers are vulnerable to adversarial attacks.
A team of University of Texas at Dallas researchers and an industry collaborator have developed an approach to give quantum computers an extra layer of protection against such attacks. Their solution, Quantum Noise Injection for Adversarial Defense (QNAD), counteracts the impact of attacks designed to disrupt inference—AI’s ability to make decisions or solve tasks.
The team will present research that demonstrates the method at the IEEE International Symposium on Hardware Oriented Security and Trust held May 6–9 in Washington, D.C.
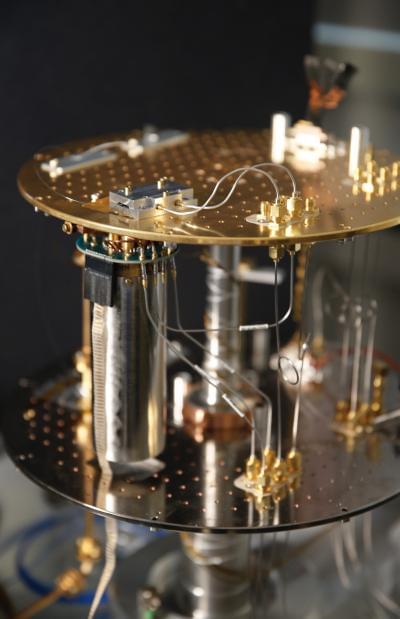
Superconducting circuits, which conduct electricity without resistance, are among the most promising technologies for quantum computing and ultrafast logic circuits. However, finding a practical way to work with these materials that require extremely cold temperatures has been a challenge.
In a step toward that goal, a team of researchers led by Prof. Hong Tang developed and successfully demonstrated a device that presents a viable solution in transferring a very weak signal from a computing device stored at cryogenic temperatures to room temperature electronics to achieve a fast data transfer with very low energy consumption. The results are published in Nature Photonics.
The practical use of superconducting circuits requires connecting them to room temperature electronics. But doing so has largely relied on coaxial cables, which have a limited bandwidth and limited thermal conductivity – two factors that negate the benefits of superconducting circuits.

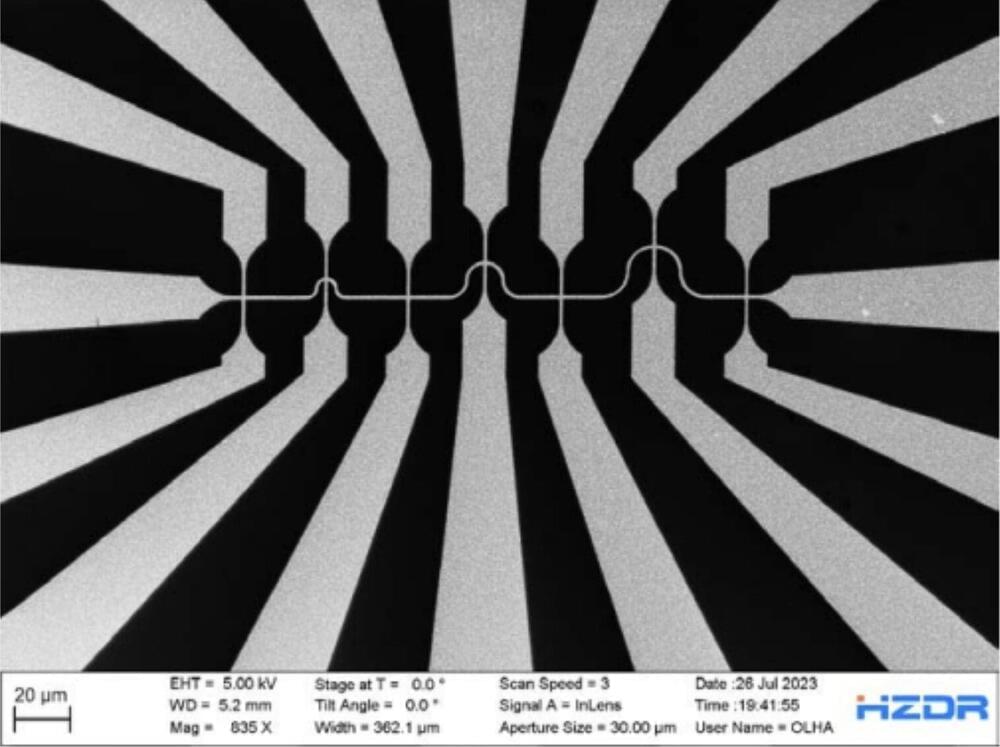
A research team from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) and the University of Salerno in Italy has discovered that thin films of elemental bismuth exhibit the so-called non-linear Hall effect, which could be applied in technologies for the controlled use of terahertz high-frequency signals on electronic chips.
Bismuth combines several advantageous properties not found in other systems to date, as the team reports in Nature Electronics. In particular, the quantum effect is observed at room temperature. The thin-layer films can be applied even on plastic substrates and could therefore be suitable for modern high-frequency technology applications.
“When we apply a current to certain materials, they can generate a voltage perpendicular to it. We physicists call this phenomenon the Hall effect, which is actually a unifying term for effects with the same impact, but which differ in the underlying mechanisms at the electron level. Typically, the Hall voltage registered is linearly dependent on the applied current,” says Dr. Denys Makarov from the Institute of Ion Beam Physics and Materials Research at HZDR.
After the advent of 5G, engineers have been trying to devise techniques to further enhance wireless communication technology. To increase these systems’ data transmission rate, they will ultimately need to extend their carrier frequency beyond 100 gigahertz, reaching the terahertz range.
Existing devices and technologies, however, have proved to be unable to achieve such high carrier frequencies. One proposed solution to reach this goal entails the use of some quantum materials that exhibit the so-called non-linear Hall effect.
Researchers at Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) e. V. and University of Salerno have identified a promising material for the development of next generation wireless communication systems, namely thin film elemental bismuth. Their paper, published in Nature Electronics, shows that this material exhibits a room-temperature nonlinear Hall effect.
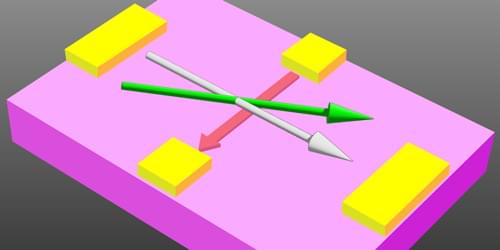
Throughout many branches of physics, a connection can be drawn between geometry and dynamics. In general relativity, for example, the motion of stars and planets is governed by the geometry of spacetime. In condensed matter, the motion of electrons in solids is influenced by the so-called quantum geometry, which describes how the electronic wave function evolves in momentum space. The quantum geometry can explain a wide range of observed phenomena, such as topological phases and quantum Hall effects, but it can also lead researchers to new electromagnetic responses. Guided by quantum-geometry predictions, Lujunyu Wang from Peking University and colleagues present experimental evidence of a new Hall effect, the magneto-nonlinear Hall effect, which is proportional to both an in-plane electric field and an in-plane magnetic field [1] (Fig. 1). The effect, which was isolated in a magnet with triangular symmetry, offers a new way to probe in the quantum geometry of materials.
Quantum geometry is a representation of the phase of the Bloch wave functions, which describe electronic behavior in a periodic potential. In the case of a two-level system, this phase can be represented by a unit vector in the momentum space of the electrons. In certain materials, this vector rotates as the momentum changes, an effect that can be characterized by two fundamental geometrical properties: the “quantum metric” and the “Berry curvature.” These two aspects of quantum geometry can describe many phenomena including surface currents in topological insulator and anomalous Hall effects in which the transverse Hall current occurs in the absence of an external magnetic field.
Recently, researchers have uncovered a connection between quantum geometry and nonlinear electromagnetic effects [2– 10]. Here, the nonlinearity is a higher-order response to the input electromagnetic fields. Nonlinear electrical transport is the foundation of applications such as rectification and wave mixing. Classically, the most well-known nonlinear device is a p-n junction. In quantum materials, nonlinear transport suggests novel device applications but also provides a powerful probe of the quantum geometry of the conduction electrons.

Physicists successfully measure gravity in the quantum world, detecting weak gravitational pull on a tiny particle with a new technique that uses levitating magnets, putting scientists closer to solving mysteries of the universe.
Scientists are a step closer to unraveling the mysterious forces of the universe after working out how to measure gravity on a microscopic level.
Experts have never fully understood how the force discovered by Isaac Newton works in the tiny quantum world.