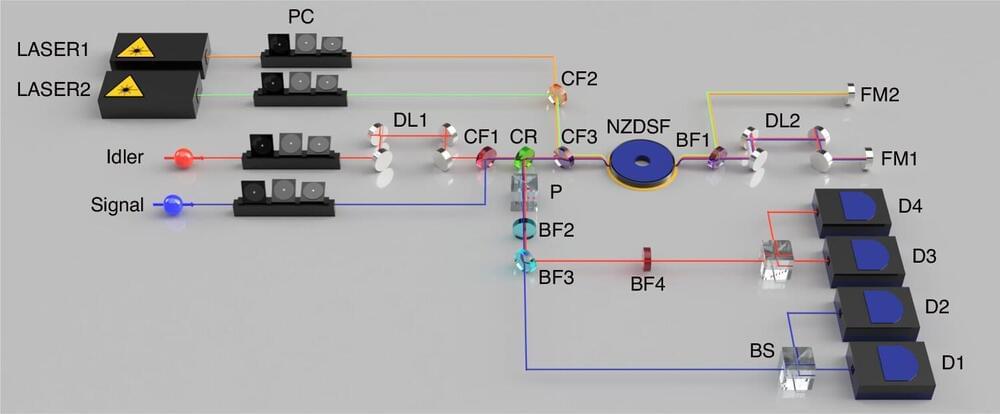
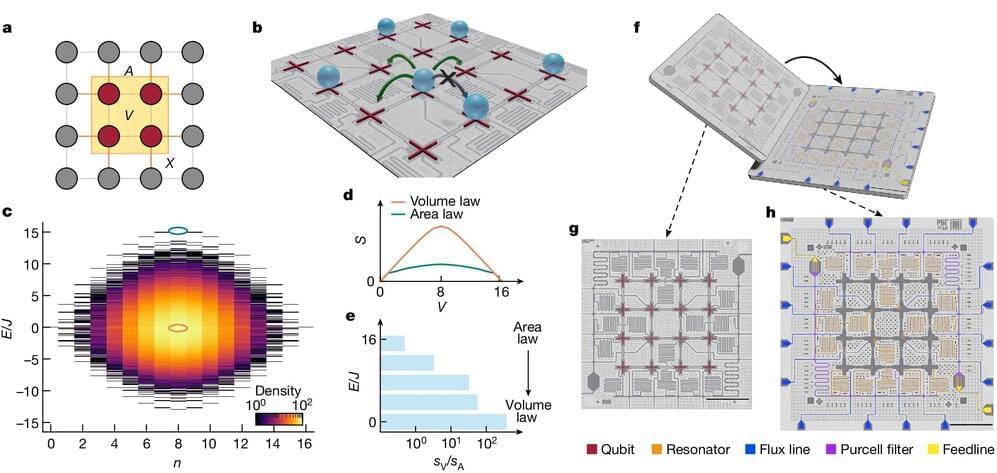
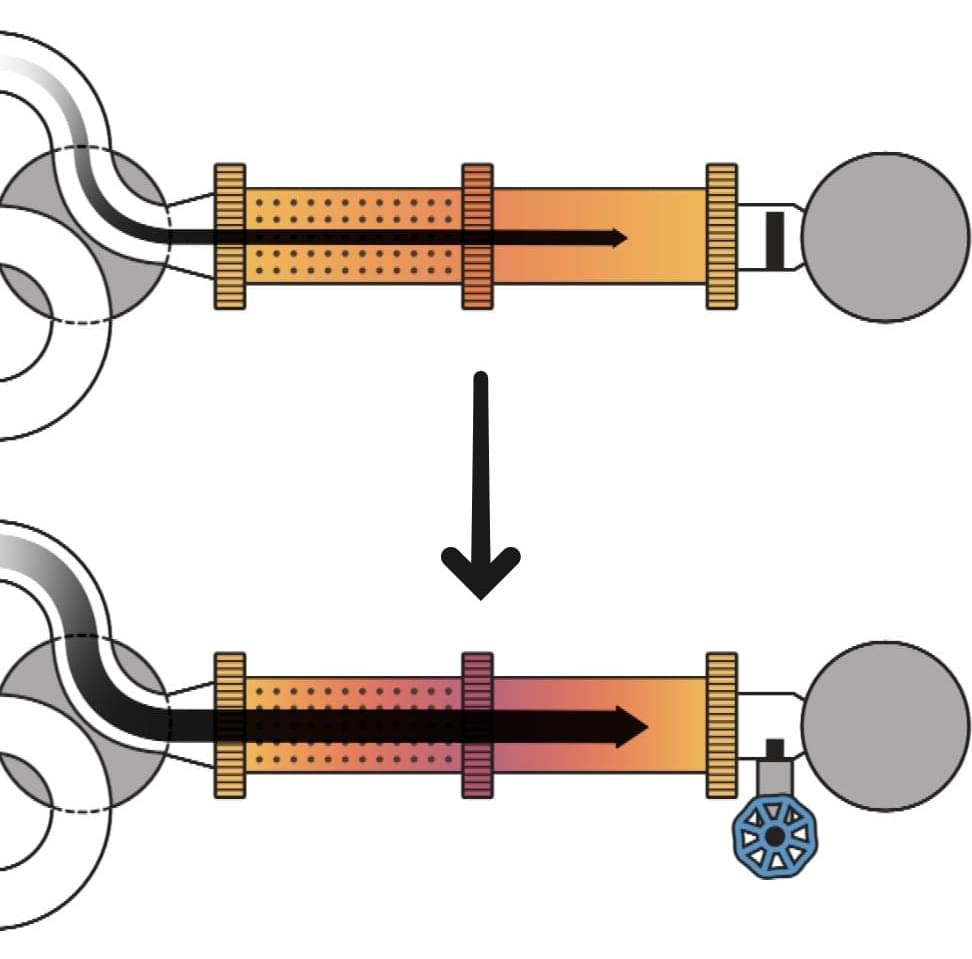
Scientists have introduced a form of quantum entanglement known as frequency-domain photon number-path entanglement. This advance in quantum physics involves an innovative tool called a frequency beam splitter, which has the unique ability to alter the frequency of individual photons with a 50% success rate.
For years, the scientific community has delved into spatial-domain photon number-path entanglement, a key player in the realms of quantum metrology and information science.
This concept involves photons arranged in a special pattern, known as NOON states, where they’re either all in one pathway or another, enabling applications like super-resolution imaging that surpasses traditional limits, the enhancement of quantum sensors, and the development of quantum computing algorithms designed for tasks requiring exceptional phase sensitivity.