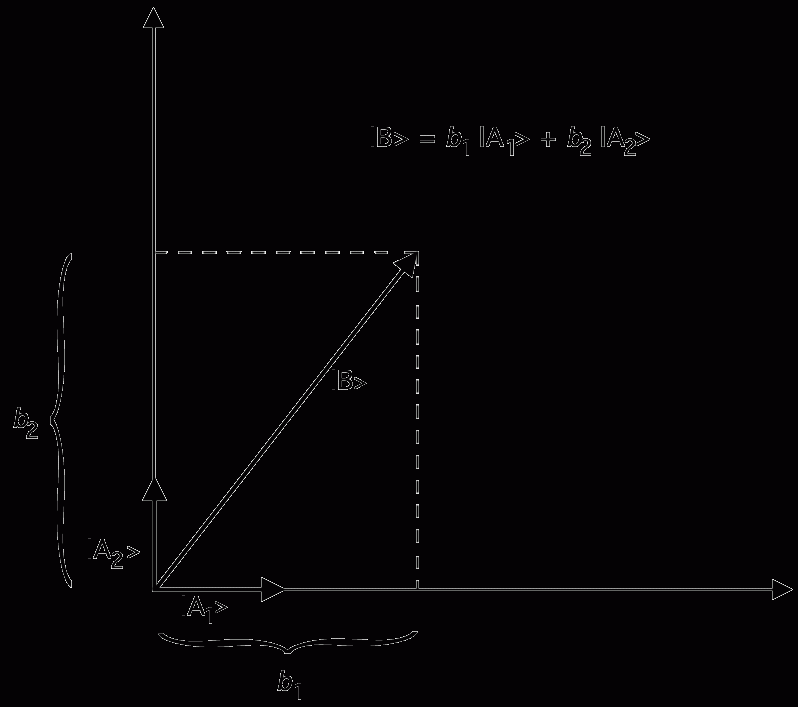Quantum mechanics is, at least at first glance and at least in part, a mathematical machine for predicting the behaviors of microscopic particles — or, at least, of the measuring instruments we use to explore those behaviors — and in that capacity, it is spectacularly successful: in terms of power and precision, head and shoulders above any theory we have ever had. Mathematically, the theory is well understood; we know what its parts are, how they are put together, and why, in the mechanical sense (i.e., in a sense that can be answered by describing the internal grinding of gear against gear), the whole thing performs the way it does, how the information that gets fed in at one end is converted into what comes out the other. The question of what kind of a world it describes, however, is controversial; there is very little agreement, among physicists and among philosophers, about what the world is like according to quantum mechanics. Minimally interpreted, the theory describes a set of facts about the way the microscopic world impinges on the macroscopic one, how it affects our measuring instruments, described in everyday language or the language of classical mechanics. Disagreement centers on the question of what a microscopic world, which affects our apparatuses in the prescribed manner, is, or even could be, like intrinsically; or how those apparatuses could themselves be built out of microscopic parts of the sort the theory describes.[1]
That is what an interpretation of the theory would provide: a proper account of what the world is like according to quantum mechanics, intrinsically and from the bottom up. The problems with giving an interpretation (not just a comforting, homey sort of interpretation, i.e., not just an interpretation according to which the world isn’t too different from the familiar world of common sense, but any interpretation at all) are dealt with in other sections of this encyclopedia. Here, we are concerned only with the mathematical heart of the theory, the theory in its capacity as a mathematical machine, and — whatever is true of the rest of it — this part of the theory makes exquisitely good sense.