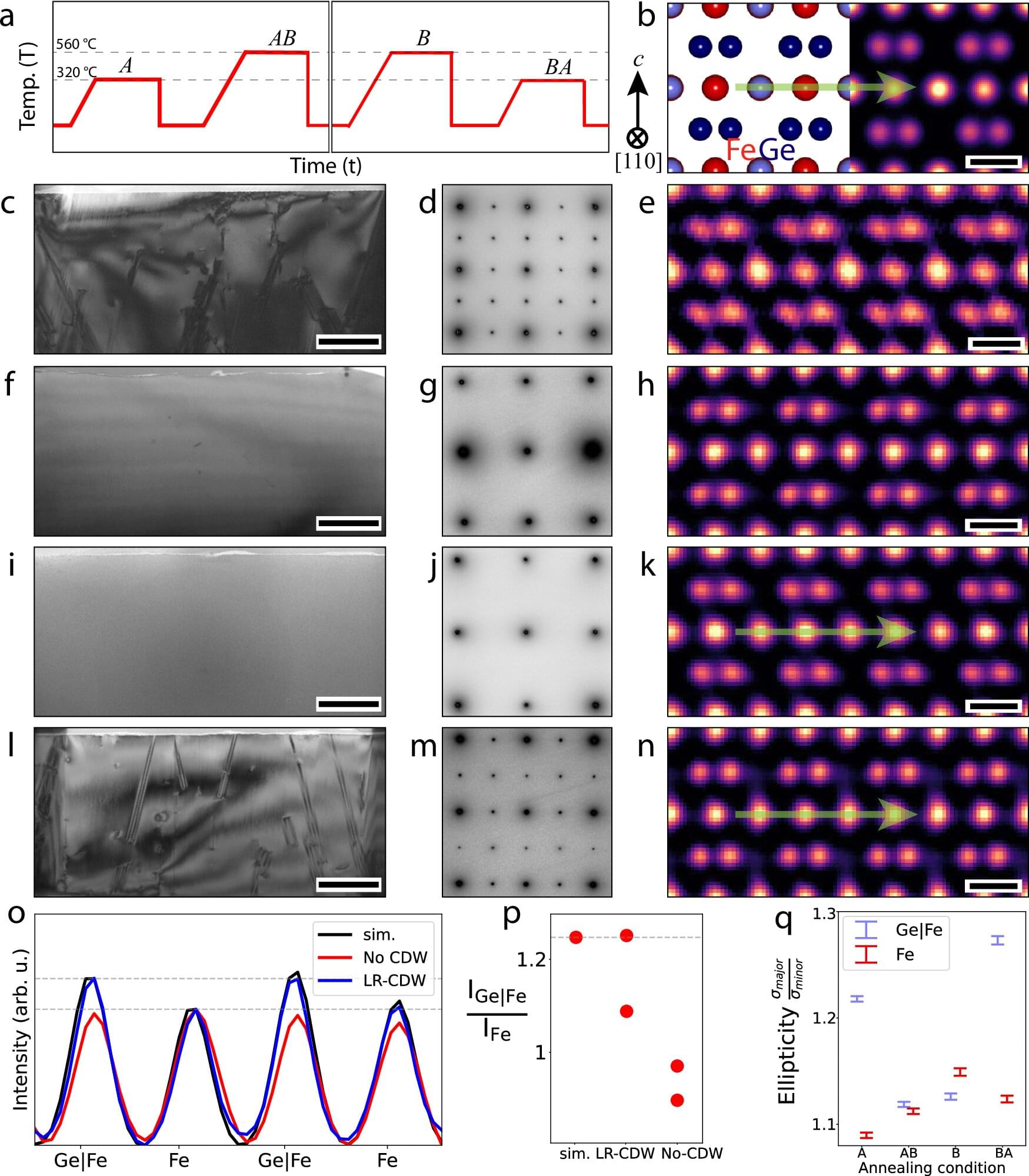
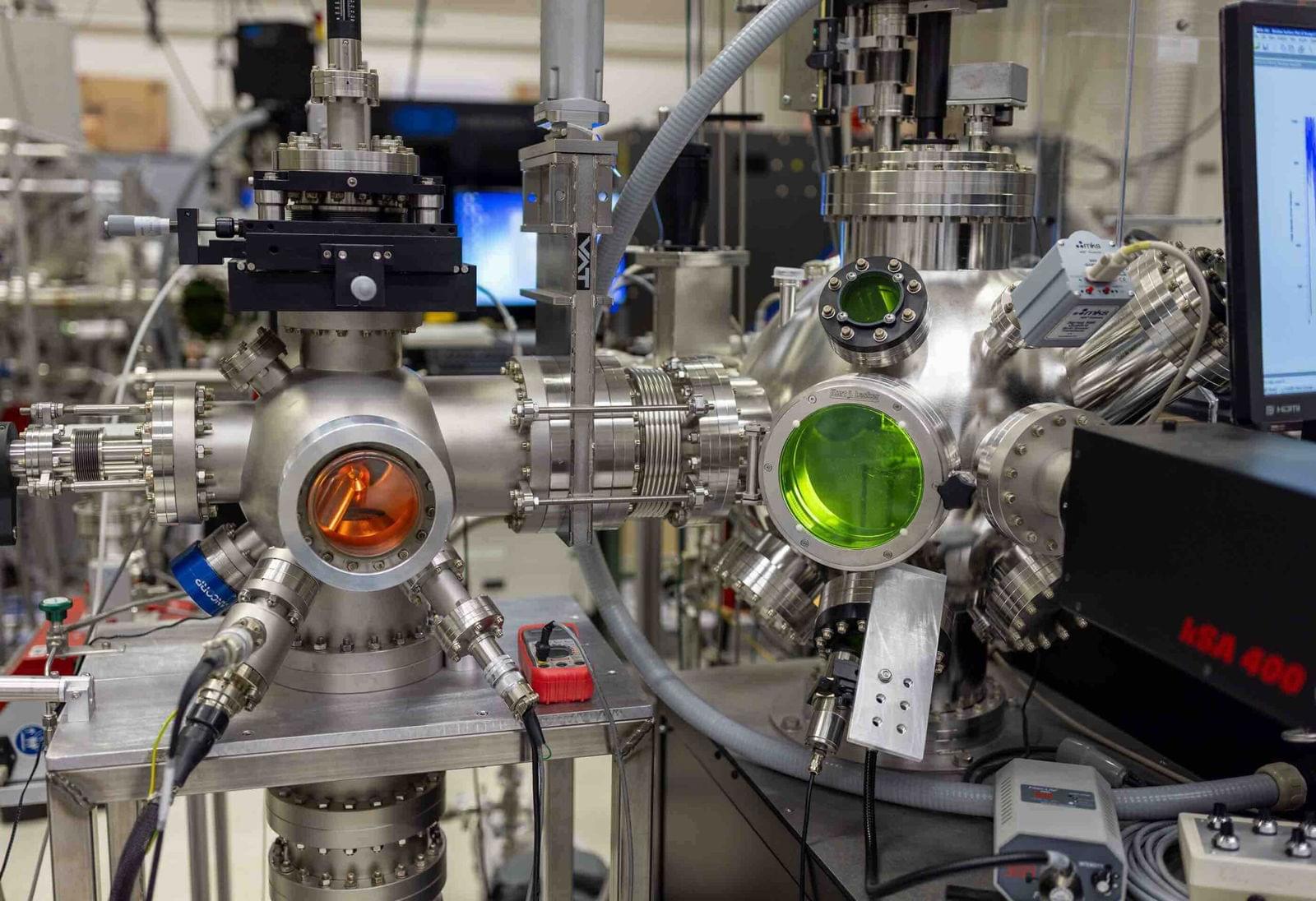
A new study published in Nature Communications April 7 could reshape the future of magnetic and electronic technology. Scientists at Rice University have discovered how a disappearing electronic pattern in a quantum material can be revived under specific thermal conditions. The finding opens new doors for customizable quantum materials and in-situ engineering, where devices are manufactured or manipulated directly at their point of use.
Led by Pengcheng Dai, the Sam and Helen Worden Professor of Physics and Astronomy, the researchers uncovered the cause behind a vanishing electronic phenomenon in a class of crystalline materials known as kagome lattice, a geometric arrangement of corner-sharing triangles named after a traditional Japanese basket pattern.
This discovery reveals how heating methods impact the presence of a charge density wave (CDW), a quantum pattern of electron arrangement, in the kagome metal iron germanide (FeGe). It also demonstrates how its reappearance enhances magnetic and electronic properties.