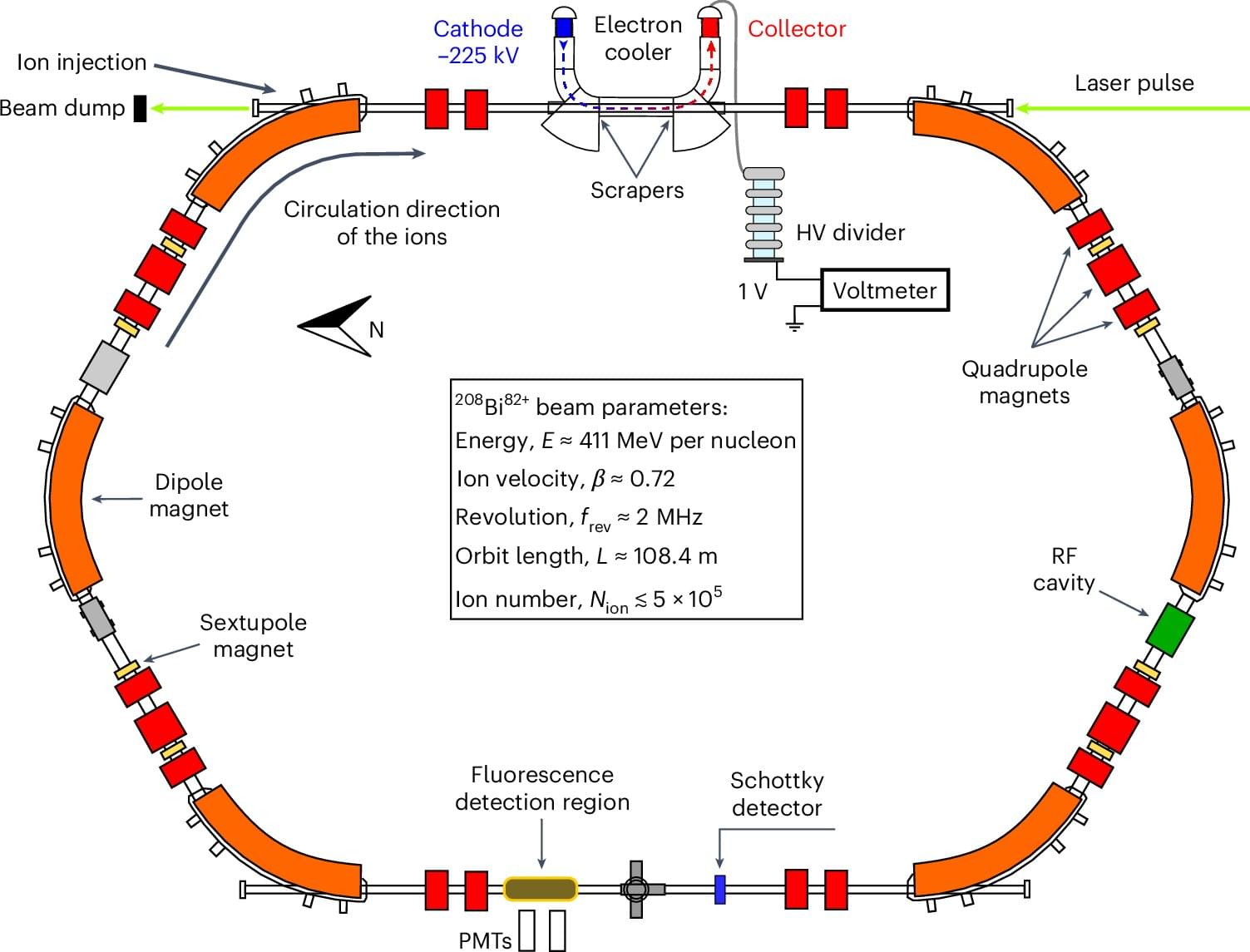
Many atomic nuclei have a magnetic field similar to that of Earth. However, directly at the surface of a heavy nucleus such as lead or bismuth, it is trillions of times stronger than Earth’s field and more comparable to that of a neutron star. Whether we understand the behavior of an electron in such strong fields is still an open question.
A research team led by TU Darmstadt at the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research has now taken an important step toward clarifying this question. Their findings have been published in Nature Physics. The results confirm the theoretical predictions.
Hydrogen-like ions, i.e., atomic nuclei to which only a single electron is bound, are theoretically particularly easy to describe. In the case of heavy nuclei with a high proton number—bismuth, for example, has 83 positively charged protons in its nucleus—the strong electrical attraction binds the electron close to the nucleus and thus within this extreme magnetic field. There, the electron aligns its own magnetic field with that of the nucleus like a compass needle.