All that I can say is “WOW!”
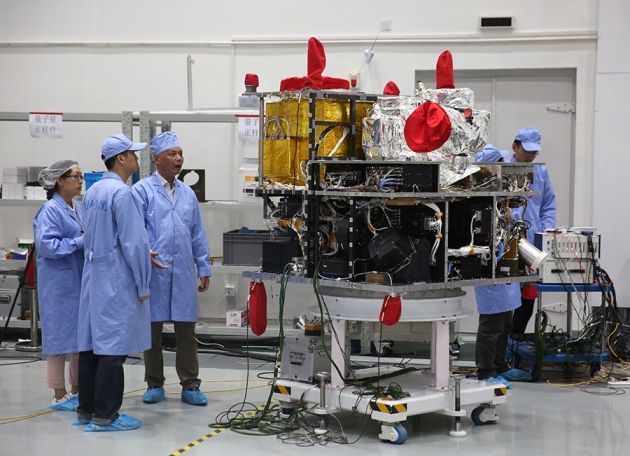
CHINA is on the brink of launching a groundbreaking new satellite capable of conducting quantum experiments in space, leading some to predict it will usher in the beginning of a new space race.
The world will be watching very closely after the Chinese-led satellite launches in August. If it proves successful in carrying out the quantum experiments, China is expected to follow it with many more in a bid to create a super secure network that uses an encryption technique based on the principles of quantum communication.
The reason world powers will be paying such close attention is that quantum-enabled spacecrafts are able to provide communication pathways that are completely unhackable. While the technology has been trialled on the ground over short distances, the capability to do so across the globe would be a huge game changer — it holds the promise of a world with completely secure digital communication.