Hula hooping is so commonplace that we may overlook some interesting questions it raises: “What keeps a hula hoop up against gravity?” and “Are some body types better for hula hooping than others?” A team of mathematicians explored and answered these questions with findings that also point to new ways to better harness energy and improve robotic positioners.
The results are the first to explain the physics and mathematics of hula hooping.
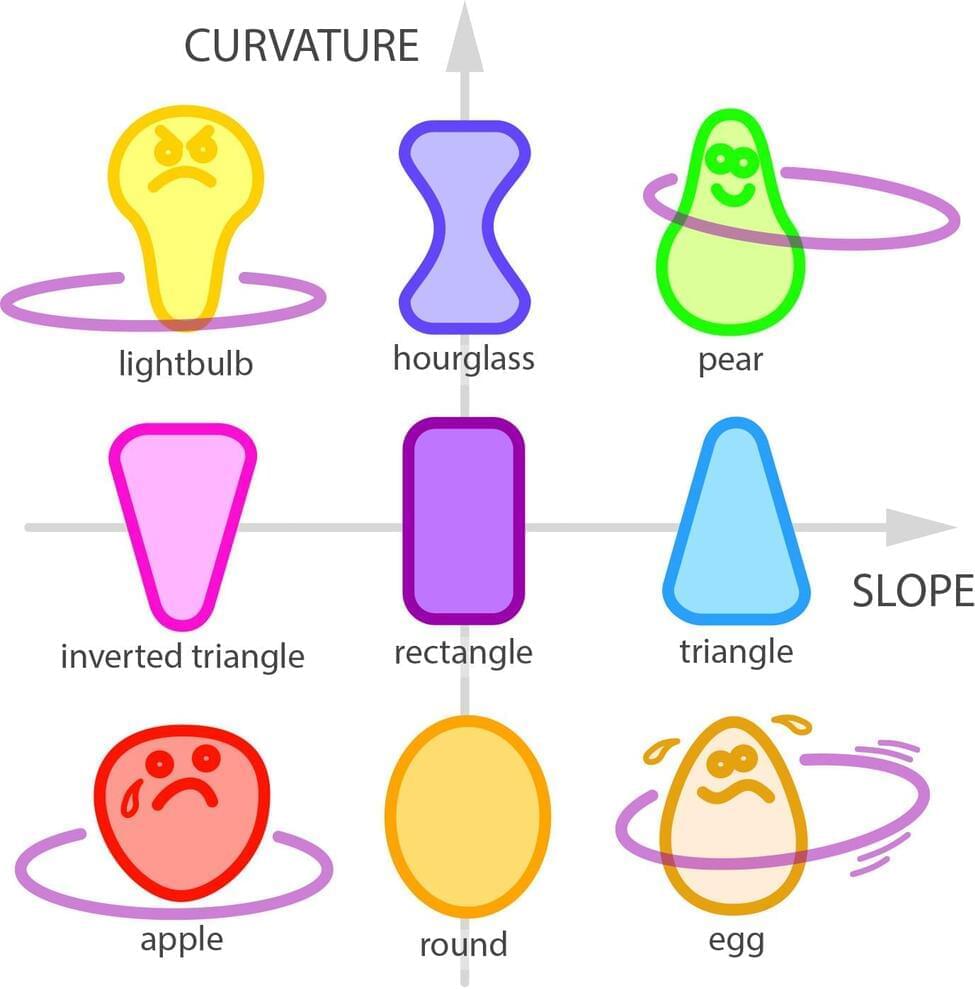
“We were specifically interested in what kinds of body motions and shapes could successfully hold the hoop up and what physical requirements and restrictions are involved,” explains Leif Ristroph, an associate professor at New York University’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and the senior author of the paper, which appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.