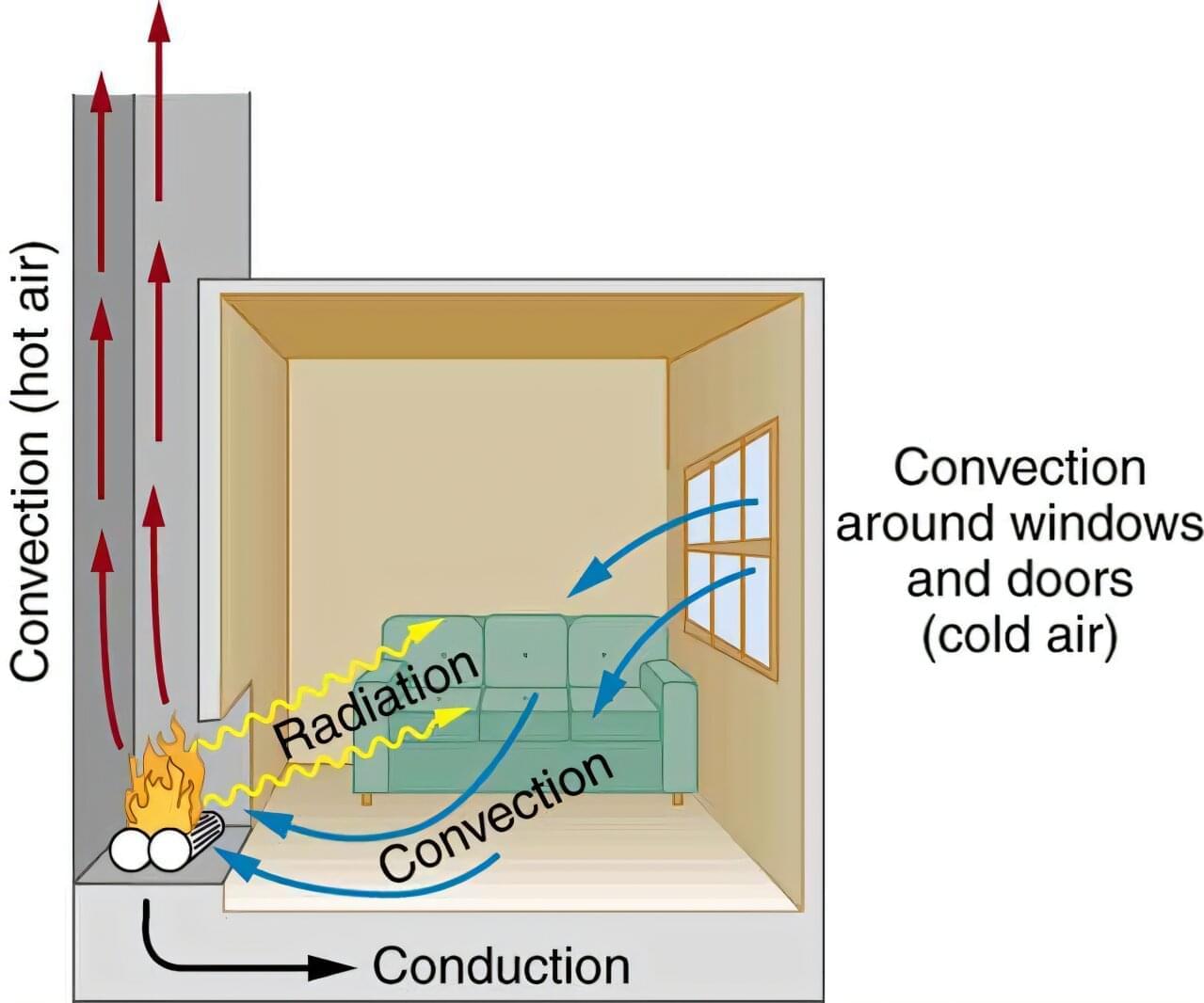
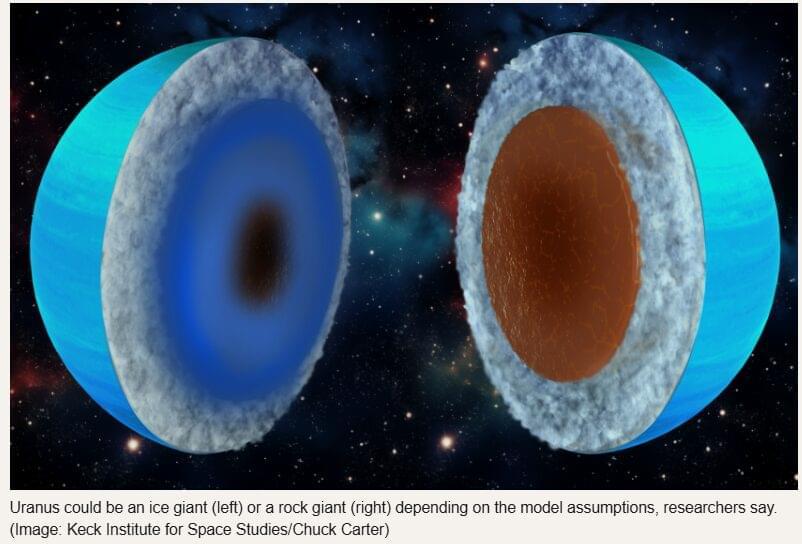
Uranus and Neptune may not be the icy worlds we’ve long imagined. A new Swiss-led study uses innovative hybrid modeling to reveal that these planets could just as easily be dominated by rock as by water-rich ices. The findings also help explain their bizarre, multi-poled magnetic fields and open the door to a wider range of possible interior structures. But major uncertainties remain, and only future space missions will The Solar System is commonly grouped by planetary composition: four rocky terrestrial planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars), two massive gas giants (Jupiter and Saturn), and a pair of ice giants (Uranus and Neptune). However, new research from a scientific team at the University of Zurich (UZH) suggests that Uranus and Neptune may contain far more rock than previously assumed. The study does not argue that these planets must be either water-rich or rock-rich. Instead, it questions the long-standing idea that an ice-heavy interior is the only conclusion supported by available data. This broader interpretation also aligns with the finding that Pluto, a dwarf planet, is dominated by rock.
To better understand what lies inside Uranus and Neptune, the researchers created a specialized simulation technique. “The ice giant classification is oversimplified as Uranus and Neptune are still poorly understood,” says Luca Morf, PhD student at the University of Zurich and lead author of the work. “Models based on physics were too assumption-heavy, while empirical models are too simplistic. We combined both approaches to get interior models that are both “agnostic” or unbiased and yet, are physically consistent.”
The process begins with a randomly generated density profile representing the interior of each planet. The team then determines the gravitational field that would match observational measurements and uses that information to infer the possible composition. The cycle is repeated until the model best fits all available data.