A puzzling discovery in NGC 1068 shows a flood of neutrinos but weak gamma rays. Scientists now suspect helium atoms exploding near a black hole are the source, opening a whole new view of how particles behave in deep space.


We know that all the other forces governed by quantum mechanics are transmitted by indivisible particles: photons for the electromagnetic force, which governs light and the basic chemistry of matter; gluons for the strong force, which sticks together protons and neutrons inside atoms; and W and Z bosons for the weak force, which enables certain particles to radioactively decay. If gravity has the same underlying theory as these forces, it should also be carried by its own particle: a graviton. Now researchers, including Claudia Du Rham at Imperial in London, are in the hunt for these mysterious and vanishingly weak particles.
–
Learn more ➤ https://www.newscientist.com/article/.… ➤ https://bit.ly/NSYTSUBS Get more from New Scientist: Official website: https://bit.ly/NSYTHP Facebook: https://bit.ly/NSYTFB Twitter: https://bit.ly/NSYTTW Instagram: https://bit.ly/NSYTINSTA LinkedIn: https://bit.ly/NSYTLIN About New Scientist: New Scientist was founded in 1956 for “all those interested in scientific discovery and its social consequences”. Today our website, videos, newsletters, app, podcast and print magazine cover the world’s most important, exciting and entertaining science news as well as asking the big-picture questions about life, the universe, and what it means to be human. New Scientist https://www.newscientist.com/
Subscribe ➤ https://bit.ly/NSYTSUBS
Get more from New Scientist:
Official website: https://bit.ly/NSYTHP
Facebook: https://bit.ly/NSYTFB
Twitter: https://bit.ly/NSYTTW
Instagram: https://bit.ly/NSYTINSTA
LinkedIn: https://bit.ly/NSYTLIN
About New Scientist:
New Scientist was founded in 1956 for “all those interested in scientific discovery and its social consequences”. Today our website, videos, newsletters, app, podcast and print magazine cover the world’s most important, exciting and entertaining science news as well as asking the big-picture questions about life, the universe, and what it means to be human.
New Scientist.
https://www.newscientist.com/
Check out my course about quantum mechanics on Brilliant! First 30 days are free and 20% off the annual premium subscription when you use our link ➜ https://brilliant.org/sabine.
Correction to the screen text at 05:04: It’s in the range of microgram. What I say is correct, the text isn’t. Sorry about that.
This video comes with a quiz which you can take here: https://quizwithit.com/start_thequiz/.… are one of the most sought-after particles in physics. They could help physicists combine quantum physics with gravity to create a theory of “quantum gravity.” We thought until recently they were for all practical purposes impossible to detect, but now scientists are coming up with some ideas for how graviton-detecting experiments could work for real. Let’s take a look. 🤓 Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/ 💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg 📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/ 👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine 📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle… 👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl… 🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder 🖼️ On instagram ➜
/ sciencewtg #science #sciencenews #physics #gravity.
Gravitons are one of the most sought-after particles in physics. They could help physicists combine quantum physics with gravity to create a theory of \.
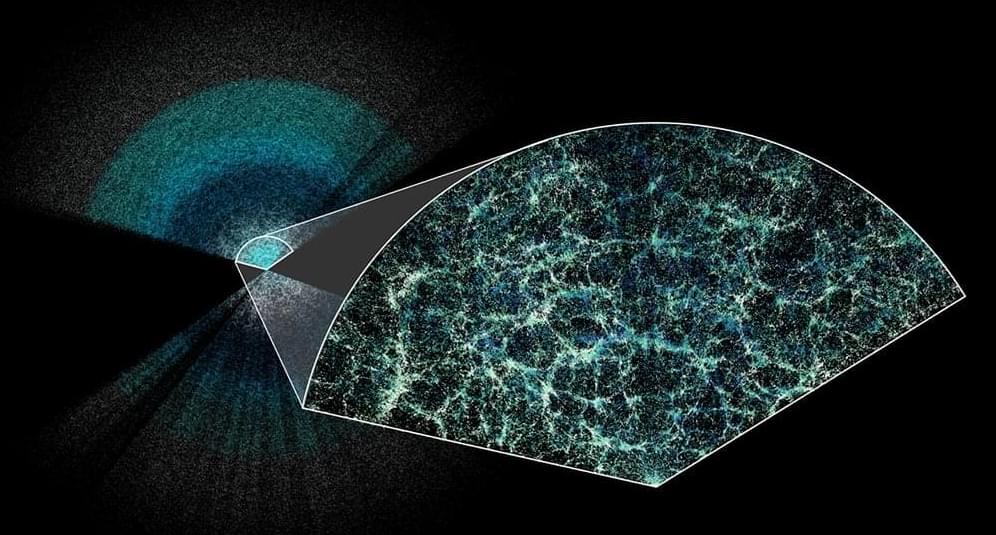
For a while now, there has been a problematic mystery at the heart of the standard cosmological model. Although all observations support the expanding Universe model, observations of the early period of the cosmos give a lower rate of acceleration than more local observations. We call it the Hubble tension problem, and we have no idea how to solve it. Naturally, there have been several proposed ideas: what if general relativity is wrong; what if dark matter doesn’t exist; what if the rate of time isn’t uniform; heck, what if the entire Universe rotates. So, let’s add a new idea to the pile: what if dark matter evolves?
While there have been several models proposing an evolving dark energy, the idea of evolving dark matter hasn’t been widely considered. The reason for this is twofold. First, the observations we have of dark matter are excellent. They point to the presence of some kind of material that doesn’t interact strongly with light. The only major weak point is that we haven’t observed dark matter particles directly. Second, the vast majority of folk opposed to dark matter focus on eliminating it altogether through things like modified gravity. They figure dark matter is fundamentally wrong, not something to be tweaked. That makes this new idea rather interesting.
In this work, the authors look at both evolving dark energy and evolving dark matter and argue that the latter is a much better fit to observational data. The first thing they note is that the two models are somewhat related. Since the evolution of the cosmos depends in part on the ratio of energy density to matter density, a model with constant dark matter and evolving dark energy will always appear similar to a model with evolving dark matter and constant dark energy.
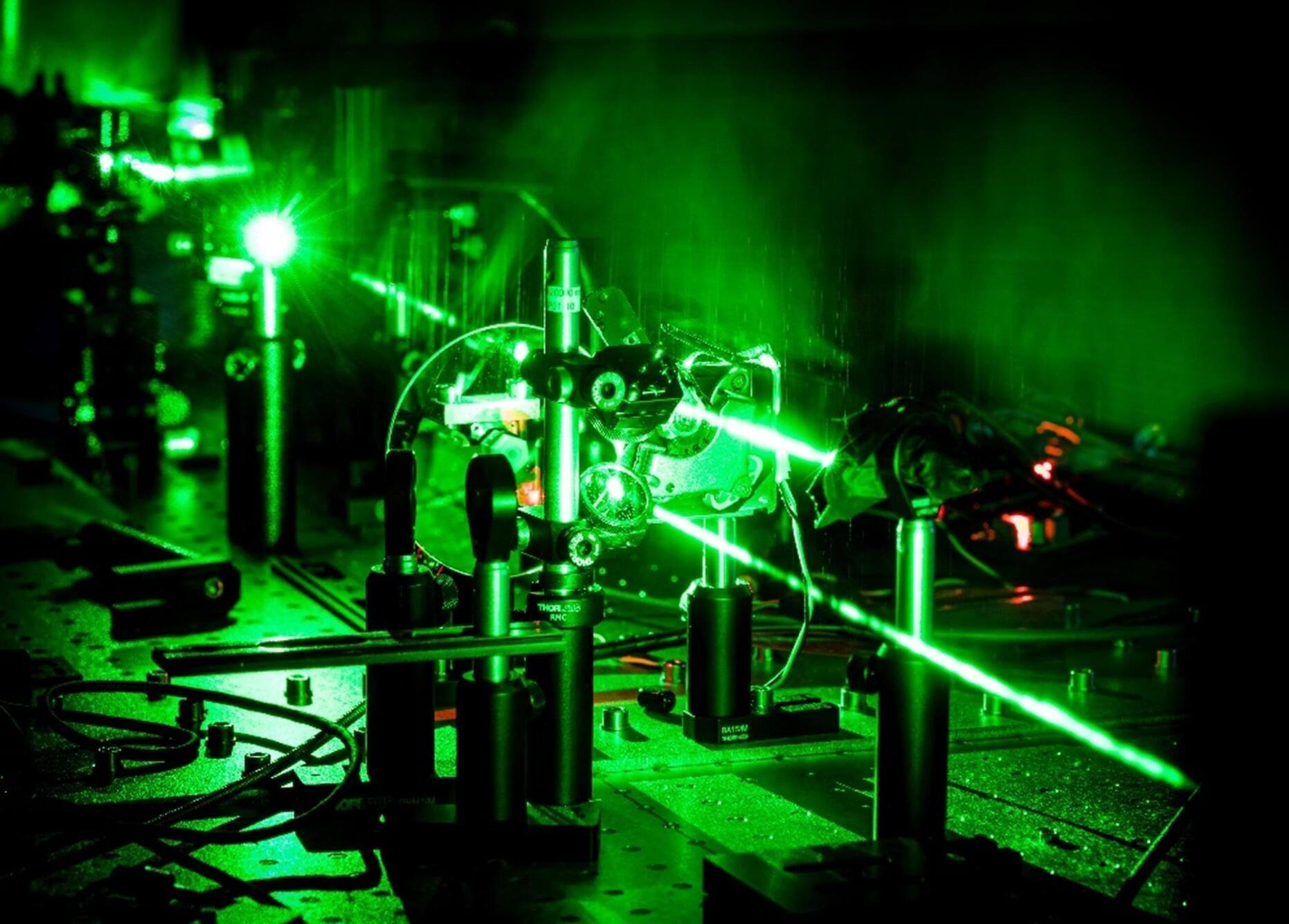
Researchers at the University of Turku in Finland have developed a simple method to explore a complex area of quantum science. The discovery makes research in this field cheaper and more accessible, which could significantly impact the development of future laser, quantum and high-tech display technologies.
A team of researchers developed a new method for fabricating small structures known as optical microcavities. These structures allow scientists to study how light interacts with matter in a very precise process that can lead to the creation of novel quantum states called polaritons. Polaritons are unusual hybrid particles made from light and matter.
The results have been published in the journal Advanced Optical Materials.

Medieval alchemists dreamed of transmuting lead into gold. Today, we know that lead and gold are different elements, and no amount of chemistry can turn one into the other.
But our modern knowledge tells us the basic difference between an atom of lead and an atom of gold: the lead atom contains exactly three more protons. So can we create a gold atom by simply pulling three protons out of a lead atom?
As it turns out, we can. But it’s not easy.

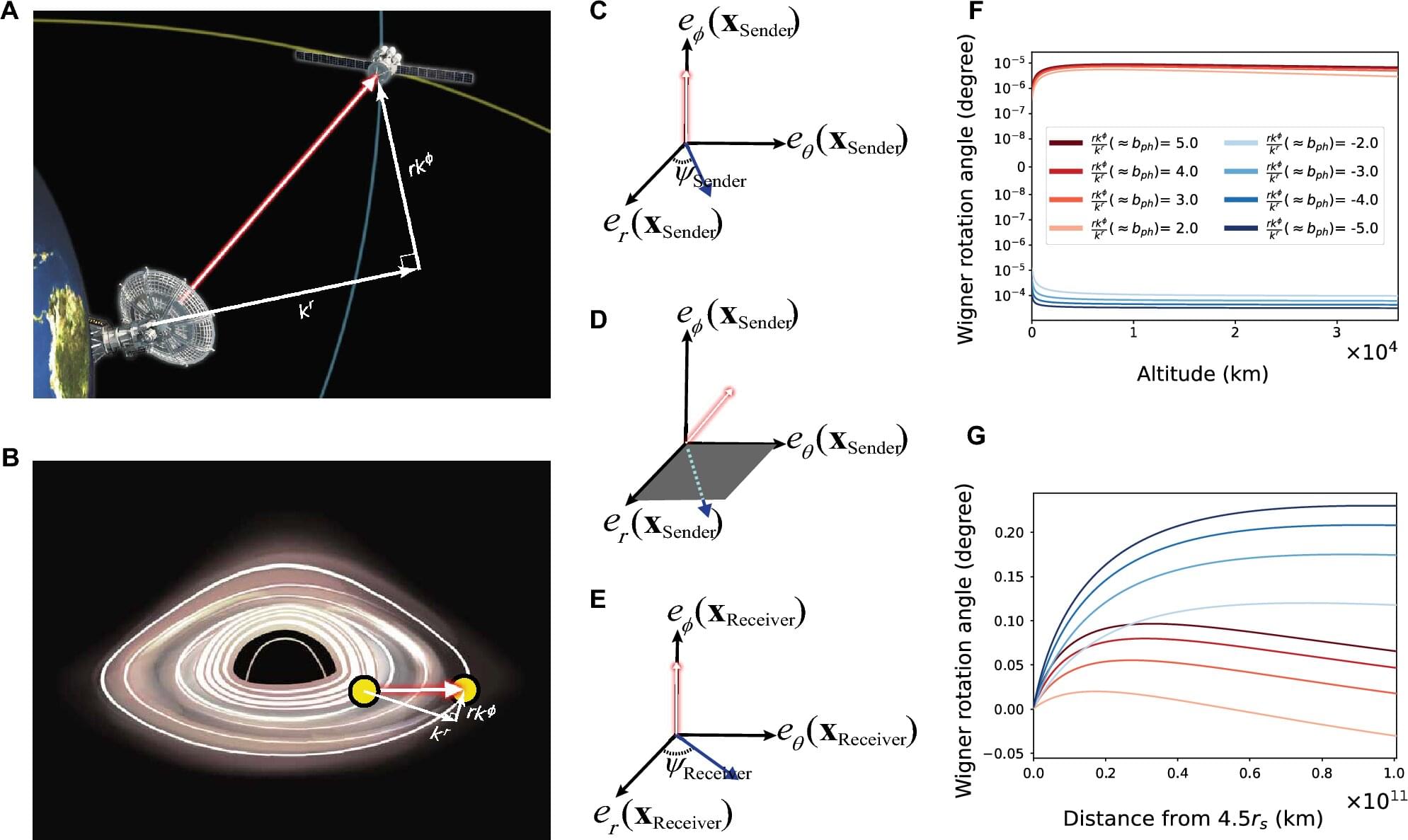
A team of physicists has uncovered a surprising new way to explore one of science’s greatest challenges: uniting the two fundamental theories that explain how our universe works—Einstein’s theory of gravity and quantum mechanics.
Despite decades of effort, no one has fully explained how gravity—which governs massive objects like planets and stars—fits with quantum mechanics, which describes the behavior of the tiniest particles in the universe. But now, scientists believe light may hold the key.
Warner A. Miller, Ph.D., co-author and a professor in the Department of Physics at Florida Atlantic University’s Charles E. Schmidt College of Science in collaboration with scientists at the University of Seoul and Seoul National University, South Korea, found that light’s polarization —the direction it vibrates as it travels—can behave in an unexpected way when passing through curved space. Normally, this polarization shifts slightly due to the warping of space by gravity, a well-known effect.
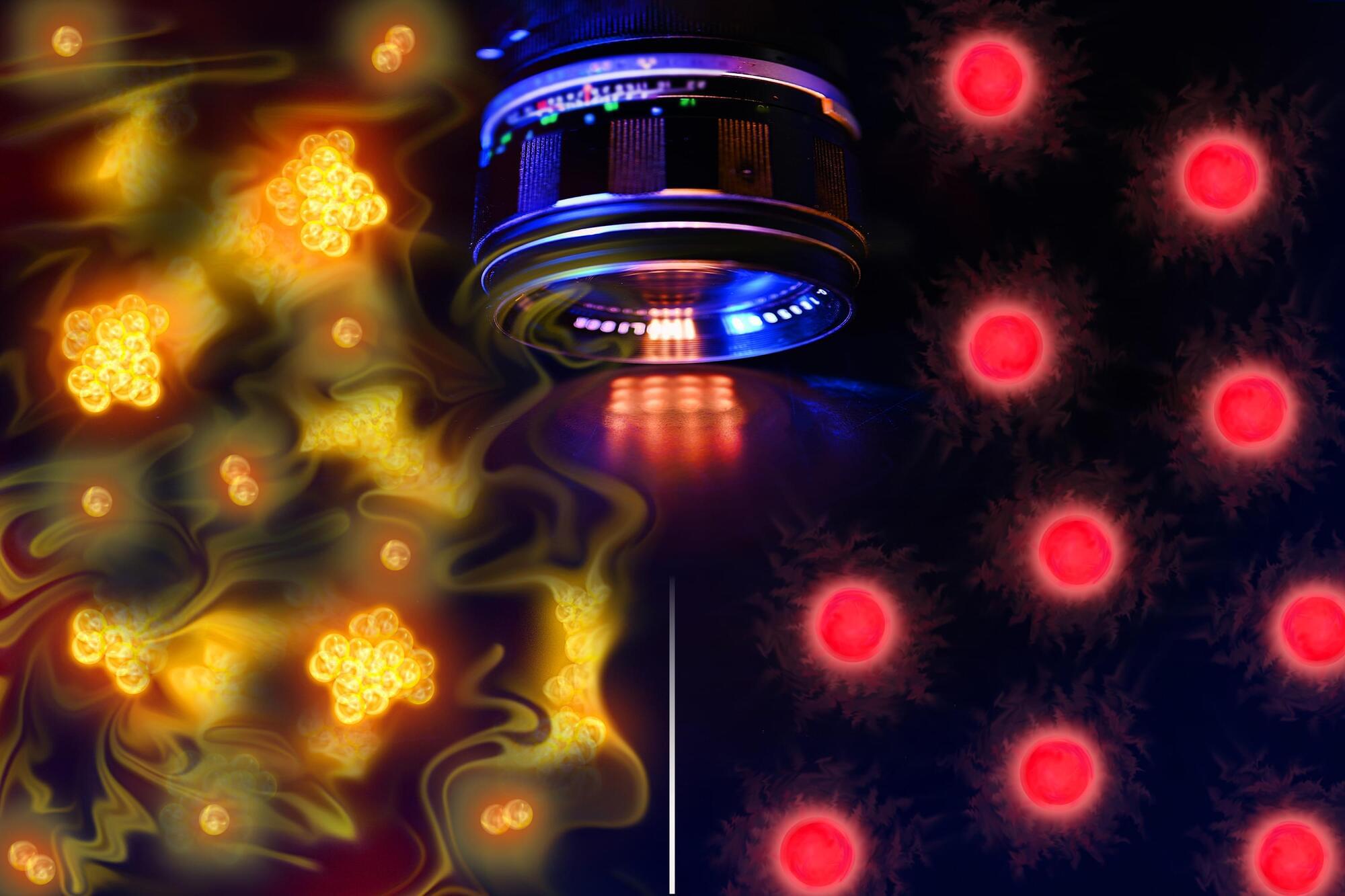

MIT physicists have captured the first images of individual atoms freely interacting in space. The pictures reveal correlations among the “free-range” particles that until now were predicted but never directly observed. Their findings, appearing today in the journal Physical Review Letters, will help scientists visualize never-before-seen quantum phenomena in real space.
The images were taken using a technique developed by the team that first allows a cloud of atoms to move and interact freely. The researchers then turn on a lattice of light that briefly freezes the atoms in their tracks, and apply finely tuned lasers to quickly illuminate the suspended atoms, creating a picture of their positions before the atoms naturally dissipate.
The physicists applied the technique to visualize clouds of different types of atoms, and snapped a number of imaging firsts. The researchers directly observed atoms known as “bosons,” which bunched up in a quantum phenomenon to form a wave. They also captured atoms known as “fermions” in the act of pairing up in free space — a key mechanism that enables superconductivity.