Nice.
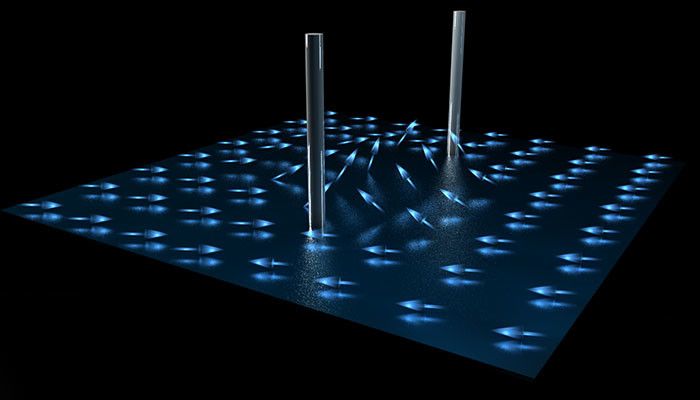
Scientists have enlisted the exotic properties of graphene, a one-atom-thick layer of carbon, to function like the film of an incredibly sensitive camera system in visually mapping tiny electric fields in a liquid. Researchers hope the new method will allow more extensive and precise imaging of the electrical signaling networks in our hearts and brains.
The ability to visually depict the strength and motion of very faint electrical fields could also aid in the development of so-called lab-on-a-chip devices that use very small quantities of fluids on a microchip-like platform to diagnose disease or aid in drug development, for example, or that automate a range of other biological and chemical analyses. The setup could potentially be adapted for sensing or trapping specific chemicals, too, and for studies of light-based electronics (a field known as optoelectronics).
“This was a completely new, innovative idea that graphene could be used as a material to sense electrical fields in a liquid,” said Jason Horng, a co-lead author of a study published Dec. 16 in Nature Communications that details the first demonstration of this graphene-based imaging system.