Dr. Fatima Ebrahimi designed a fusion rocket that uses magnetic fields to shoot plasma particles from a craft, which could take humans to Mars 10 times faster than current devices.
Category: particle physics – Page 538
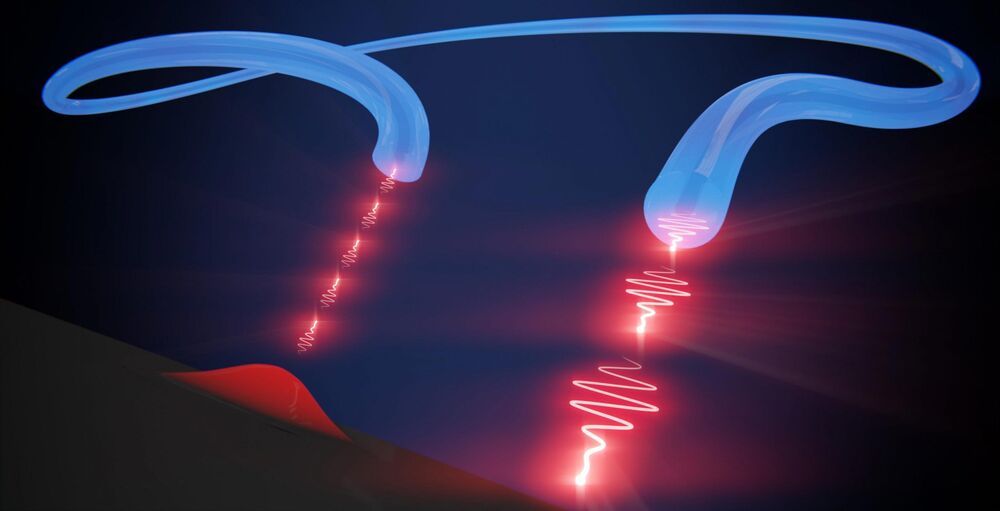
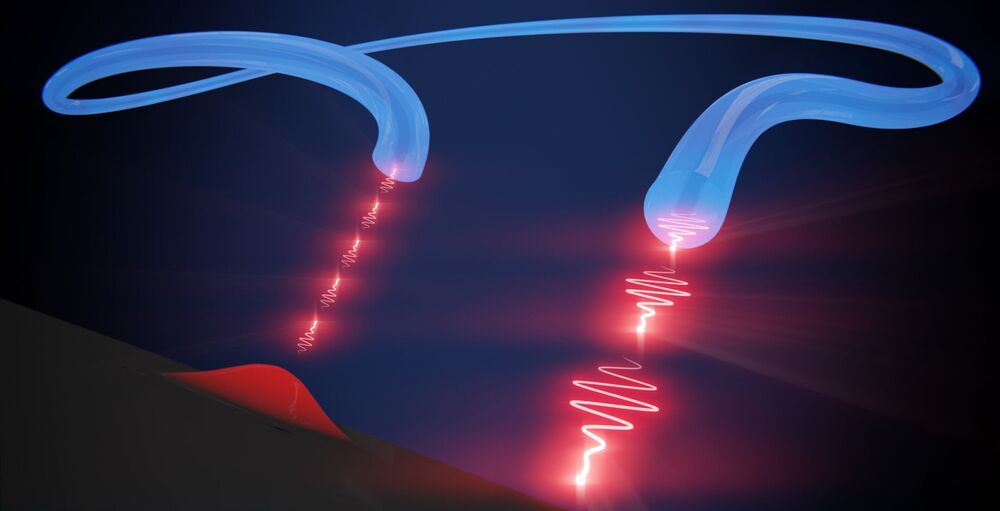
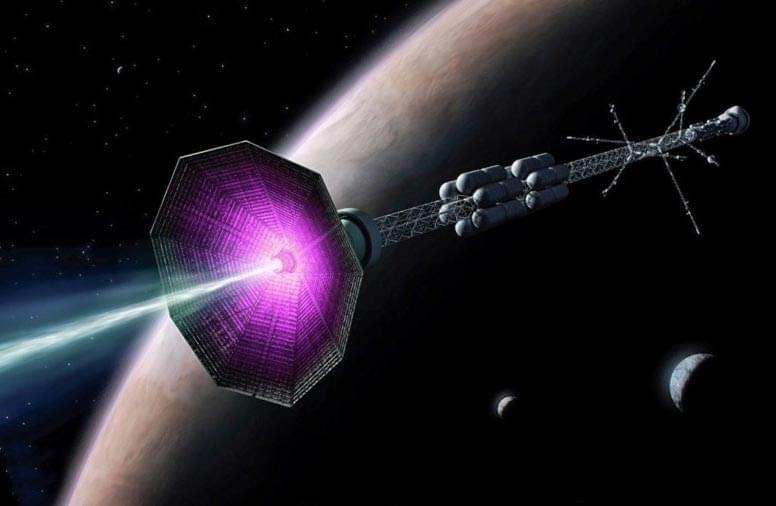



New Rocket Thruster Concept Exploits the Mechanism Behind Solar Flares
A new type of rocket thruster that could take humankind to Mars and beyond has been proposed by a physicist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL).
The device would apply magnetic fields to cause particles of plasma (link is external), electrically charged gas also known as the fourth state of matter, to shoot out the back of a rocket and, because of the conservation of momentum, propel the craft forward. Current space-proven plasma thrusters use electric fields to propel the particles.
The new concept would accelerate the particles using magnetic reconnection, a process found throughout the universe, including the surface of the sun, in which magnetic field lines converge, suddenly separate, and then join together again, producing lots of energy. Reconnection also occurs inside doughnut-shaped fusion (link is external) devices known as tokamaks (link is external).
BASE Antimatter Experiment opens up new possibilities in the search for cold dark matter
BASE opens up new possibilities in the search for cold dark matter.
The Baryon Antibaryon Symmetry Experiment (BASE) at CERN’s Antimatter Factory has set new limits on how easily axion-like particles in a narrow mass range around 2.97 neV can turn into photons, the particles of light. BASE’s new result, published by Physical Review Letters, describes this pioneering method and opens up new experimental possibilities in the search for cold dark matter.
Axions, or axion-like particles, are candidates for cold dark matter. From astrophysical observations, we believe that around 27% of the matter-energy content of the universe is made up of dark matter. These unknown particles feel the force of gravity, but they barely respond to the other fundamental forces, if they experience them at all. The best accepted theory of fundamental forces and particles, called the Standard Model of particle physics, does not contain any particles that have the right properties to be cold dark matter.
Since the Standard Model leaves many questions unanswered, physicists have proposed theories that go beyond it, some of which explain the nature of dark matter. Among such theories are those that suggest the existence of axions or axion-like particles. These theories need to be tested, and many experiments have been set up around the world to look for these particles, including at CERN. For the first time, BASE has turned the tools developed to detect single antiprotons, the antimatter equivalent of a proton, to the search for dark matter. This is especially significant as BASE was not designed for such studies.
“BASE has extremely sensitive detection systems to study the properties of single trapped antiprotons. These detectors can also be used to search for signals of particles other than those produced by antiprotons in traps. In this work, we used one of our detectors as an antenna to search for a new type of axion-like particles,” says Jack Devlin, a CERN research fellow working on the experiment.
Compared to the large detectors installed in the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), BASE is a small experiment. It is connected to CERN’s Antiproton Decelerator, which supplies it with antiprotons. BASE captures and suspends these particles in a Penning trap, a device that combines electric and strong magnetic fields. To avoid collisions with ordinary matter, the trap is operated at 5 kelvins (around-268 degrees Celsius), a temperature at which exceedingly low pressures, similar to those in deep space, are reached. In this extremely well-isolated environment, clouds of trapped antiprotons can exist for years at a time. By carefully adjusting the electric fields, the physicists at BASE can isolate individual antiprotons and move them to a separate part of the experiment. In this region, very sensitive superconducting resonant detectors can pick up the tiny electrical currents generated by single antiprotons as they move around the trap.
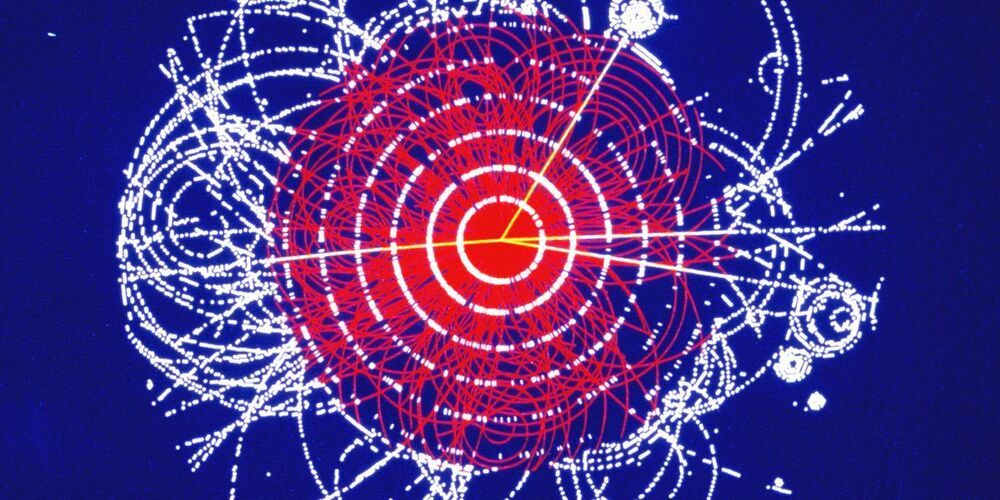

Researchers guide a single ion through a Bose-Einstein condensate
Transport processes are ubiquitous in nature, but still raise many questions. The research team around Florian Meinert from the Fifth Institute of Physics at the University of Stuttgart has now developed a new method to observe a single charged particle on its path through a dense cloud of ultracold atoms. The results were published in Physical Review Letters and are further reported in a Viewpoint column in the journal Physics.
Meinert’s team used a Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) for their experiments. This exotic state of matter consists of a dense cloud of ultracold atoms. By means of sophisticated laser excitation, the researchers created a single Rydberg atom within the gas. In this giant atom, the electron is a thousand times further away from the nucleus than in the ground state and thus only very weakly bound to the core. With a specially designed sequence of electric field pulses, the researchers snatched the electron away from the atom. The formerly neutral atom turned into a positively charged ion that remained nearly at rest despite the process of detaching the electron.
In the next step, the researchers used precise electric fields to pull the ion in a controlled way through the dense cloud of atoms in the BEC. The ion picked up speed in the electric field, collided on its way with other atoms, slowed down and was accelerated again by the electric field. The interplay between acceleration and deceleration by collisions led to a constant motion of the ion through the BEC.
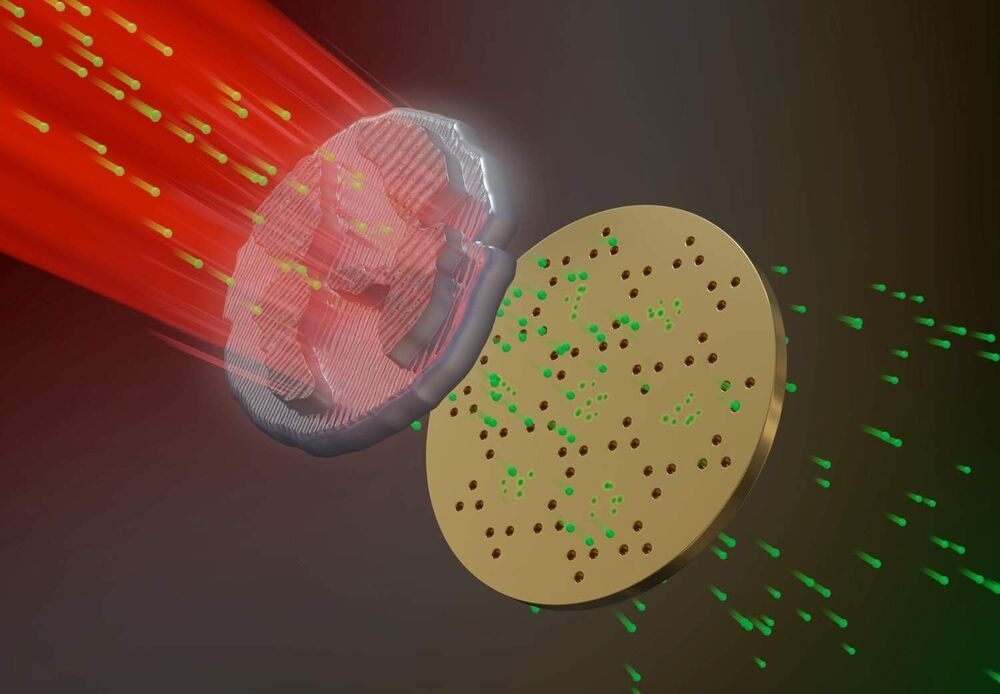
Physicists succeed in filming phase transition with extremely high spatial and temporal resolution
Laser beams can be used to change the properties of materials in an extremely precise way. This principle is already widely used in technologies such as rewritable DVDs. However, the underlying processes generally take place at such unimaginably fast speeds and at such a small scale that they have so far eluded direct observation. Researchers at the University of Göttingen and the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Biophysical Chemistry in Göttingen have now managed to film, for the first time, the laser transformation of a crystal structure with nanometre resolution and in slow motion in an electron microscope. The results have been published in the journal Science.
The team, which includes Thomas Danz and Professor Claus Ropers, took advantage of an unusual property of a material made up of atomically thin layers of sulfur and tantalum atoms. At room temperature, its crystal structure is distorted into tiny wavelike structures—a “charge-density wave” is formed. At higher temperatures, a phase transition occurs in which the original microscopic waves suddenly disappear. The electrical conductivity also changes drastically, an interesting effect for nano-electronics.
In their experiments, the researchers induced this phase transition with short laser pulses and recorded a film of the charge-density wave reaction. “What we observe is the rapid formation and growth of tiny regions where the material was switched to the next phase,” explains first author Thomas Danz from Göttingen University. “The ultrafast transmission electron microscope developed in Göttingen offers the highest time resolution for such imaging in the world today.” The special feature of the experiment lies in a newly developed imaging technique, which is particularly sensitive to the specific changes observed in this phase transition. The Göttingen physicists use it to take images that are composed exclusively of electrons that have been scattered by the crystal’s waviness.
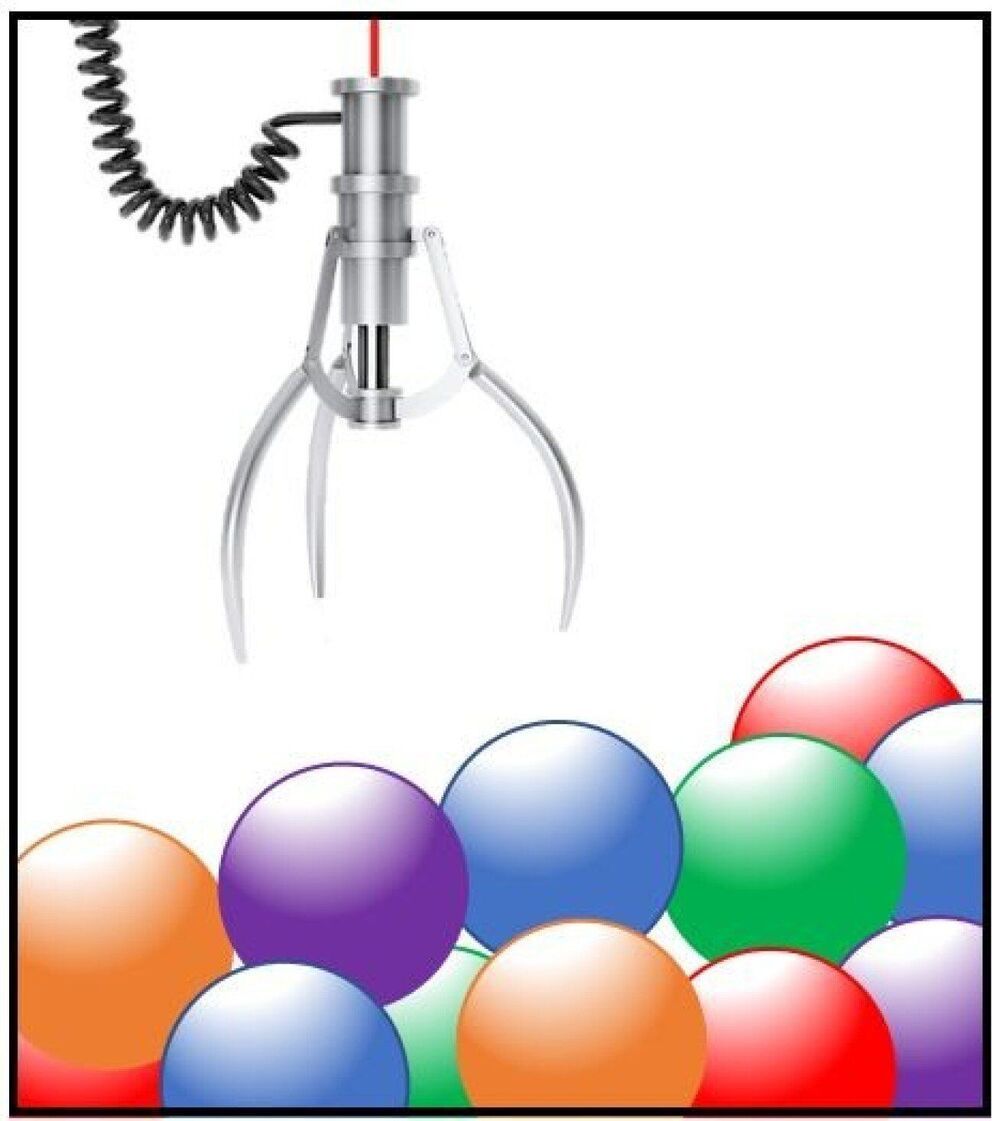
Adding or subtracting single quanta of sound
Researchers perform experiments that can add or subtract a single quantum of sound—with surprising results when applied to noisy sound fields.
Quantum mechanics tells us that physical objects can have both wave and particle properties. For instance, a single particle—or quantum—of light is known as a photon, and, in a similar fashion, a single quantum of sound is known as a phonon, which can be thought of as the smallest unit of sound energy.
A team of researchers spanning Imperial College London, University of Oxford, the Niels Bohr Institute, University of Bath, and the Australian National University have performed an experiment that can add or subtract a single phonon to a high-frequency sound field using interactions with laser light.
How Explainable Artificial Intelligence Can Help Humans Innovate
I like this idea. I don’t want AI to be a black box, I want to know what’s happening and how its doing it.
The field of artificial intelligence has created computers that can drive cars, synthesize chemical compounds, fold proteins, and detect high-energy particles at a superhuman level.
However, these AI algorithms cannot explain the thought processes behind their decisions. A computer that masters protein folding and also tells researchers more about the rules of biology is much more useful than a computer that folds proteins without explanation.
Therefore, AI researchers like me are now turning our efforts toward developing AI algorithms that can explain themselves in a manner that humans can understand. If we can do this, I believe that AI will be able to uncover and teach people new facts about the world that have not yet been discovered, leading to new innovations.