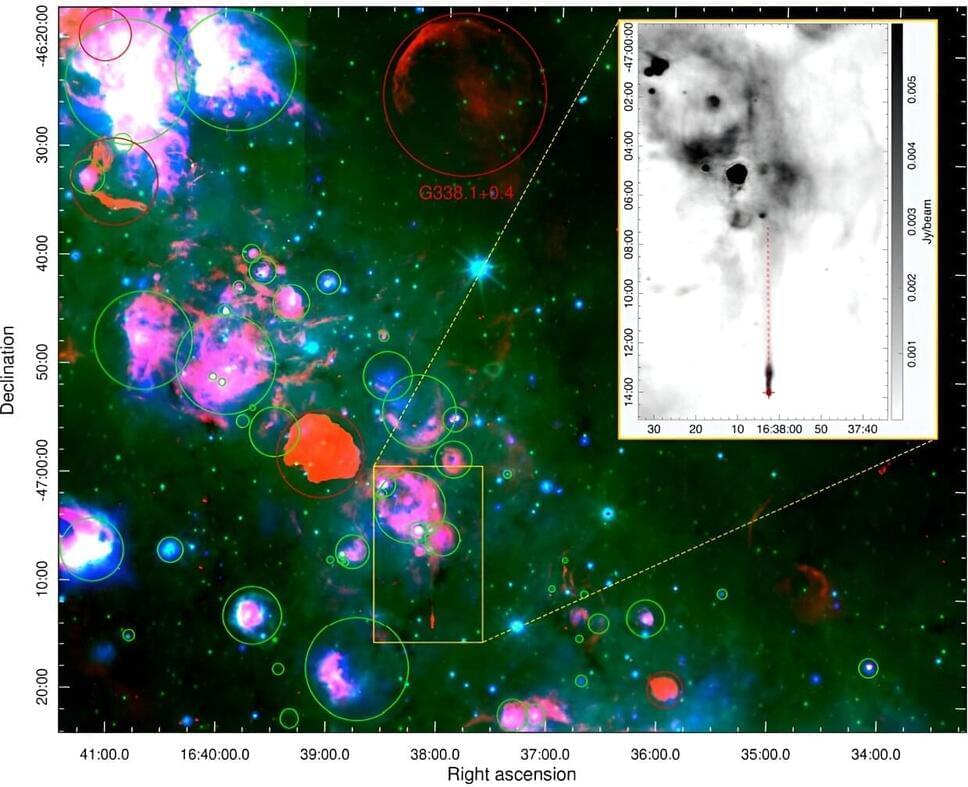
Astronomers from the Western Sydney University in Australia and elsewhere report the detection of a new pulsar wind nebula and a pulsar that powers it. The discovery, presented in a paper published Dec. 12 on the pre-print server arXiv, was made using the Australian Square Kilometer Array Pathfinder (ASKAP), as well as MeerKAT and Parkes radio telescopes.
Pulsar wind nebulae (PWNe) are nebulae powered by the wind of a pulsar. Pulsar wind is composed of charged particles; when it collides with the pulsar’s surroundings, in particular with the slowly expanding supernova ejecta, it develops a PWN.
Particles in PWNe lose their energy to radiation and become less energetic with distance from the central pulsar. Multiwavelength studies of these objects, including X-ray observations, especially using spatially-integrated spectra in the X-ray band, have the potential to uncover important information about particle flow in these nebulae. This could unveil important insights into the nature of PWNe in general.