What happened in the first few moments of our Universe’s existence? Today, scientists armed with giant telescopes and powerful particle accelerators, are probing the outer reaches of matter and the cosmos.
Guido’s book \.
What happened in the first few moments of our Universe’s existence? Today, scientists armed with giant telescopes and powerful particle accelerators, are probing the outer reaches of matter and the cosmos.
Guido’s book \.

Top minds at the world’s largest atom smasher have released a blueprint for a much bigger successor that could vastly improve research into the remaining enigmas of physics.
The plans for the Future Circular Collider—a nearly 91-kilometer (56.5-mile) loop along the French-Swiss border and below Lake Geneva—published late Monday put the finishing details on a project roughly a decade in the making at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research.
The FCC would carry out high-precision experiments in the mid-2040s to study “known physics” in greater detail, then enter a second phase—planned for 2070—that would conduct high-energy collisions of protons and heavy ions that would “open the door to the unknown,” said Giorgio Chiarelli, a research director at Italy’s National Institute of Nuclear Physics.
(/ ˈ m ʌr i ˈ ɡ ɛ l ˈ m æ n / ; September 15, 1929 – May 24, 2019) [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 6 ] was an American theoretical physicist who played a preeminent role in the development of the theory of elementary particles. Gell-Mann introduced the concept of quarks as the fundamental building blocks of the strongly interacting particles, and the renormalization group as a foundational element of quantum field theory and statistical mechanics. He played key roles in developing the concept of chirality in the theory of the weak interactions and spontaneous chiral symmetry breaking in the strong interactions, which controls the physics of the light mesons. In the 1970s he was a co-inventor of quantum chromodynamics (QCD) which explains the confinement of quarks in mesons and baryons and forms a large part of the Standard Model of elementary particles and forces.
Murray Gell-Mann received the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the theory of elementary particles.
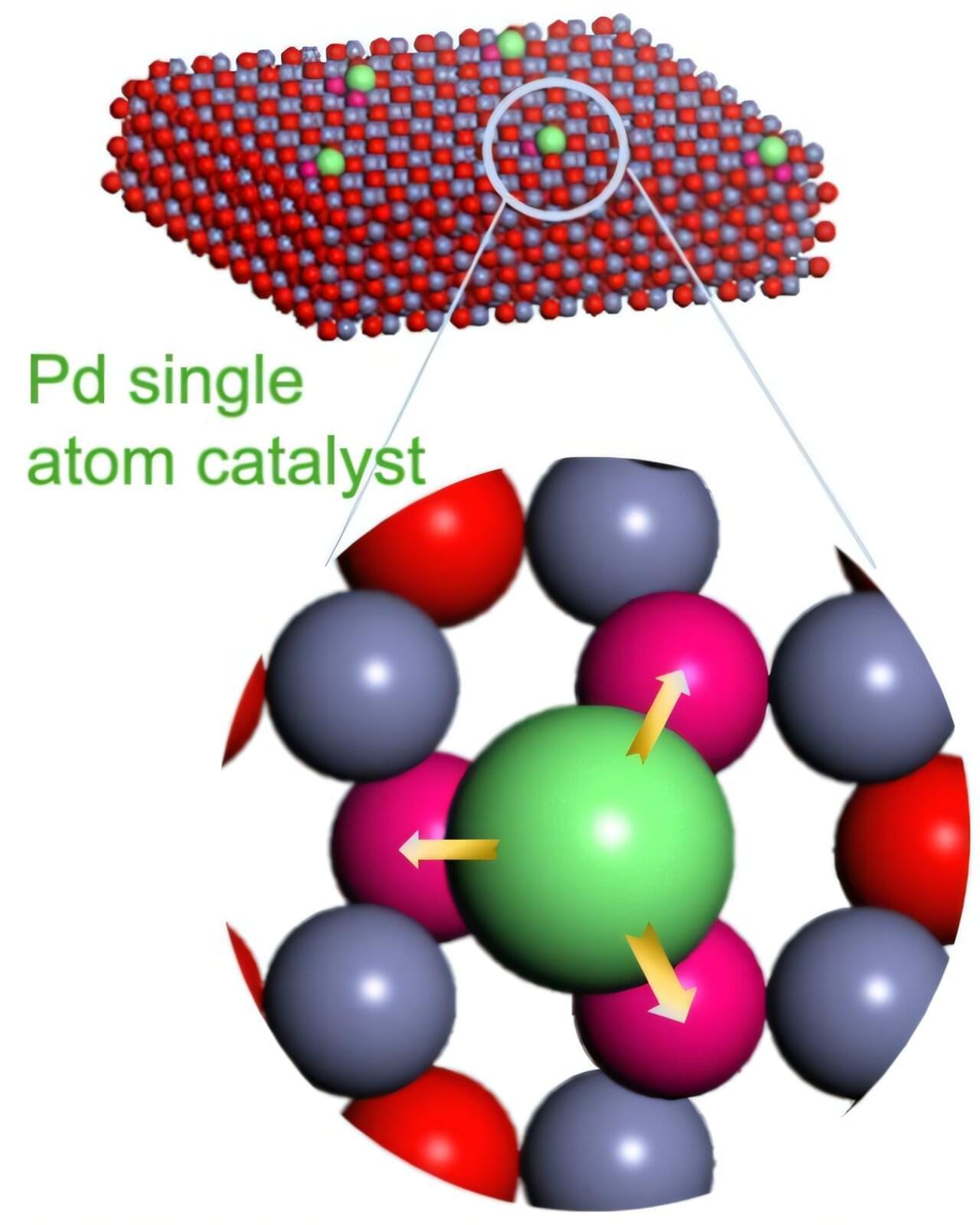
A chemical reaction that’s vital to a range of commercial and industrial goods may soon be initiated more effectively and less expensively thanks to a collaboration that included Oregon State University College of Engineering researchers.
The study, published in Nature, involves hydrogenation —adding the diatomic hydrogen molecule, H2, to other compounds.
“Hydrogenation is a critical and diverse reaction used to create food products, fuels, commodity chemicals and pharmaceuticals,” said Zhenxing Feng, associate professor of chemical engineering. “However, for the reaction to be economically viable, a catalyst such as palladium or platinum is invariably required to increase its reaction rate and thus lower cost.”
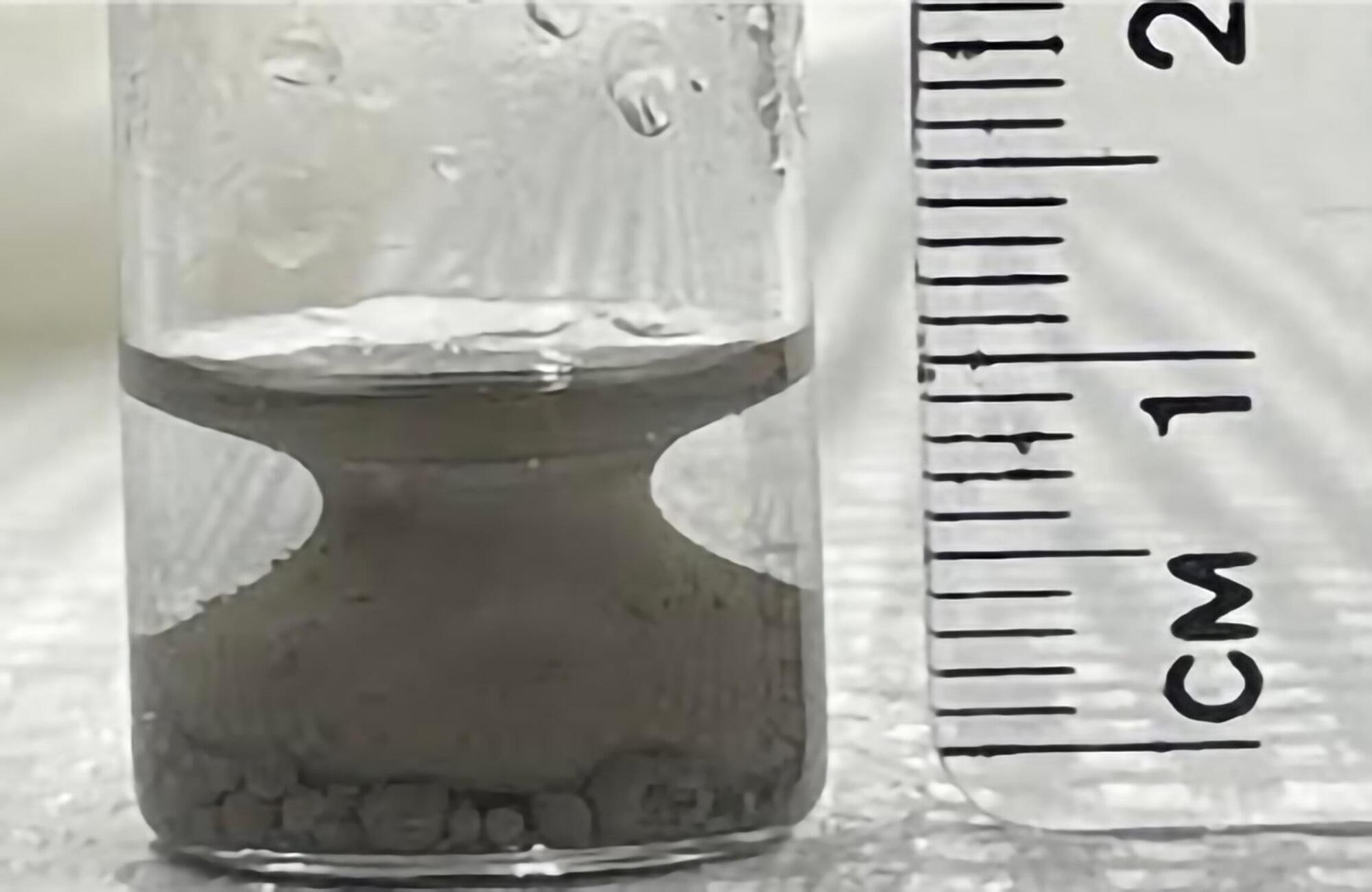


A team of researchers led by a physics graduate student at the University of Massachusetts Amherst made the surprising discovery of what they call a “shape-recovering liquid,” which defies some long-held expectations derived from the laws of thermodynamics.
The research, published in Nature Physics, details a mixture of oil, water and magnetized particles that, when shaken, always quickly separates into what looks like the classically curvaceous lines of a Grecian urn.
“Imagine your favorite Italian salad dressing,” says Thomas Russell, Silvio O. Conte Distinguished Professor of Polymer Science and Engineering at UMass Amherst and one of the paper’s senior authors.

Quantum states can only be prepared and observed under highly controlled conditions. A research team from Innsbruck, Austria, has now succeeded in creating so-called hot Schrödinger cat states in a superconducting microwave resonator. The study, published in Science Advances, shows that quantum phenomena can also be observed and used in less perfect, warmer conditions.
Schrödinger cat states are a fascinating phenomenon in quantum physics in which a quantum object exists simultaneously in two different states. In Erwin Schrödinger’s thought experiment, it is a cat that is alive and dead at the same time.
In real experiments, such simultaneity has been seen in the locations of atoms and molecules and in the oscillations of electromagnetic resonators.
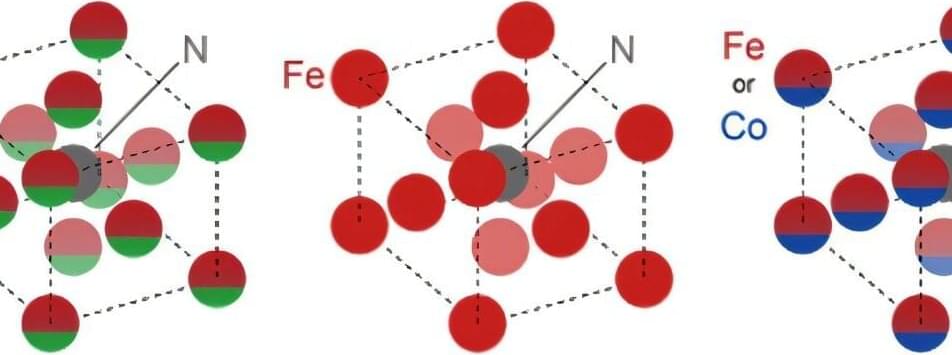
The field of spintronics, which integrates the charge and spin properties of electrons to develop electronic devices with enhanced functionality and energy efficiency, has expanded into new applications.
Beyond current technologies such as hard disk drive read heads and magnetic random-access memory (MRAM), researchers are now investigating flexible spintronics for use in wearable devices and sheet-type sensors.
For these applications, detecting small changes in mechanical stress through electrical resistance modulation is essential. This requires not only materials with significant magnetoresistance effects but also control over their magnetoelastic properties.

A pair of top quarks has been detected in the detritus spraying forth from the collision of two atoms of lead.
It’s the first time that this specific quark-antiquark pair has been spotted in a collision between two nuclei. The detection strengthens evidence that all six quark flavors existed at the dawn of time, in the soupy quark-gluon plasma thought to have suffused the Universe in the moments after the Big Bang.
This means that we’re a step closer to taking new measurements of this primordial soup, and gleaning new insights into how our Universe formed from the very beginning.