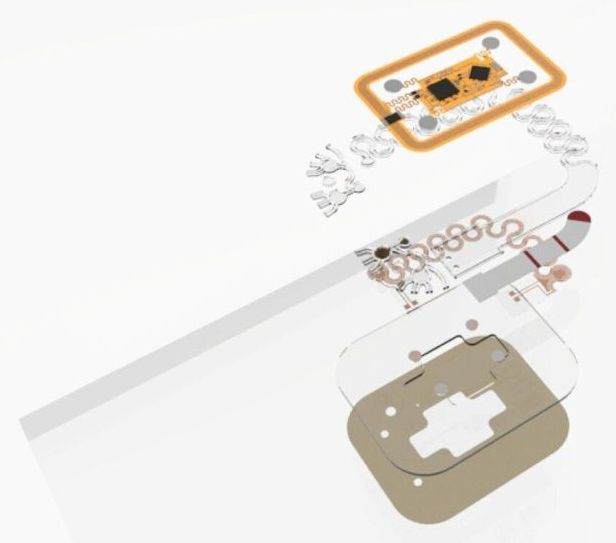
An international team of researchers has developed a multifunctional skin-mounted microfluidic device that is able to measure stress in people in multiple ways. In their paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the group describes their device and how it could be useful.
Prior research has shown that long-term stress can damage a person’s health. It can lead to diabetes, depression, obesity and a host of other problems. Some have suggested that one of the ways to combat stress is to create a means for alerting a person to their heightened stress so that they might take action to reduce it. To that end, prior teams have developed skin-adhesive devices that that collect sweat samples. The tiny samples contain small amounts of cortisol, a hormone that can be used as a marker of stress levels. In this new effort, the researchers have improved on these devices by developing one that measures more than just cortisol levels and is much more comfortable.
The researchers began with the notion that in order to convince people to wear a device full time, it had to be both useful and comfortable. The solved the latter issue by making their device out of soft materials that adhere gently to the skin. They also used a skeletal design for their microfluidic sweat-collection apparatus—a flexible mesh. They also added more functionality. In addition to cortisol, their device is able to measure glucose and vitamin C levels. They also added electrodes underneath that are able to measure sweat rate and electrical conductivity of the skin, both of which change in response to stress. They also added a wireless transmitter that sends all of the data to a nearby smartphone running the device’s associated app.