Circa 2015 brain immortality through aldehyde stabilized cryopreservation.
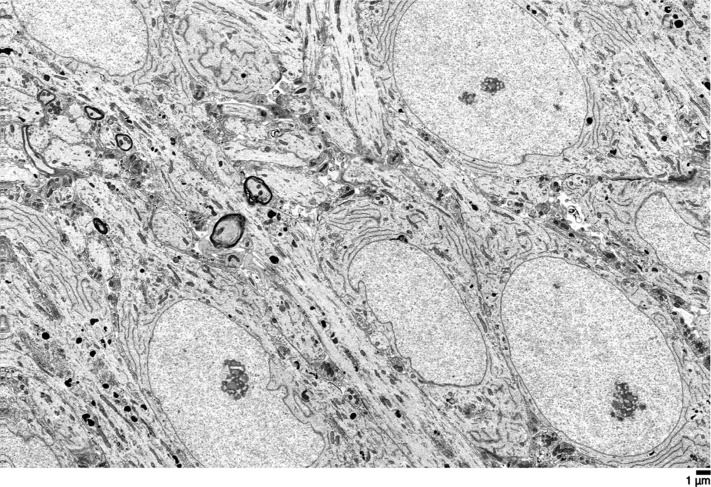
We describe here a new cryobiological and neurobiological technique, aldehyde-stabilized cryopreservation (ASC), which demonstrates the relevance and utility of advanced cryopreservation science for the neurobiological research community. ASC is a new brain-banking technique designed to facilitate neuroanatomic research such as connectomics research, and has the unique ability to combine stable long term ice-free sample storage with excellent anatomical resolution. To demonstrate the feasibility of ASC, we perfuse-fixed rabbit and pig brains with a glutaraldehyde-based fixative, then slowly perfused increasing concentrations of ethylene glycol over several hours in a manner similar to techniques used for whole organ cryopreservation. Once 65% w/v ethylene glycol was reached, we vitrified brains at −135 °C for indefinite long-term storage. Vitrified brains were rewarmed and the cryoprotectant removed either by perfusion or gradual diffusion from brain slices. We evaluated ASC-processed brains by electron microscopy of multiple regions across the whole brain and by Focused Ion Beam Milling and Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM) imaging of selected brain volumes. Preservation was uniformly excellent: processes were easily traceable and synapses were crisp in both species. Aldehyde-stabilized cryopreservation has many advantages over other brain-banking techniques: chemicals are delivered via perfusion, which enables easy scaling to brains of any size; vitrification ensures that the ultrastructure of the brain will not degrade even over very long storage times; and the cryoprotectant can be removed, yielding a perfusable aldehyde-preserved brain which is suitable for a wide variety of brain assays.