“In this study, for the first time, we see evidence that events which were always assumed to be occurring in the same manner, regardless of sex, may actually be completely different in males compared to females. The fact that these differences involve astrocytes, which have traditionally been ignored in neuroscience but have recently become a hot topic for study, makes them all the more intriguing.”
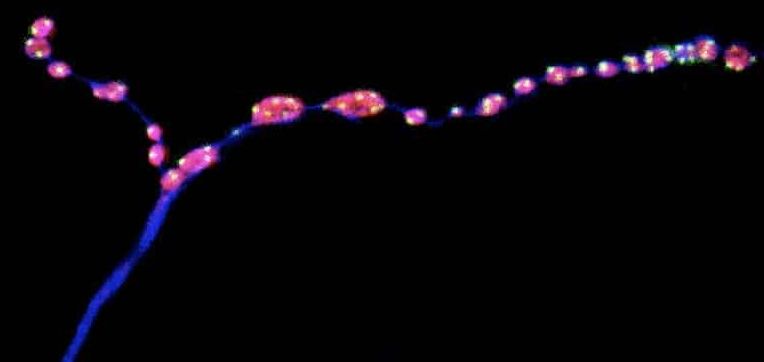
Summary: Thrombospondin-2, a protein with cell adhesion properties usually secreted by astrocytes, prompted a strong increase in synapses in male-derived neurons but showed no effect in females.
Source: Marshall University
During development, brain cells may find different ways to connect with each other based on sex, according to researchers at the Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine.
The study, recently published in eNeuro, showed a significantly more robust synaptogenic response in male-derived cells compared to female-derived cells when exposed to factors secreted from astrocytes, which are non-neuronal cells found throughout the central nervous system.