
Category: neuroscience – Page 87

Disconnected cerebral hemisphere in epilepsy patients shows sleep-like state during wakefulness
Sleep-like slow-wave patterns persist for years in surgically disconnected neural tissue of awake epilepsy patients, according to a study published in PLOS Biology by Marcello Massimini from Universita degli Studi di Milano, Italy, and colleagues.
The presence of slow waves in the isolated hemisphere impairs consciousness; however, whether they serve any functional or plastic role remains unclear.
Hemispherotomy is a surgical procedure used to treat severe cases of epilepsy in children. The goal of this procedure is to achieve maximal disconnection of the diseased neural tissue, potentially encompassing an entire hemisphere, from the rest of the brain to prevent the spread of seizures.
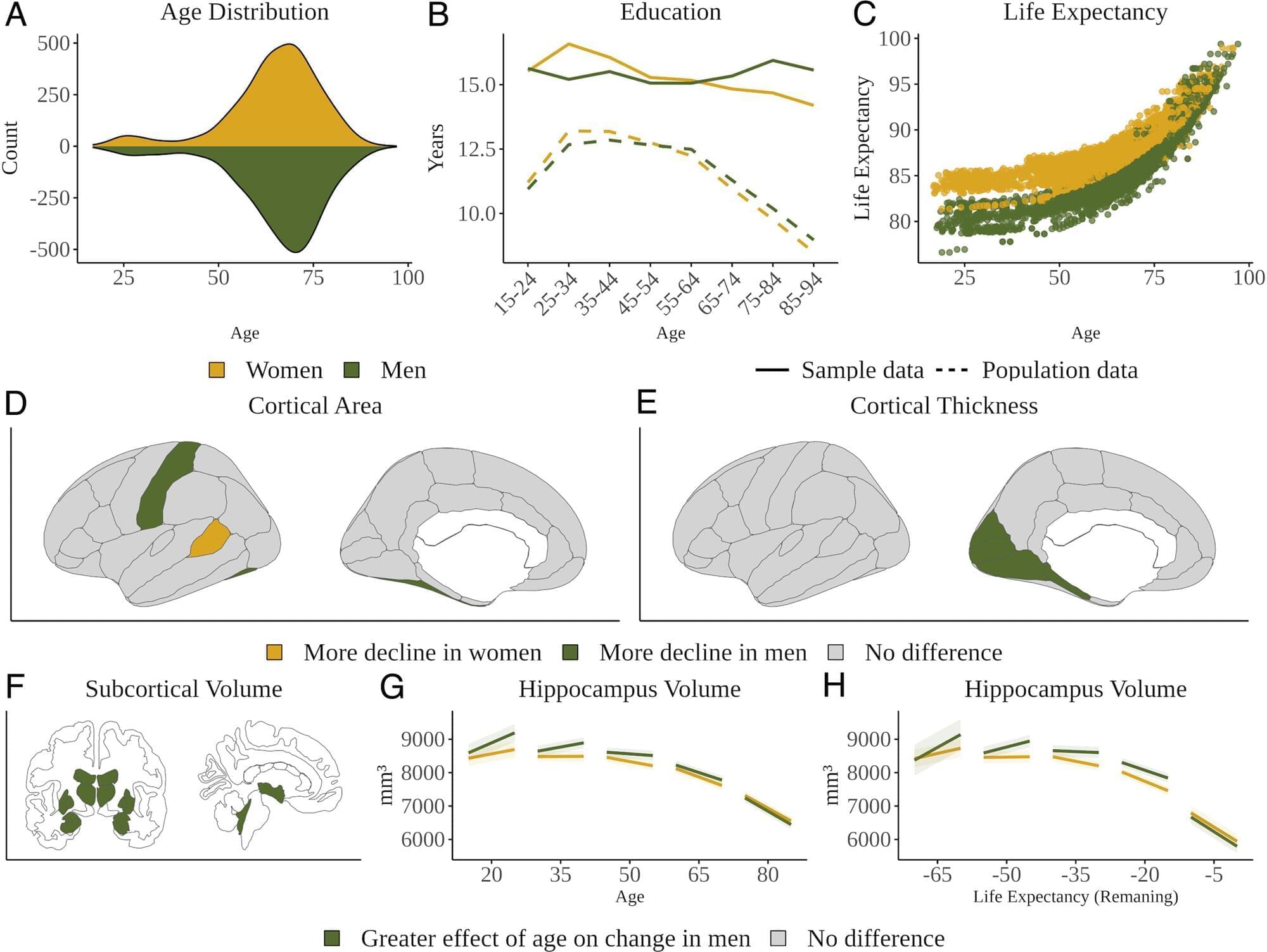
Men experience more brain atrophy with age despite women’s higher Alzheimer’s risk
Women are far more likely than men to end up with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). This may, at least partially, be due to women’s longer average lifespans, but many scientists think there is probably more to the story. It would be easy to surmise that the increased risk is also related to differences in the way men’s and women’s brains change as they age. However, the research thus far has been unclear, as results across different brain regions and methods have been inconsistent.
Now, a new study, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, indicates that it’s men who experience greater decline in more regions of the brain as they age. Researchers involved in the study analyzed 12,638 brain MRIs from 4,726 cognitively healthy participants (at least two scans per person) from the ages of 17–95 to find how age-related changes occurred and whether they differed between men and women.
The results showed that men experienced declines in cortical thickness and surface area in many regions of the brain and a decline in subcortical structures in older age. Meanwhile, women showed greater decline only in a few regions and more ventricular expansion in older adults. So, while differences in brain aging between the sexes are apparent, the cause of increased AD prevalence in women is still a bit mysterious.
A ‘flight simulator’ for the brain reveals how we learn—and why minds sometimes go off course
Every day, your brain makes thousands of decisions under uncertainty. Most of the time, you guess right. When you don’t, you learn. But when the brain’s ability to judge context or assign meaning falters, thoughts and behavior can go astray. In psychiatric disorders ranging from attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder to schizophrenia, the brain may misjudge how much evidence to gather before acting—or fail to adjust when the rules of the world change based on new information.
“Uncertainty is built into the brain’s wiring,” says Michael Halassa, a professor of neuroscience at Tufts University School of Medicine. “Picture groups of neurons casting votes—some optimistic, some pessimistic. Your decisions reflect the average.” When that balance skews, the brain can misread the world: assigning too much meaning to random events, as in schizophrenia, or becoming stuck in rigid patterns, as in obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Understanding those misfires has long challenged scientists, says Halassa. “The brain speaks the language of single neurons. But fMRI—the tool we use to study brain activity in people—tracks blood flow, not the electrical chatter of individual brain cells.”

Social conflict among strongest predictors of teen mental health concerns, research shows
Approximately 20% of American adolescents experience a mental health disorder each year, a number that has been on the rise. Genetics and life events contribute, but because so many factors are involved, and because their influence can be subtle, it’s been difficult for researchers to generate effective models for predicting who is most at risk for mental health problems.
A new study from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis provides some answers. Published Sept. 15 in Nature Mental Health, it mined an enormous set of data collected from pre-teens and teens across the U.S. and found that social conflicts—particularly family fighting and reputational damage or bullying from peers—were the strongest predictors of near-and long-term mental health issues.
The research also revealed sex differences in how boys and girls experience stress from peer conflict, suggesting that nuance is needed when assessing social stressors in teens.
Supercharged vitamin k could help the brain heal itself
Researchers have synthesized enhanced vitamin K analogues that outperform natural vitamin K in promoting neuron growth. The new compounds, which combine vitamin K with retinoic acid, activate the mGluR1 receptor to drive neurogenesis. They also efficiently cross the blood-brain barrier and show stability in vivo. This discovery could pave the way for regenerative treatments for Alzheimer’s and related diseases.

Preventing overhydration: Study uncovers a neural circuit that prompts mice to stop drinking
Identifying the neural mechanisms that support the regulation of vital physiological processes, such as drinking, eating and sleeping, is a long-standing goal within the neuroscience research community. As the disruption of these processes can severely impact people’s health and everyday functioning, uncovering their neural and biological underpinnings is of the utmost importance.
New insights gathered by neuroscientists could ultimately inform the development of more effective interventions designed to regulate vital physiological processes. Thirst and hunger are known to be regulated by homeostatic processes, biological processes that allow the body to maintain internal stability.
Yet drinking behavior can also be anticipatory, which means that animals and humans often adjust their actions (i.e., stop drinking) before the concentration of substances in the blood changes in response to drinking water. The mechanisms through which the brain predicts when it is the right time to stop drinking remain poorly understood.
New Alzheimer’s Treatment Clears Plaques From Brains of Mice Within Hours
Scientists have repaired a natural gateway into the brains of mice, allowing the clumps and tangles associated with Alzheimer’s disease to be swept away.
After just three drug injections, mice with certain genes that mimic Alzheimer’s showed a reversal of several key pathological features.
Within hours of the first injection, the animal brains showed a nearly 45 percent reduction in clumps of amyloid-beta plaques, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease.
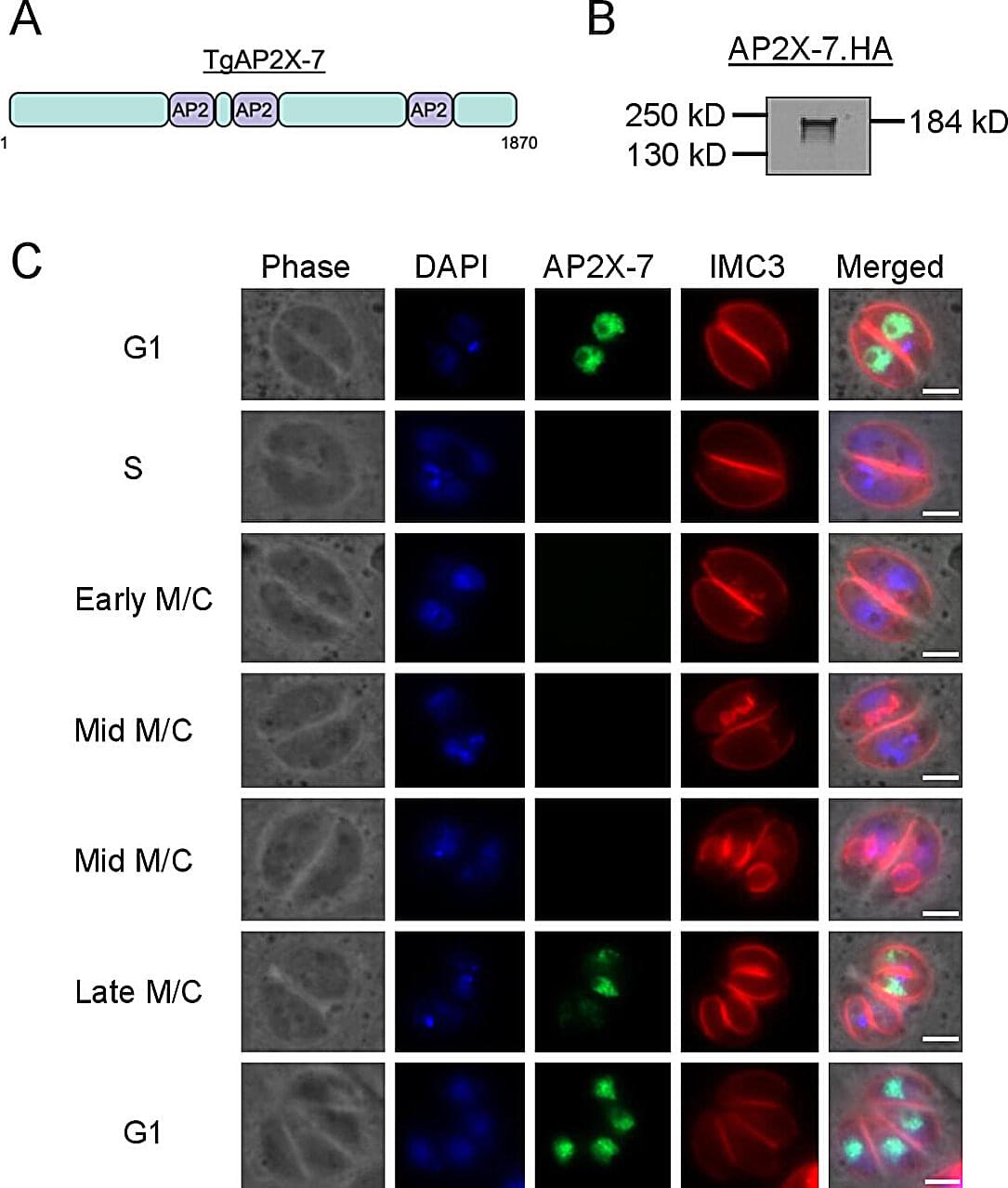
Discovery of brain parasite’s unique control protein offers hope for better toxoplasmosis treatments
Rajshekhar Gaji was staring at something that should not exist. Under his microscope, parasites that should have been thriving were instead dying—completely unable to survive without a protein his lab had managed to switch off.
“It was an amazing day,” said Gaji, assistant professor of parasitology at the Virginia–Maryland College of Veterinary Medicine. That moment of discovery could eventually help the 40 million Americans walking around with a microscopic parasite permanently residing in their brains.
The findings are published in the journal mSphere.