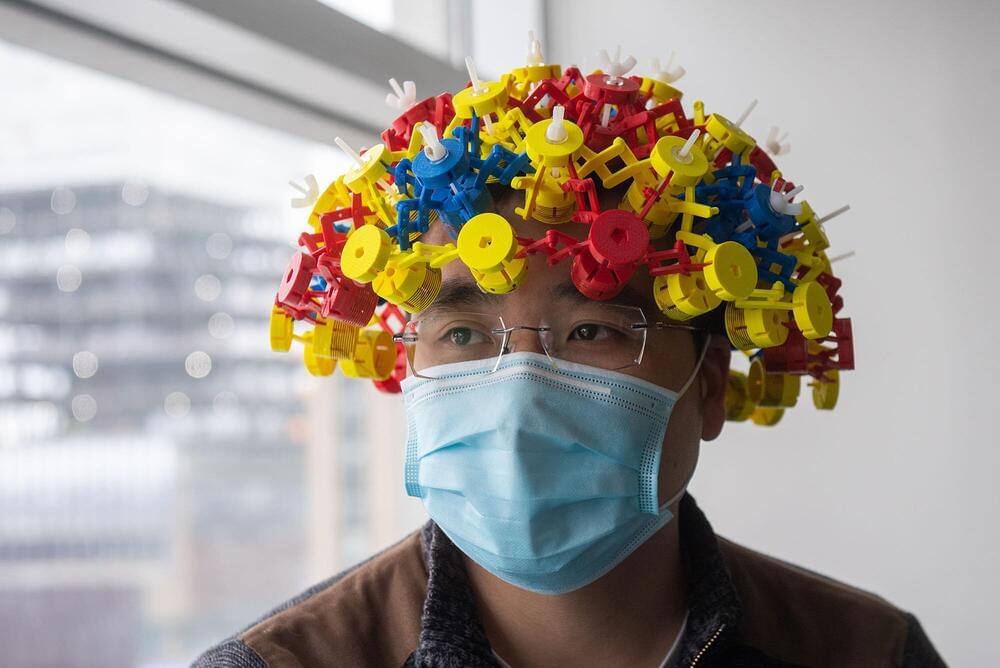
It may look like a bizarre bike helmet, or a piece of equipment found in Doc Brown’s lab in Back to the Future, yet this gadget made of plastic and copper wire is a technological breakthrough with the potential to revolutionize medical imaging. Despite its playful look, the device is actually a metamaterial, packing in a ton of physics, engineering, and mathematical know-how.
It was developed by Xin Zhang, a College of Engineering professor of mechanical engineering, and her team of scientists at BU’s Photonics Center. They’re experts in metamaterials, a type of engineered structure created from small unit cells that might be unspectacular alone, but when grouped together in a precise way, get new superpowers not found in nature. Metamaterials, for instance, can bend, absorb, or manipulate waves—such as electromagnetic waves, sound waves, or radio waves. Each unit cell, also called a resonator, is typically arranged in a repeating pattern in rows and columns; they can be designed in different sizes and shapes, and placed at different orientations, depending on which waves they’re designed to influence.
Metamaterials can have many novel functions. Zhang, who is also a professor of electrical and computer engineering, biomedical engineering, and materials science and engineering, has designed an acoustic metamaterial that blocks sound without stopping airflow (imagine quieter jet engines and air conditioners) and a magnetic metamaterial that can improve the quality of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines used for medical diagnosis.