Nighttime light pollution may quietly stress the brain, inflame the arteries, and put your heart in danger.
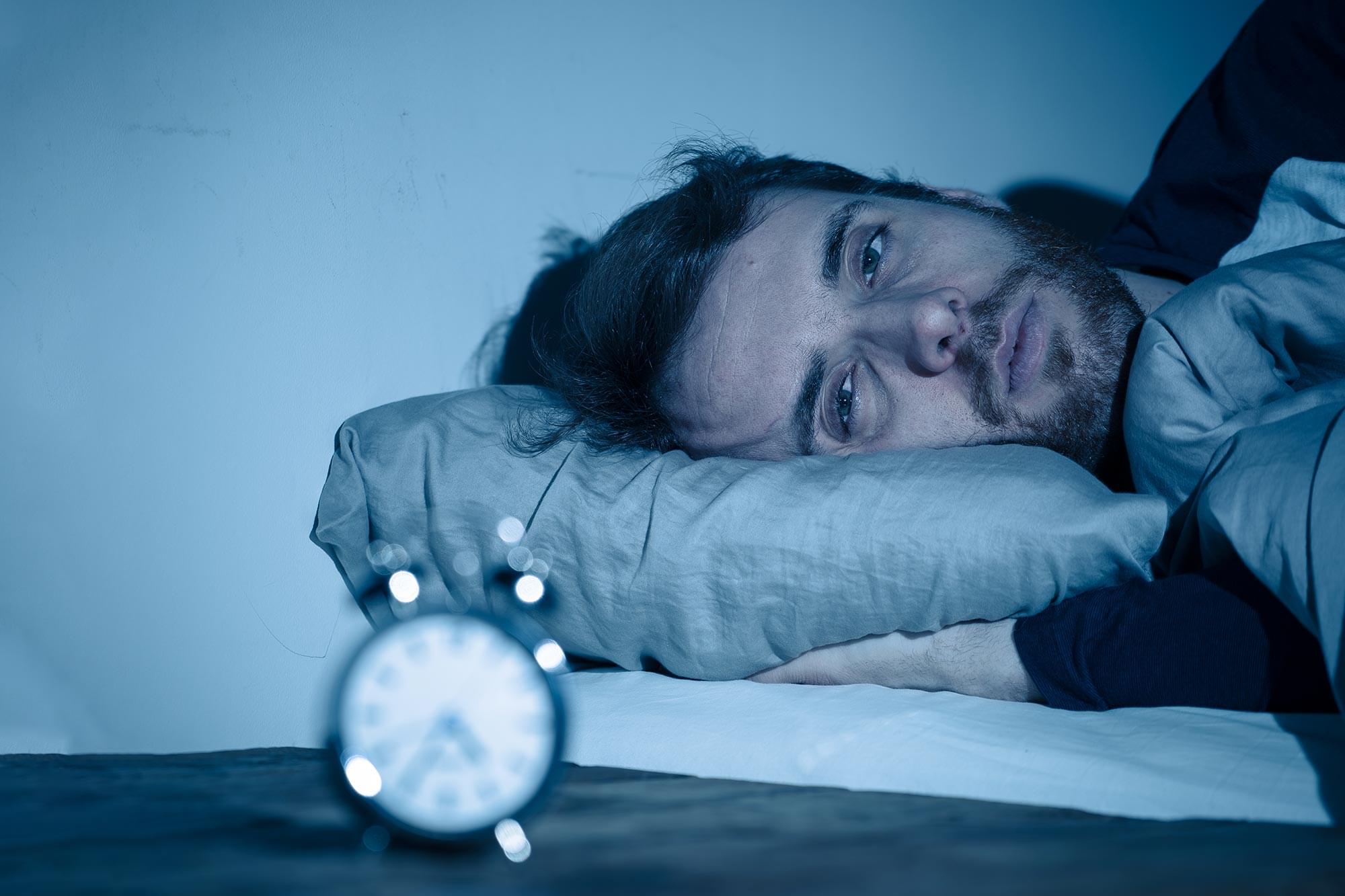
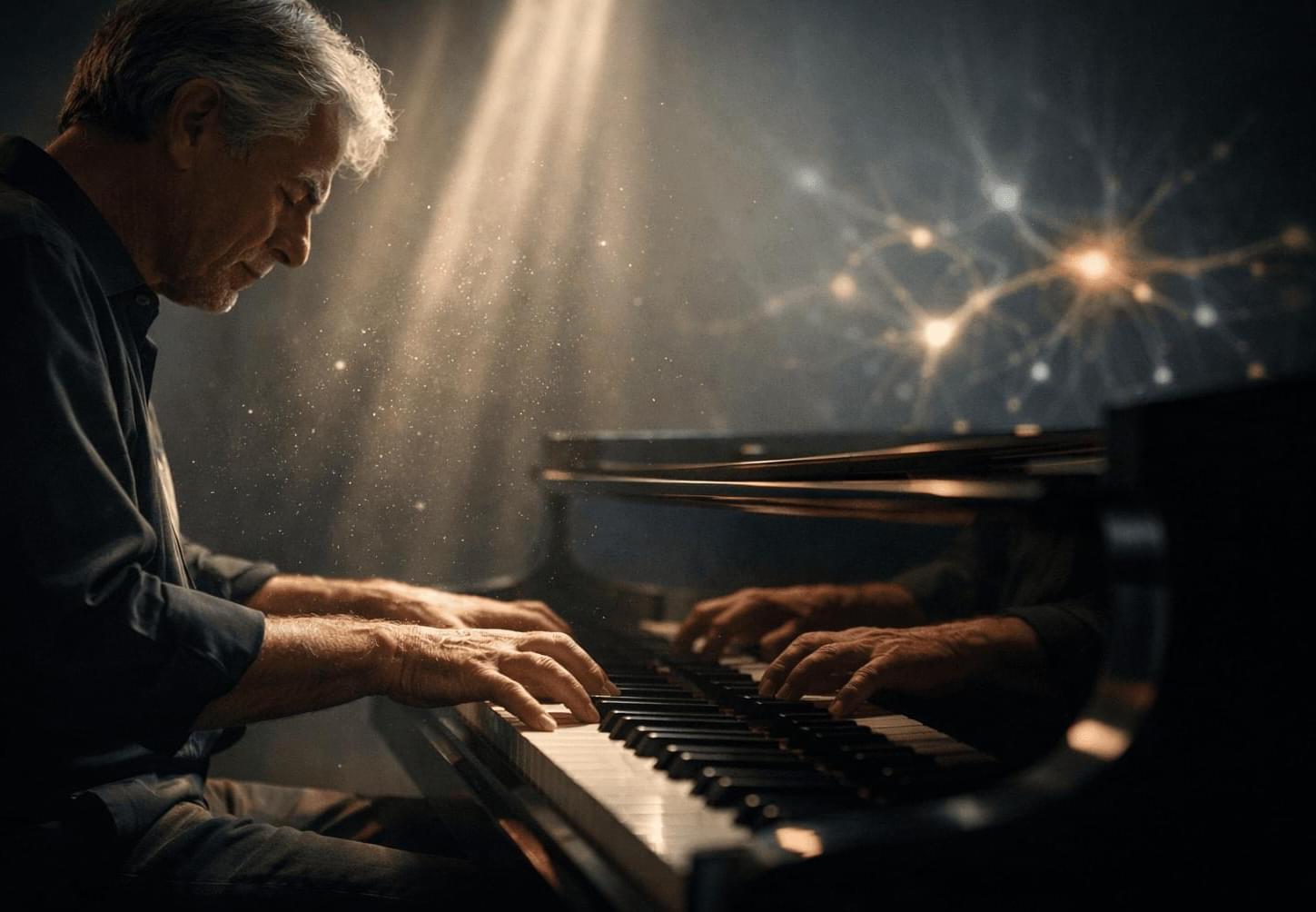





Getting older means losing things. Some are fine, like any f**ks you have left to give or your tolerance for cheap tequila. Others, like the ability to follow a conversation in a loud room, hit harder.
But scientists now think there’s a way to fight back. And it might start at a piano bench.
Researchers publishing in PLOS Biology found that older adults who have played music for decades have brains that function more like those of someone half their age, at least when it comes to understanding speech in loud environments. In brain scans, they showed cleaner, more focused activity while listening to spoken syllables buried in background noise. Their brains weren’t scrambling. They already knew what to do.
Professor John Donoghue explains why quantum physics and gravity actually work perfectly together. He tackles quadratic gravity, effective field theory, and random dynamics, arguing that grand unification and naturalness aren’t required for a theory of everything.
As a listener of TOE you can get a special 20% off discount to The Economist and all it has to offer! Visit https://www.economist.com/toe.
SUPPORT:
Support me on Substack: https://curtjaimungal.substack.com/su…
JOIN MY SUBSTACK (Personal Writings): https://curtjaimungal.substack.com LISTEN ON SPOTIFY: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b9… TIMESTAMPS:
LINKS MENTIONED:
SOCIALS:
Guests do not pay to appear. Theories of Everything receives revenue solely from viewer donations, platform ads, and clearly labelled sponsors; no guest or associated entity has ever given compensation, directly or through intermediaries. #science.
Support me on Crypto: https://commerce.coinbase.com/checkou…
Support me on PayPal: https://www.paypal.com/donate?hosted_…
JOIN MY SUBSTACK (Personal Writings): https://curtjaimungal.substack.com.
LISTEN ON SPOTIFY: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b9…
TIMESTAMPS:

Go to https://ground.news/sabine to get 40% off the Vantage plan and see through sensationalized reporting. Stay fully informed on events around the world with Ground News.
Human brains are roughly 100,000 times more energy-efficient than current AI systems. So why don’t we build computers using human brain cells? Don’t worry, researchers are one step ahead of you there – different teams across the globe are racing to develop neuron computers; processors that integrate living brain neurons into their chips. Let’s take a look at how this technology is developing and when we might see brain cells chips in the future.
Paper 1: https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/.… 2: h https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/.… 👕T-shirts, mugs, posters and more: ➜ https://sabines-store.dashery.com/ 💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg 👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine 📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/ 📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle… 👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl… 🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder 📚 Buy my book ➜ https://amzn.to/3HSAWJW #science #sciencenews #tech #neuroscience.
Paper 2: h https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/.…
👕T-shirts, mugs, posters and more: ➜ https://sabines-store.dashery.com/
💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg.
👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine.
📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/
📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle…
👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl…
🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder.
📚 Buy my book ➜ https://amzn.to/3HSAWJW
#science #sciencenews #tech #neuroscience