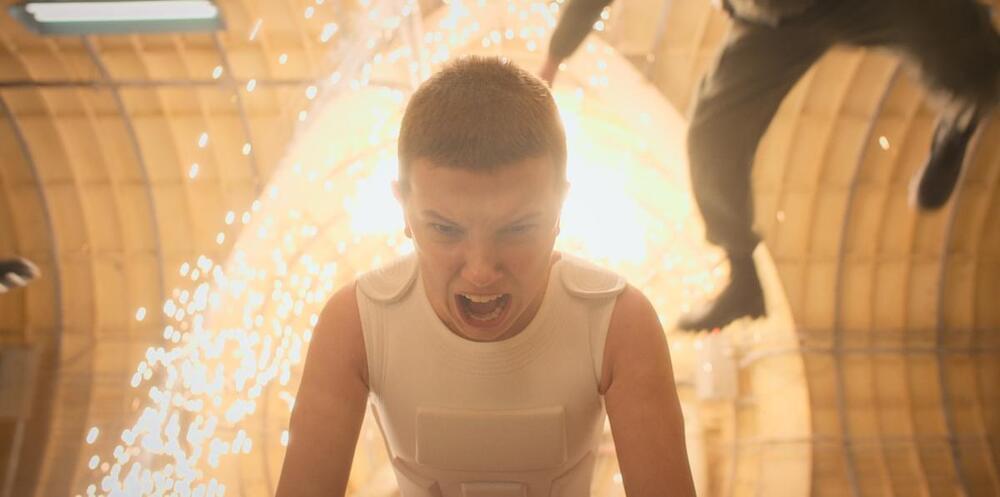
MKUltra is not referenced explicitly on Stranger Things — the popular Netflix show — but the series seems to be inspired by the controversial CIA program. In the show, a government laboratory is conducting illegal experiments on a young girl and other persons, torturing them, and harnessing their special abilities for their own purposes. This is similar to the goals of the CIA human experimentation project, which was started 70 years ago.
Controversial and unethical experiments were conducted on human subjects by the Agency for the MKUltra project, including the use of mind control techniques and the administration of drugs such as LSD and other chemicals. Electroshock, hypnosis, sensory deprivation, verbal and sexual abuse, and other forms of torture were also part of the non-consensual experiments, which were created because the CIA was convinced that communists had discovered a way to control human minds. Its activities — which were hidden and classified before their files being destroyed after an investigation — remain a subject of concern and investigation to this day.
MKUltra was a CIA program involving the research and development of chemical and biological agents. According to official documents, it was “concerned with the research and development of chemical, biological and radiological materials capable of employment in clandestine operations to control human behavior.”