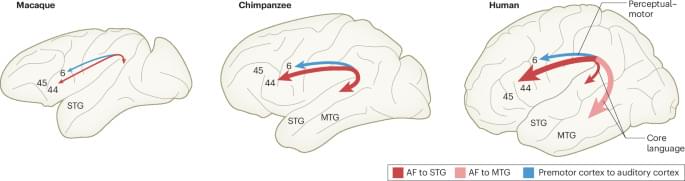
Considering what’s known about their brain structures, sensory systems and learning capacity, it appears that cephalopods as a group may be similar in intelligence to vertebrates as a group. Since many societies have animal welfare standards for mice, rats, chickens and other vertebrates, logic would suggest that there’s an equal case for regulations enforcing humane treatment of cephalopods.
Such rules generally specify that when a species is held in captivity, its housing conditions should support the animal’s welfare and natural behavior. This view has led some U.S. states to outlaw confined cages for egg-laying hens and crates too narrow for pregnant sows to turn around.
Animal welfare regulations say little about invertebrates, but guidelines for the care and use of captive cephalopods have started to appear over the past decade. In 2010, the European Union required considering ethical issues when using cephalopods for research. And in 2015, AAALAC International, an international accreditation organization for ethical animal research, and the Federation of European Laboratory Animal Science Associations promoted guidelines for the care and use of cephalopods in research. The U.S. National Institutes of Health is currently considering similar guidelines.