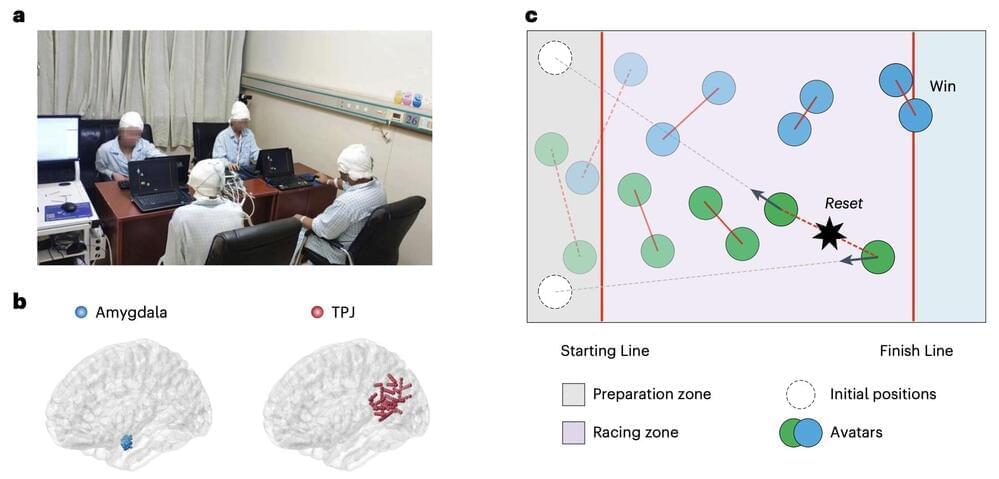
Collaboration and cooperation are key elements of human social interactions, which can contribute to the efficient achievement of shared goals. While many psychology and neuroscience studies have investigated cooperative behaviors among humans, the complex interplay between these behaviors and their neural underpinnings remain poorly understood.
A research team at Beijing Normal University, supervised by Dr. Yina Ma set out to further explore the neural basis of human cooperation, using a combination of behavioral tasks and intracranial electroencephalography (iEEG). Their paper, published in Nature Neuroscience, delineates distinctive neurocognitive profiles for different states during cooperative tasks.
“Our lab has long been dedicated to understanding how human brains communicate and interact in social contexts, such as collective decision-making, intergroup conflict and social cooperation,” Jiaxin Wang, co-first author of the paper, told Medical Xpress.