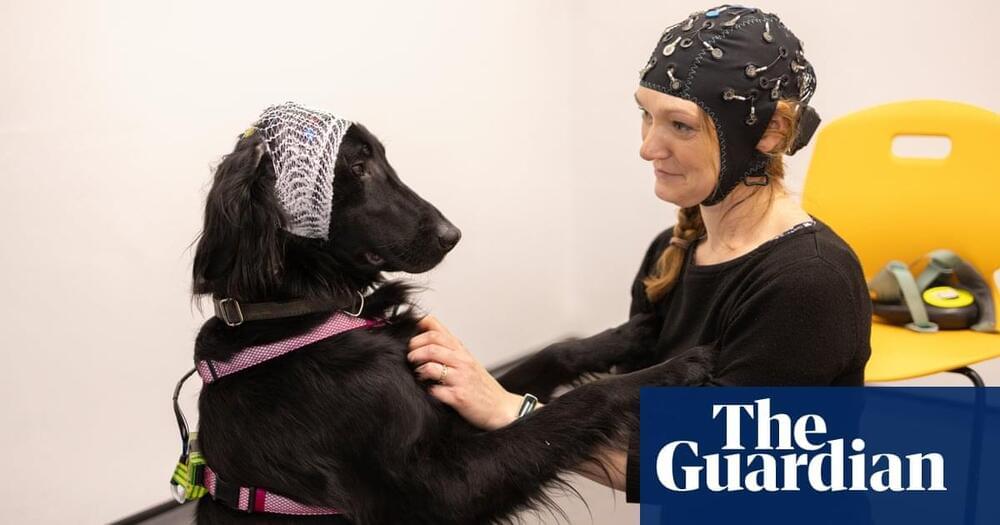
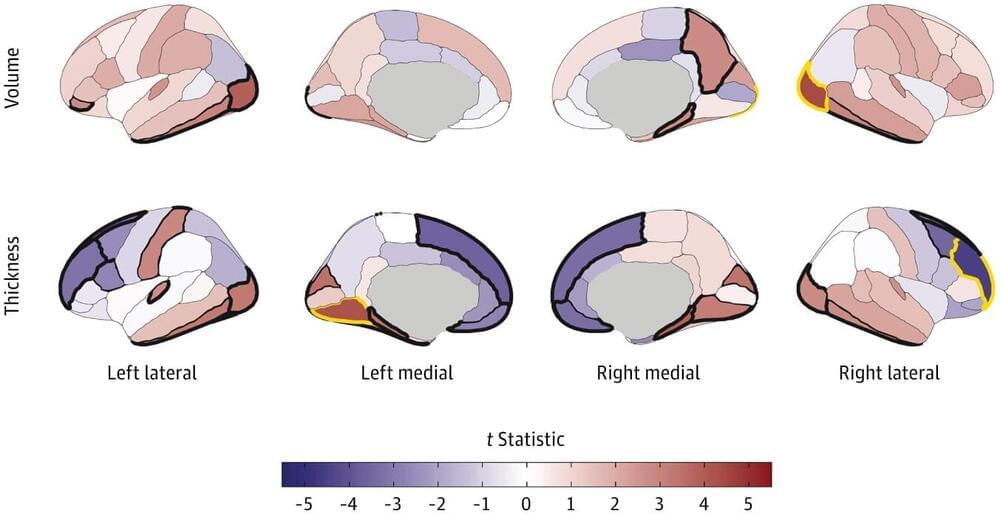
A study led by researchers from the Indiana University School of Medicine, Washington University in St. Louis, and other institutions has identified neuroanatomical differences in children associated with early substance use initiation.
Early-age substance use is strongly associated with a heightened risk for substance use disorders (SUDs) and other adverse outcomes later in life. Neuroanatomical changes in brain structure have been linked to substance use, especially in youth when the brain is undergoing substantial development.
But are the changes seen in substance user brains primarily a result of the substance use itself, or is it an inherent predisposition in some individuals with certain neuroanatomical variations?