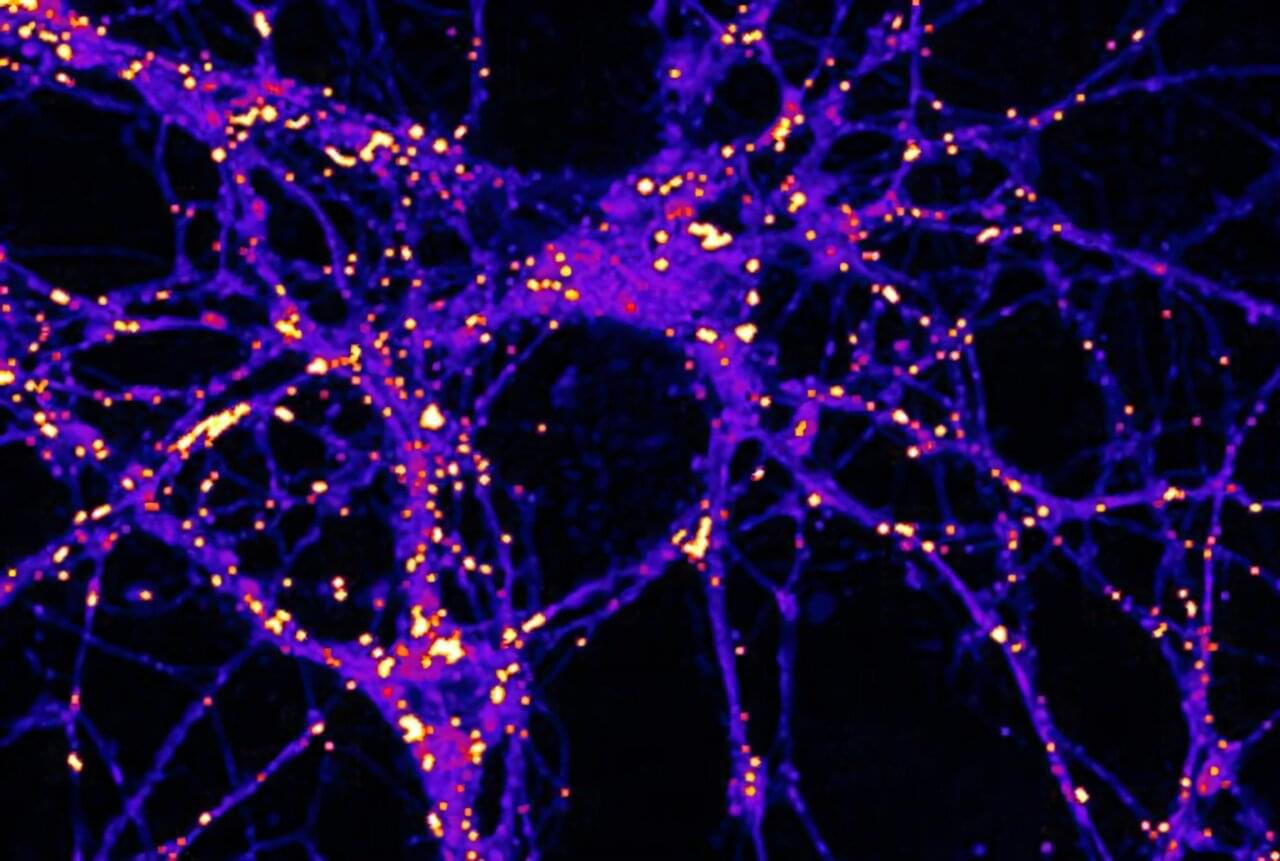
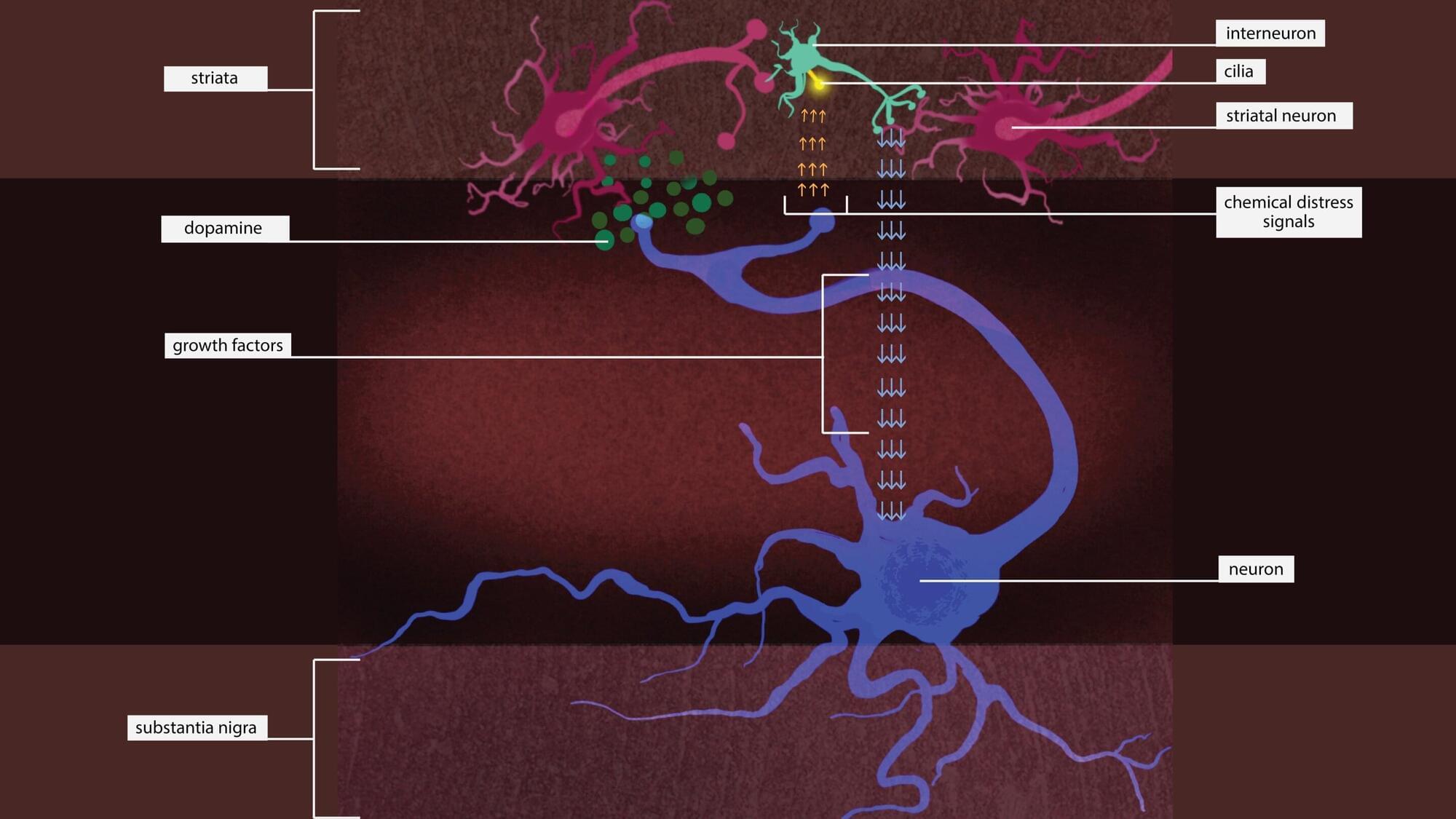
While glucose, or sugar, is a well-known fuel for the brain, Weill Cornell Medicine researchers have demonstrated that electrical activity in synapses—the junctions between neurons where communication occurs—can lead to the use of lipid or fat droplets as an energy source.
The study, published in Nature Metabolism, challenges “the long-standing dogma that the brain doesn’t burn fat,” said principal investigator Dr. Timothy A. Ryan, professor of biochemistry and of biochemistry in anesthesiology, and the Tri-Institutional Professor in the Department of Biochemistry at Weill Cornell Medicine.
The paper’s lead author, Dr. Mukesh Kumar, a postdoctoral associate in biochemistry at Weill Cornell Medicine who has been studying the cell biology of fat droplets, suggested that it makes sense that fat may play a role as an energy source in the brain like it does with other metabolically demanding tissues, such as muscle.