UConn neuroscientist and chemist receive NIH R01 grant to support their collaboration

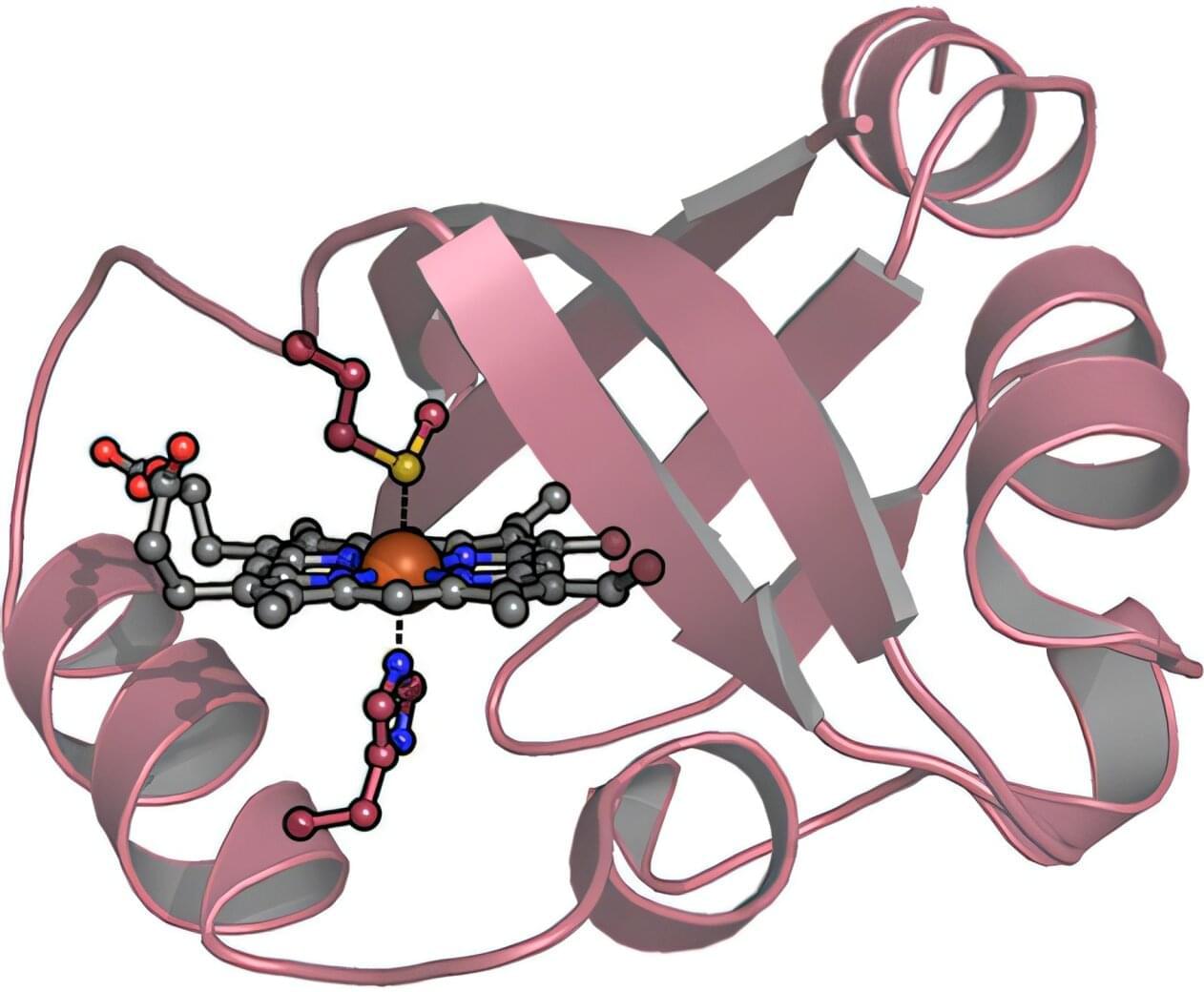
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers, along with their colleagues, engineered a new molecule that appears promising as an effective antidote for carbon monoxide poisoning with fewer side effects than other molecules currently being tested, according to a new study published in the journal PNAS.
Carbon monoxide poisoning accounts for 50,000 emergency room visits in the U.S. each year and causes about 1,500 deaths. These deaths may occur when carbon monoxide released from combustion builds up in an enclosed space, which can result from ventilation failures in indoor natural gas burning equipment, or running gasoline generators or automobiles indoors or in a closed garage. Carbon monoxide poisoning is also associated with most fires from smoke inhalation.
Currently, the only treatments for carbon monoxide poisoning are oxygen-based therapies, which help the body eliminate the toxic gas. However, even with treatment, nearly half of survivors suffer long-term heart and brain damage. This has created an urgent need for faster, more effective therapies.

Healthy brain function relies on a steady supply of blood. Disruptions in blood flow are linked to major neurological conditions like stroke, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and traumatic brain injuries. But understanding how the brain fine-tunes this flow—especially across its smallest blood vessels—remains a challenge.
The brain’s blood supply includes a vast network of vessels, ranging from large arteries to microscopic capillaries. Between these lie transitional zone (TZ) vessels—such as penetrating arterioles, precapillary arterioles, and capillary sphincters—that bridge the gap and may play a big role in regulating flow. But their exact contribution, particularly during increased brain activity, remains a subject of scientific debate.
To explore these dynamics, researchers from the College of Engineering and Computer Science at Florida Atlantic University and the FAU Sensing Institute (I-SENSE) developed a highly detailed computer model of the mouse brain’s vasculature, treating each vessel segment as a tiny, adjustable valve.
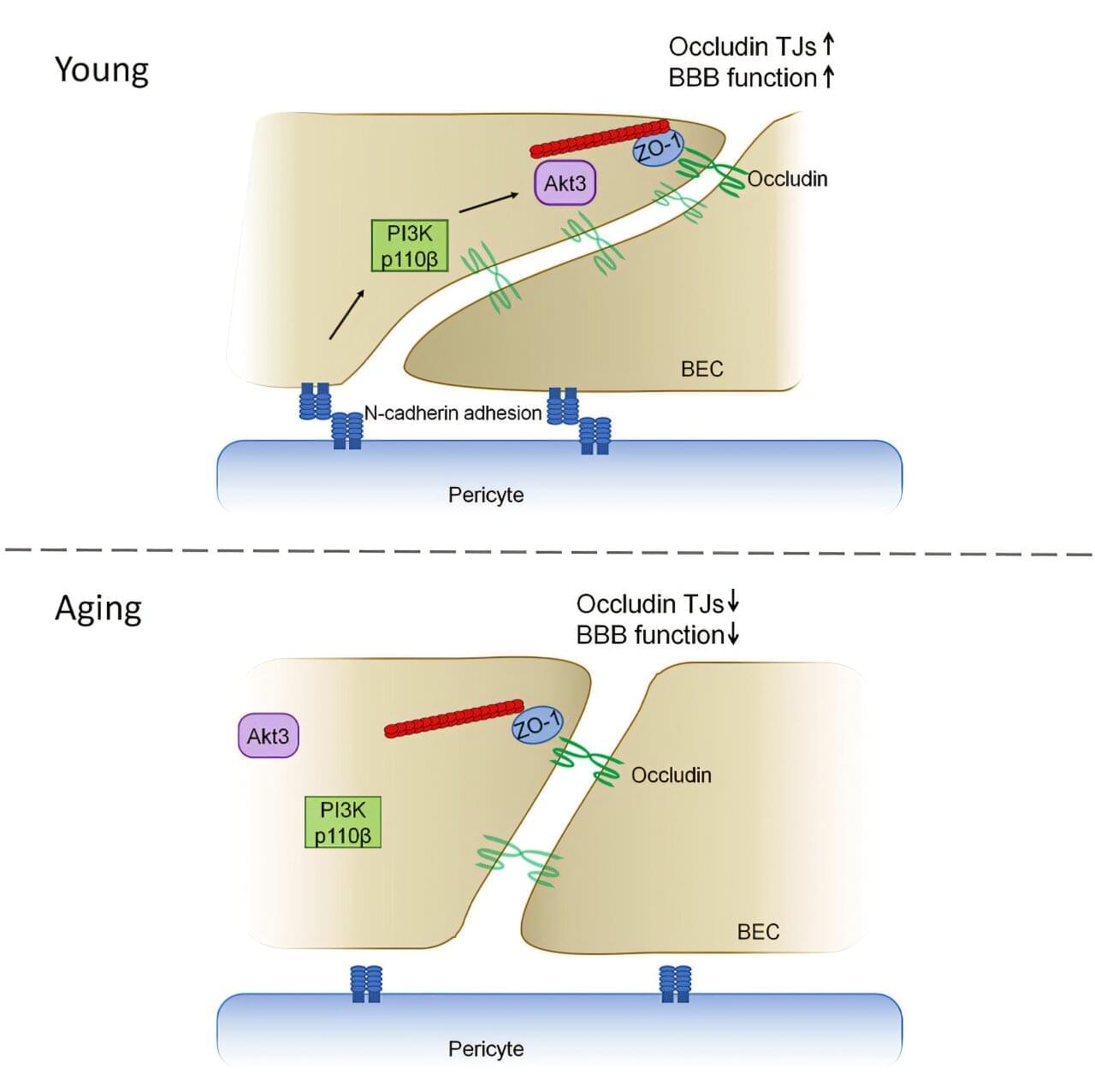
A new study from researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago reveals how the blood-brain barrier gets leakier with age, contributing to memory deficits. The study, published in Cell Reports, uncovered the molecular mechanisms behind this process and could provide new therapeutic targets to address cognitive decline earlier in the aging process.
The blood-brain barrier is a layer of cells lining the brain’s blood vessels that keep viruses, bacteria and toxins out while allowing helpful nutrients and chemicals in. A key structure of the blood-brain barrier are tight junctions that act as bridges between cells, restricting entry of molecules. A protein called occludin helps fulfill this essential role.
“It’s a highly regulatable process that allows some molecules to go through and others to remain in circulation,” said Yulia Komarova, UIC associate professor in the department of pharmacology and regenerative medicine at the College of Medicine and senior author of the study. “Basically, it’s a mechanism that separates the central nervous system from everything else.”




In studies with genetically engineered mice, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have identified a potentially new biological target involving Aplp1, a cell surface protein that drives the spread of Parkinson’s disease-causing alpha-synuclein.
The findings, published May 31 2024 in Nature Communications, reveal how Aplp1 connects with Lag3, another cell surface receptor, in a key part of a process that helps spread harmful alpha-synuclein proteins to brain cells. Those protein buildups are hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease.
Notably, the researchers say, Lag3 is already the target of a combination cancer drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that uses antibodies to “teach” the human immune system what to seek and destroy.
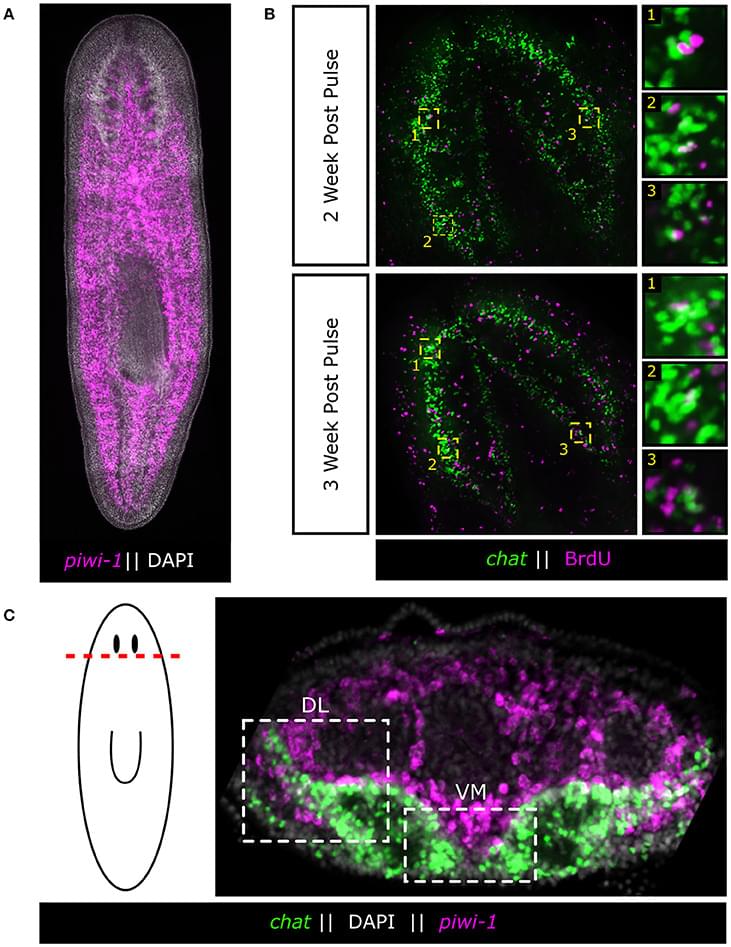
Basically I believe that the flatworm could give the genetic code for essentially brain immortality other just nad plus. But it would have to be made in the brain and controlled possibly with nanotransfection which would scan the body and modify the human brain cells to have its characteristics that may already exist in the human brain also.
Powerful genetic tools in classical laboratory models have been fundamental to our understanding of how stem cells give rise to complex neural tissues during embryonic development. In contrast, adult neurogenesis in our model systems, if present, is typically constrained to one or a few zones of the adult brain to produce a limited subset of neurons leading to the dogma that the brain is primarily fixed post-development. The freshwater planarian (flatworm) is an invertebrate model system that challenges this dogma. The planarian possesses a brain containing several thousand neurons with very high rates of cell turnover (homeostasis), which can also be fully regenerated de novo from injury in just 7 days. Both homeostasis and regeneration depend on the activity of a large population of adult stem cells, called neoblasts, throughout the planarian body. Thus, much effort has been put forth to understand how the flatworm can continually give rise to the diversity of cell types found in the adult brain. Here we focus on work using single-cell genomics and functional analyses to unravel the cellular hierarchies from stem cell to neuron. In addition, we will review what is known about how planarians utilize developmental signaling to maintain proper tissue patterning, homeostasis, and cell-type diversity in their brains. Together, planarians are a powerful emerging model system to study the dynamics of adult neurogenesis and regeneration.
The adult brain has long been thought to be a fixed structure due to its immense complexity as is illustrated succinctly in the following quote from prominent nineteenth century neuroscientist and Nobel laureate Santiago Ramón y Cajal:
“Once the development was ended, the founts of growth and regeneration of the axons and dendrites dried up irrevocably. In the adult centers, the nerve paths are something fixed, ended, and immutable. Everything may die, nothing may be regenerated. It is for the science of the future to change, if possible, this harsh decree.”

Scientists have discovered a direct cause-and-effect link between faulty mitochondria and the memory loss seen in neurodegenerative diseases. By creating a novel tool to boost mitochondrial activity in mouse models, researchers restored memory performance, suggesting mitochondria could be a powerful new target for treatments. The findings not only shed light on the early drivers of brain cell degeneration but also open possibilities for slowing or even preventing diseases like Alzheimer’s.