Crypto news: Facebook” s Libra, a new cryptocurrency is announced as a peer-to-peer payment within messenger apps. Cross-border transactions near zero fees is a major step towards the Global Brain.


Though serotonin is well known as a brain neurotransmitter, it is estimated that 90 percent of the body’s serotonin is made in the digestive tract. In fact, altered levels of this peripheral serotonin have been linked to diseases such as irritable bowel syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and osteoporosis. New research at Caltech, published in the April 9 issue of the journal Cell, shows that certain bacteria in the gut are important for the production of peripheral serotonin.
Scientists develop a new vaccine for alzheimer’s disease.

I had a little more invested in BCI.
Brain-machine interface—once the stuff of science fiction novels—is coming to a computer near you. The only question is: How soon? While the technology is in its infancy, it is already helping people with spinal cord injuries. Our authors examine its potential to be the ultimate game changer for any number of neurodegenerative diseases, as well as behavior, learning, and memory.
In a new study, Yale researchers offer insight into leptin, a hormone that plays a key role in appetite, overeating, and obesity. Their findings advance knowledge about leptin and weight gain, and also suggest a potential strategy for developing future weight-loss treatments, they said.
The study, led by investigators at Yale and Harvard, was published the week of June 17, 2019, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Leptin, which is secreted by fat cells, informs the brain when fuel stored in body fat and in the liver is becoming depleted. It has not been well understood how low leptin concentrations in plasma — the largest component of blood — increase appetite. The researchers studied the biology of leptin in rodents. They also investigated the influence of nerve cells in the brain known as AgRP neurons, which regulate eating behavior.
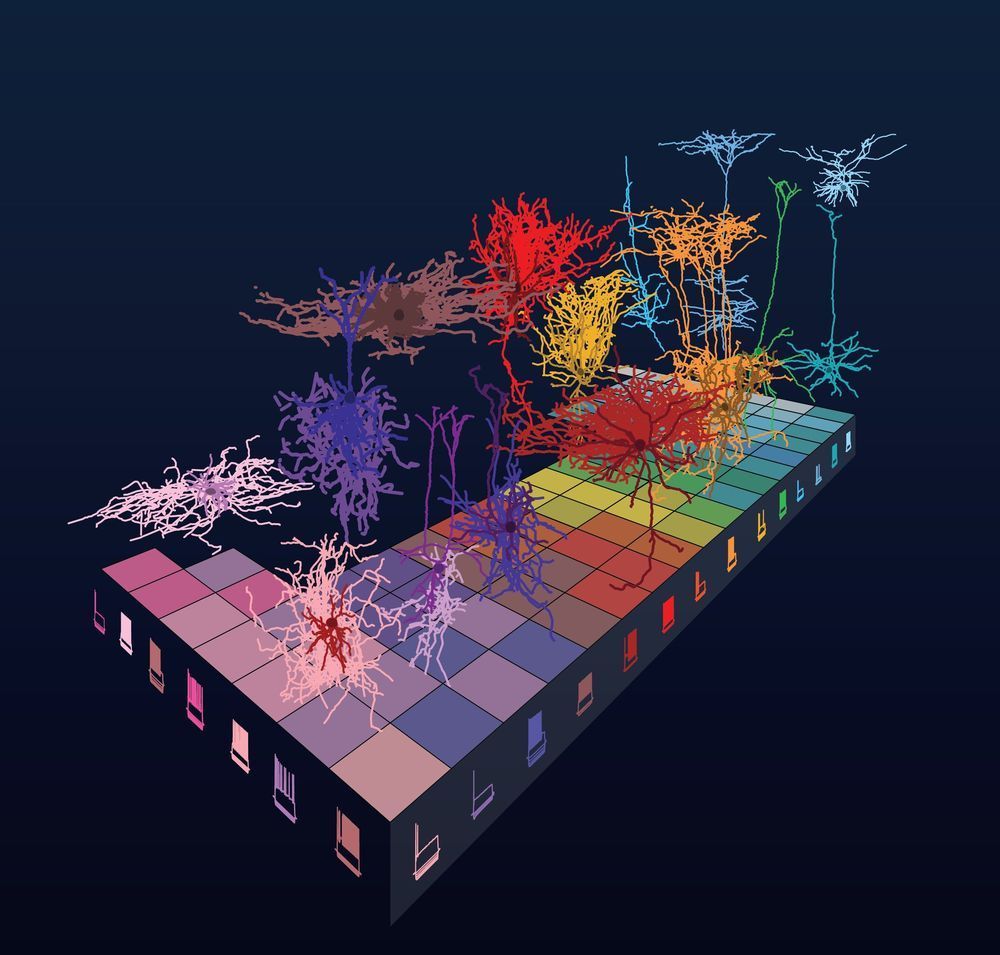
To understand our brains, scientists need to know their components. This theme underlies a growing effort in neuroscience to define the different building blocks of the brain—its cells.
With the mouse’s 80 million neurons and our 86 billion, sorting through those delicate, microscopic building blocks is no small feat. A new study from the Allen Institute for Brain Science, which was published today in the journal Nature Neuroscience, describes a large profile of mouse neuron types based on two important characteristics of the cells: their 3D shape and their electrical behavior.
The study, which yielded the largest dataset of its kind from the adult laboratory mouse to date, is part of a larger effort at the Allen Institute to discover the brain’s “periodic table” through large-scale explorations of brain cell types. The researchers hope a better understanding of cell types in a healthy mammalian brain will lay the foundation for uncovering the cell types that underlie human brain disorders and diseases.

A team of UK scientists have identified the mechanism behind hardening of the arteries, and shown in animal studies that a generic medication normally used to treat acne could be an effective treatment for the condition.
The team, led by the University of Cambridge and King’s College London, found that a molecule once thought only to exist inside cells for the purpose of repairing DNA is also responsible for hardening of the arteries, which is associated with dementia, heart disease, high blood pressure and stroke.
There is no current treatment for hardening of the arteries, which is caused by build-up of bone-like calcium deposits, stiffening the arteries and restricting blood flow to organs and tissues.

In March, a team of Chinese scientists published a study detailing how they made monkeys smarter by splicing a human gene into their DNA.
The news was met by a wave of backlash. But now, one of the scientists behind the study is defending the team’s work — and pledging to push forward on the controversial research.

There are many nutritional and delicious benefits of eating lobster. Some of them include protecting heart health, increasing energy, decreasing inflammation, speeding healing, promoting growth, boosting brain functioning and building strong bones. Lobsters are shelled marine creatures which are taking parts of crustaceans. They have the scientific name Homarus nephrops. This scientific name is the North Atlantic variety. This undersea creature is having old look and it is considered to be luxury or delicacy food in many parts of the world. Nowadays lobster is exported to many parts of the world. They are particularly popular in North America. Lobsters are delicious food but they have high prices which is a reason why they are not consumed a lot. It is important to know that the lobster has high amounts of cholesterol and sodium. If you suffer from cardiovascular issues, high blood pressure or any other health condition, then you should not consume lobster because it has minerals and nutrients which are not ideal for these conditions. Every food should be consumed in moderation. Lobster is ideal food for people to get many vitamins and minerals that are essential for their health. People who live in North American coasts can have lobster in every time because here the price of it is very low.