The blood-brain barrier, a region of dense cells and blood vessels, keeps drugs from reaching deep parts of the brain. West Virginia University scientists temporarily opened it with ultrasound.

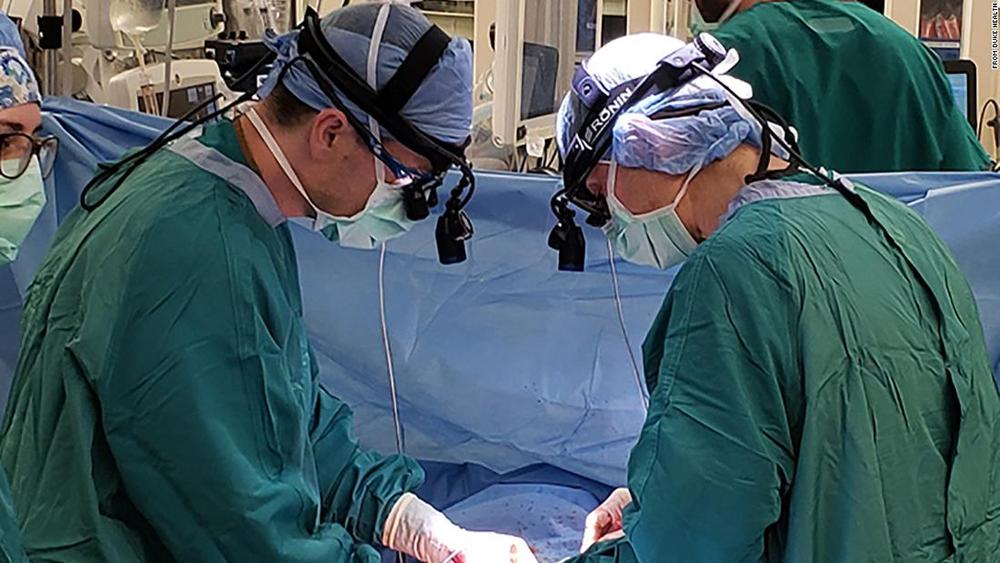
Doctors at Duke University Medical Center this month “reanimated” a heart for a first-of-its-kind transplant performed on an adult in the United States.
Heart transplants typically come from donations after brain death, in which the still-beating heart of a person who has been declared brain dead is transplanted into a recipient. The approach used at Duke is known as a donation after circulatory death (DCD), and it relies on hearts that have stopped beating and are essentially reanimated and begin beating again.
The TransMedics Organ Care System, a warm perfusion pump, allows doctors to resuscitate and preserve hearts for transplantation. The system was used for the adult donation after circulatory death transplant at Duke University Medical Center, one of five centers in the United States approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for clinical trials of the TransMedics system.

Drugs that tamp down inflammation in the brain could slow or even reverse the cognitive decline that comes with age.
University of California, Berkeley, and Ben-Gurion University scientists report that senile mice given one such drug had fewer signs of brain inflammation and were better able to learn new tasks, becoming almost as adept as mice half their age.
“We tend to think about the aged brain in the same way we think about neurodegeneration: Age involves loss of function and dead cells. But our new data tell a different story about why the aged brain is not functioning well: It is because of this “fog” of inflammatory load,” said Daniela Kaufer, a UC Berkeley professor of integrative biology and a senior author, along with Alon Friedman of Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Israel and Dalhousie University in Canada. “But when you remove that inflammatory fog, within days the aged brain acts like a young brain. It is a really, really optimistic finding, in terms of the capacity for plasticity that exists in the brain. We can reverse brain aging.”

New evidence suggests that the cause of Alzheimer’s – which is the most common form of dementia – is actually the result of leakage from the brains ‘filtration system’ known as the blood-brain barrier. The blood-brain barrier is a border within the brain that separates circulating blood from a variety of different fluids in the central nervous system. Previous MRI scans have found that the blood-brain barrier breaks down in nearly 60% of people by the age of 70, and it is believed that this allows harmful chemicals to seep through which is triggering inflammation and fog throughout the brain.
A groundbreaking new study that has seen scientists successfully reverse the effects of dementia is changing the way the scientific world once viewed the disease.
The majority of dementia treatments have focused on trying to remove amyloid plaque from the brain, however, the latest study published in Science Translational Medicine suggest that targeting brain inflammation is the silver-bullet for curing dementia.
New evidence suggests that the cause of Alzheimer’s – which is the most common form of dementia – is actually the result of leakage from the brains ‘filtration system’ known as the blood-brain barrier.
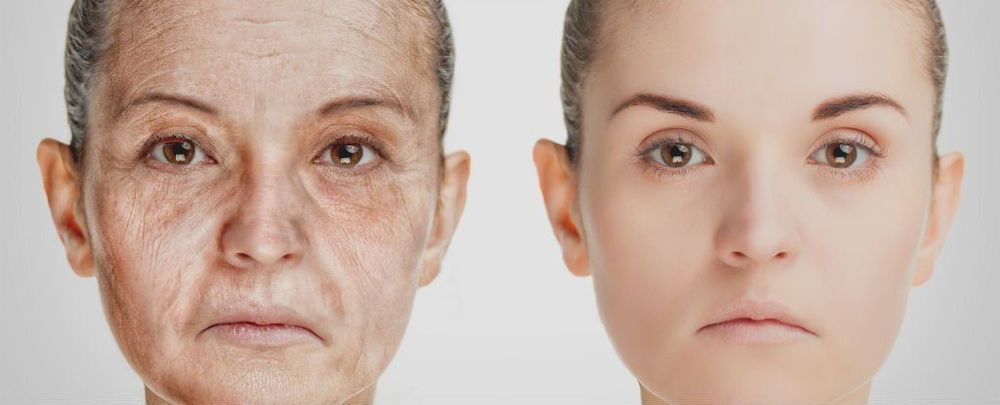


In terms of biological ageing, the body seems to shift gears three times during our lifespans, new research suggests – with 34 years, 60 years and 78 years the key thresholds.
In other words, we now have evidence that ageing isn’t one long, continuous process that moves at the same speed throughout our lives.
The findings might help us understand more about how our bodies start to break down as we get older, and how specific age-related diseases – including Alzheimer’s or cardiovascular disease – could be better tackled.



Lancaster University researchers have discovered, for the first time, how a genetic alteration that increases the risk of developing Autism and Tourette’s impacts on the brain.
Their research also suggests that ketamine, or related drugs, may be a useful treatment for both of these disorders.
Autism affects an estimated 2.8 million people in the UK while Tourette’s Syndrome — a condition that causes a person to make involuntary sounds and movements called tics –affects an estimated 300,000 people in the UK. The treatments available for both disorders are limited and new treatments are urgently required. Recent research has also shown that these disorders are genetically linked.