Alkali and alkaline earth metal hydrides hold great promise for hydrogen storage and hydrogen-involved chemical transformations due to the unique properties of hydridic hydrogen (H-). However, bulk hydrides often suffer from high lattice energy and limited exposure of active sites, hindering their catalytic performance.
In a study published in Nature Communications, a research group led by Prof. Guo Jianping and Prof. Chen Ping from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, collaborating with Prof. Chang Fei from Yongjiang Laboratory and Prof. Rao Li, from Central China Normal University, developed atomically dispersed barium hydride catalysts for the synthesis of deuterated alkylarenes.
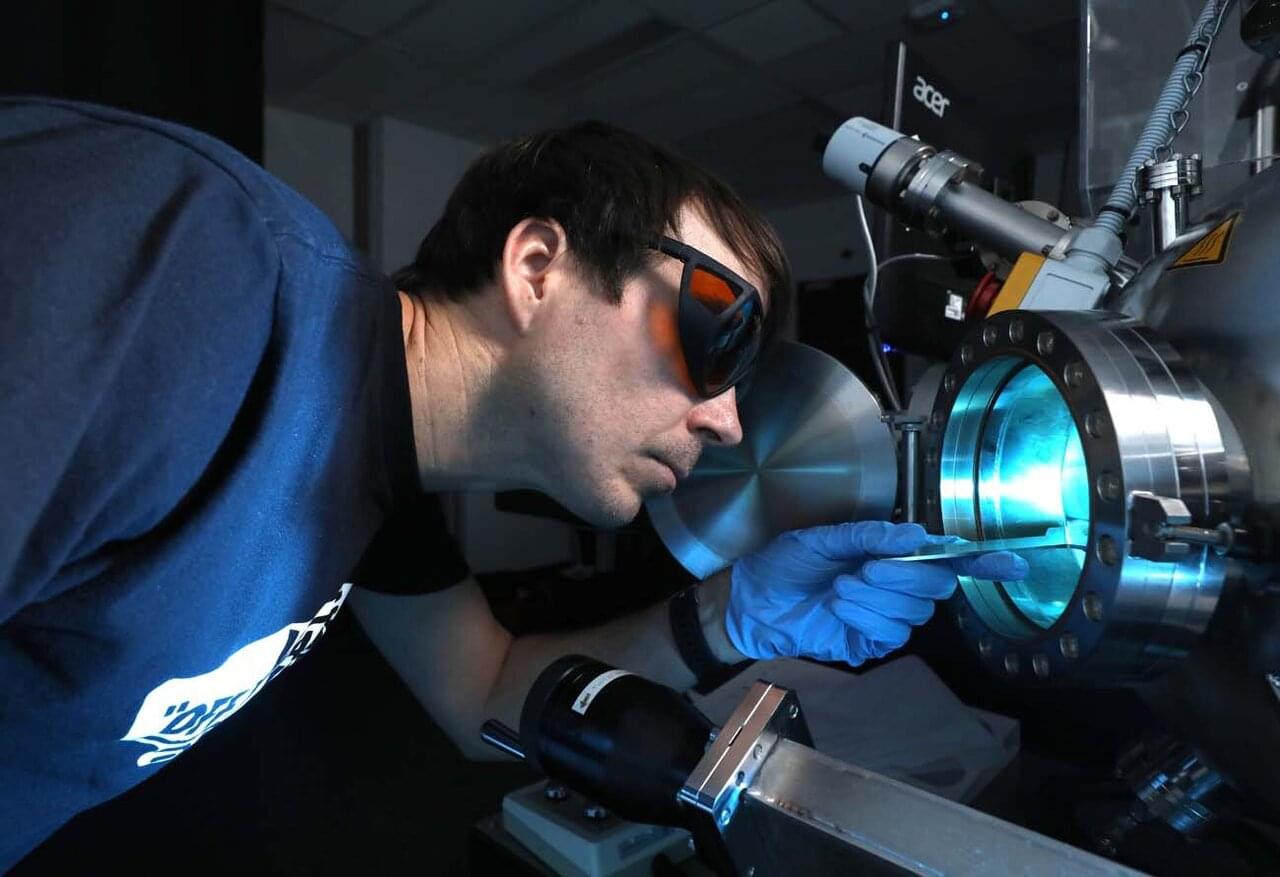
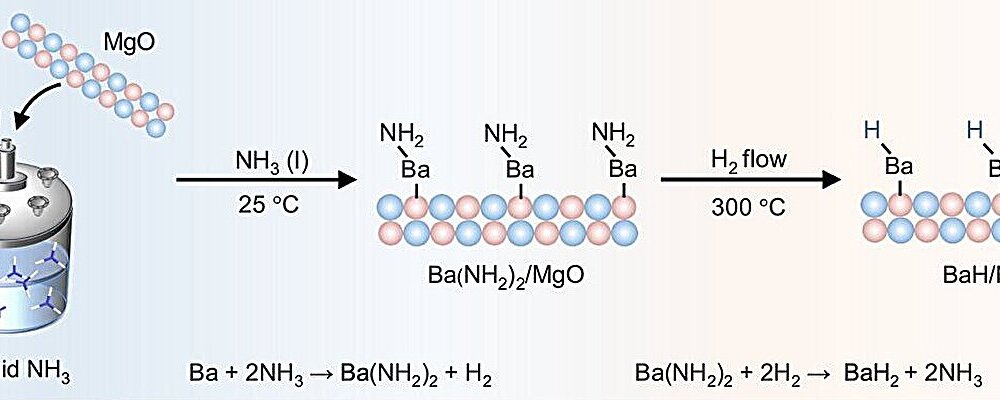
Researchers synthesized atomically dispersed barium hydride catalysts on magnesium oxide (BaH/MgO) using a convenient impregnation-hydrogenation method. This (sub)nanostructured hydride material acted as an efficient, transition metal-free heterogeneous catalyst for hydrogen activation and hydrogen isotope exchange reactions across a range of nonactivated alkylarene substrates.