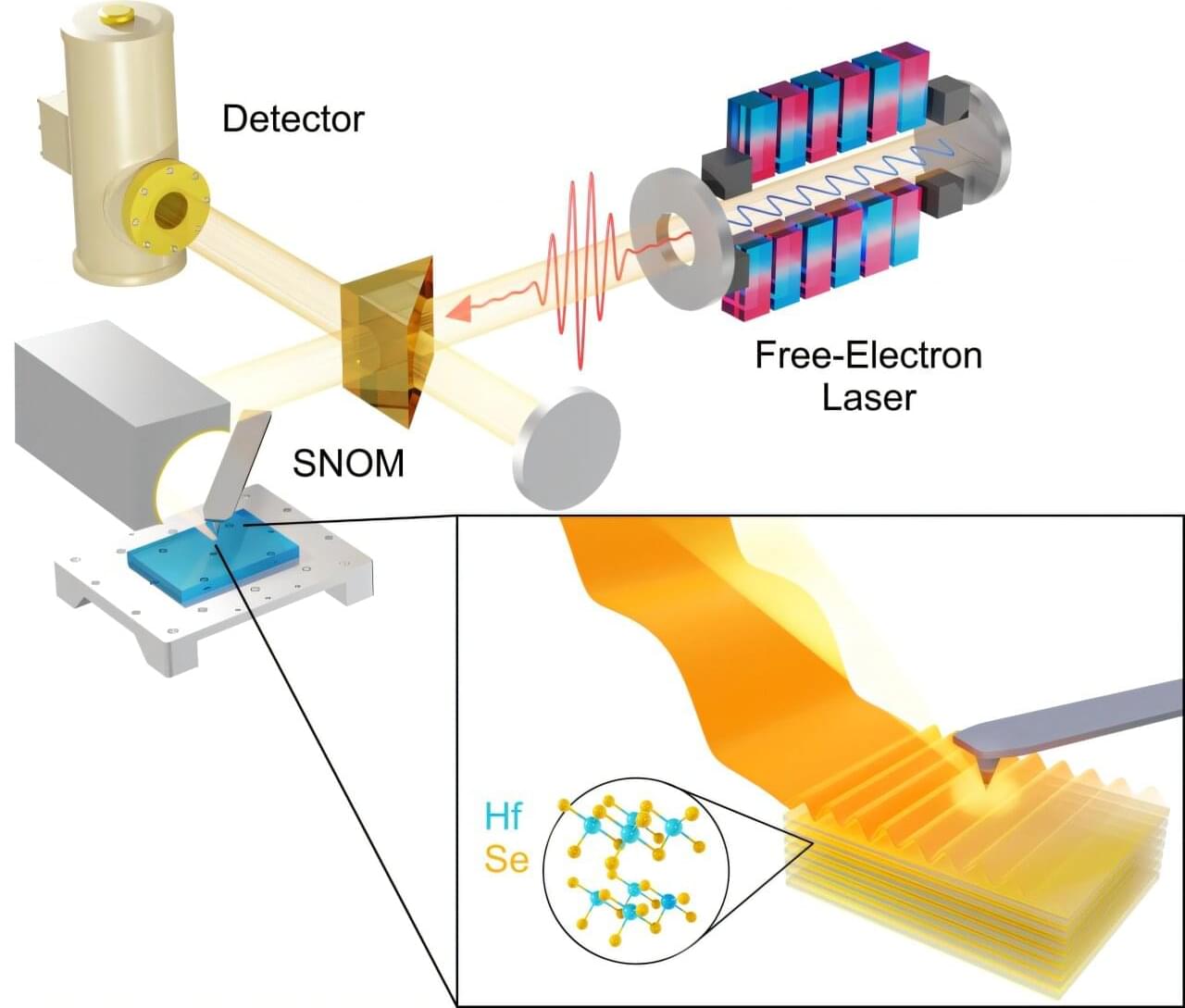
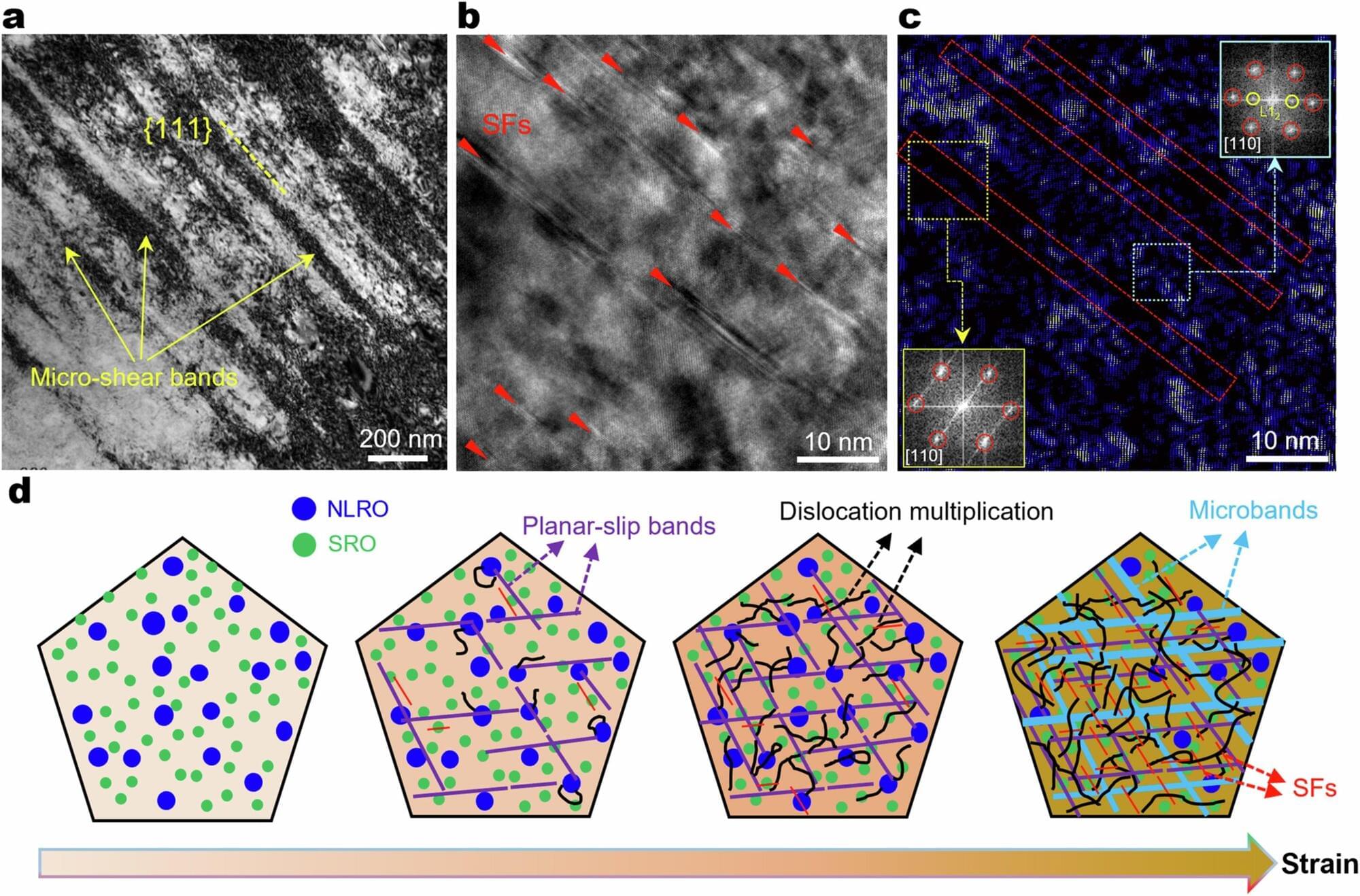
A new study has successfully demonstrated the confinement of terahertz (THz) light to nanoscale dimensions using a new type of layered material. This could lead to improvements in optoelectronic devices such as infrared emitters used in remote controls and night vision and terahertz optics desired for physical security and environmental sensing.
The paper, “Ultraconfined terahertz phonon polaritons in hafnium dichalcogenides,” is published in Nature Materials. The research was led by Josh Caldwell, professor of mechanical engineering and Director of the Interdisciplinary Materials Science graduate program at Vanderbilt University, and Alex Paarmann of the Fritz Haber Institute in collaboration with Prof. Lukas M. Eng from the Technische Universität Dresden (TUD), Germany.
While THz technology promises high-speed data processing, integrating it into compact devices has been challenging due to its long wavelength. Traditional materials have struggled to confine THz light effectively, limiting the potential for miniaturization.