Read writing from Sebastian Schepis on Medium. Software engineer, CTO, Co-Pi@Daigle Labs, mystic, meditator, father, friend. My interests include consciousness, prime numbers, math, music, people, nature.


Hula hooping is so commonplace that we may overlook some interesting questions it raises: “What keeps a hula hoop up against gravity?” and “Are some body types better for hula hooping than others?” A team of mathematicians explored and answered these questions with findings that also point to new ways to better harness energy and improve robotic positioners.
The results are the first to explain the physics and mathematics of hula hooping.
“We were specifically interested in what kinds of body motions and shapes could successfully hold the hoop up and what physical requirements and restrictions are involved,” explains Leif Ristroph, an associate professor at New York University’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and the senior author of the paper, which appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
A new study explores tetraquarks, predicts new exotic particles, and offers deeper insights into their complex structure and behavior.
A new study offers significant advancements in the understanding of tetraquarks — a rare and complex type of particle.
By developing a new approach that combines advanced mathematical methods with a simpler model of how particles interact, the researchers have made important discoveries about the inner structure and mass of these particles.
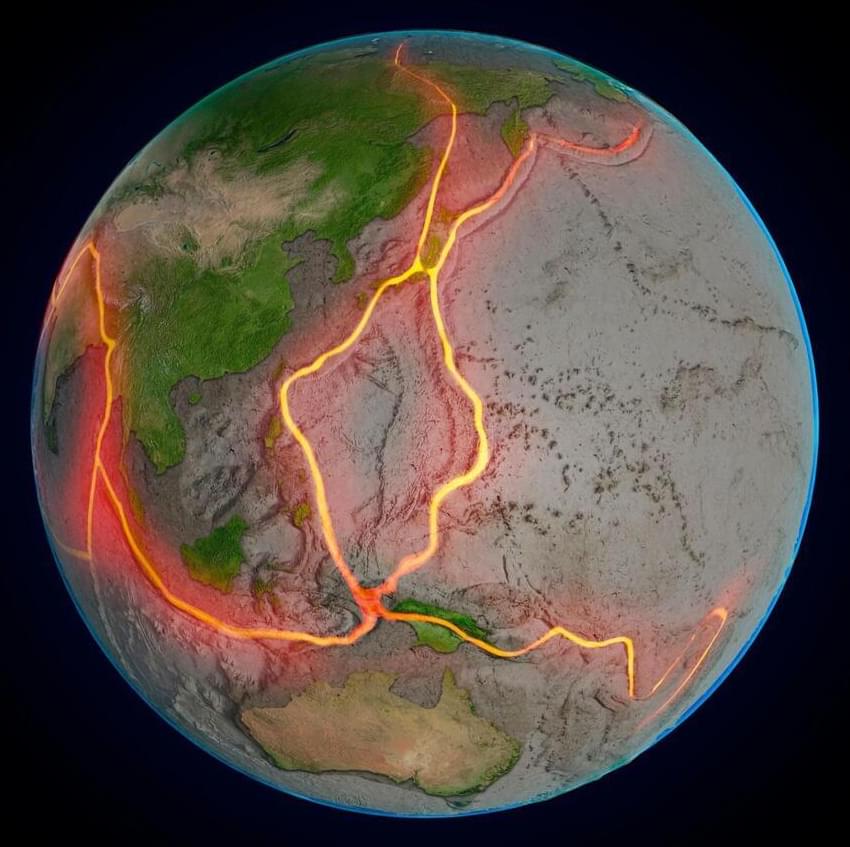

New research on the Denali Fault reveals three geologic sites were once united in a suture zone, marking the integration of Wrangellia into North America. The study uses inverted metamorphism and monazite analysis to trace tectonic history.
New research has revealed that three sites along a 620-mile segment of Alaska’s Denali Fault were once part of a smaller, unified geologic structure, marking the final connection of two ancient land masses. Over millions of years, this structure was torn apart by tectonic forces.
The study, led by Sean Regan, an associate professor at the University of Alaska Fairbanks (UAF) Geophysical Institute and the UAF College of Natural Science and Mathematics, is featured on the cover of the December issue of Geology, the journal of the Geological Society of America.
What is the deepest level of reality? In this Quanta explainer, Vijay Balasubramanian, a physicist at the University of Pennsylvania, takes us on a journey through space-time to investigate what it’s made of, why it’s failing us, and where physics can go next.
Explore black holes, holograms, “alien algebra,” and more space-time geometry: https://www.quantamagazine.org/the-un…
00:00 — The Planck length, an intro to space-time.
1:23 — Descartes and Newton investigate space and time.
2:04 — Einstein’s special relativity.
2:32 — The geometry of space-time and the manifold.
3:16 — Einstein’s general relativity: space-time in four dimensions.
3:35 — The mathematical curvature of space-time.
4:57 — Einstein’s field equation.
6:04 — Singularities: where general relativity fails.
6:50 — Quantum mechanics (amplitudes, entanglement, Schrödinger equation)
8:32 — The problem of quantum gravity.
9:38 — Applying quantum mechanics to our manifold.
10:36 — Why particle accelerators can’t test quantum gravity.
11:28 — Is there something deeper than space-time?
11:45 — Hawking and Bekenstein discover black holes have entropy.
13:54 — The holographic principle.
14:49 — AdS/CFT duality.
16:06 — Space-time may emerge from entanglement.
17:44 — The path to quantum gravity.
——-
VISIT our website: https://www.quantamagazine.org.
LIKE us on Facebook: / quantanews.
FOLLOW us Twitter: / quantamagazine.
Quanta Magazine is an editorially independent publication supported by the Simons Foundation: https://www.simonsfoundation.org

Sir Roger Penrose, a name synonymous with genius, has tirelessly pursued the secrets of the universe with the fervour of a true renaissance seer. His intellectual contributions span a breathtaking range, from the intricate beauty of Penrose tilings to the vast expanse of cosmology, and even the enigmatic depths of human consciousness.
A non-technical introduction to platonism in the philosophy of mathematics.
Philosophy of mathematics is important, especially for philosophers interested in metaphysics. Suppose, for instance, you have nominalist tendencies, and you argue against the existence of abstract objects. Well, probably the most important kind of abstract objects are found in mathematics. Any serious nominalist needs to give an account of them.
Yet philosophy of mathematics is also, for obvious reasons, quite technical, and it can be pretty daunting for those who have less mathematical training. Nevertheless, I think the basic arguments can be made accessible to anyone who’s interested, and that’s what I’ve tried to do in this video.
For further reading on phil of mathematics, I recommend: “Thinking About Mathematics” by Stewart Shapiro and “Introducing Philosophy of Mathematics” by Michele Friend. These are both fairly orthodox introductions. For an introduction that focuses more on contemporary issues (it has just a few pages devoted to formalism, logicism, and intuitionism, yet a whole chapter on paraconsistent mathematics), I recommend “An Introduction to the Philosophy of Mathematics” by Mark Colyvan.
There is some debate about how exactly to formulate the Quine-Putnam Indispensability Argument. In this video, I’ve followed Colyvan (see his aforementioned “Introduction”).
Re 43:26: I’m not sure why I said that. Obviously, Von Neumann did not hold the absurd belief that every ordinal *is* the ordinal before it; rather he believed that every ordinal is *the set of* all ordinals before it.

Users of Google’s Chrome browser can rest easy knowing that their surfing is secure, thanks in part to cryptographer Joppe Bos. He’s coauthor of a quantum-secure encryption algorithm that was adopted as a standard by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in August and is already being implemented in a wide range of technology products, including Chrome.
Rapid advances in quantum computing have stoked fears that future devices may be able to break the encryption used by most modern technology. These approaches to encryption typically rely on mathematical puzzles that are too complex for classical computers to crack. But quantum computers can exploit quantum phenomena like superposition and entanglement to compute these problems much faster, and a powerful enough machine should be able to break current encryption.
Simulations deliver hints on how the multiverse produced according to the many-worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics might be compatible with our stable, classical Universe.
We understand quantum mechanics well enough to make stunningly accurate predictions, ranging from atomic spectra to the structure of neutron stars, and to successfully exploit these predictions in devices such as lasers, MRI machines, and tunneling microscopes. Yet there is no generally accepted explanation of how the solid reality of such devices—or of objects such as cats, moons, and people—arise from a nebulous quantum wave in an abstract mathematical space. Some physicists prefer to ignore the problem, suggesting that we should just “shut up and calculate!” Others seek answers by modifying quantum theory in various ways or by searching for ways to explain how stable structures can emerge from quantum theory itself.
