By extending the scope of the key insight behind Fermat’s Last Theorem, four mathematicians have made great strides toward building a “grand unified theory” of math.



The universe speaks in mathematics, yet we experience it in poetry. This fundamental paradox — that objective quantities somehow give rise to subjective qualities — represents perhaps the most profound mystery in the architecture of consciousness. At the precise intersection where measurable physical magnitudes transform into felt experience lies perception itself, functioning as the universe’s most elegant translation device, converting the quantitative substrate of reality into the qualitative texture of conscious life.
Consider the photon, that discrete packet of electromagnetic energy oscillating at precisely 550 nanometers. Physics describes it with mathematical precision: wavelength, frequency, amplitude — pure quantity divorced from any subjective dimension. Yet when this photon encounters the rhodopsin molecules within our retinal cells, something extraordinary occurs. The quantitative description remains accurate but suddenly insufficient. The same electromagnetic radiation that physics measures as wavelength 550nm becomes, through the alchemy of perception, the irreducible experience we call “green.” This transformation represents not merely a change in descriptive language but a fundamental ontological shift — the emergence of an entirely new category of being.
Maurice Merleau-Ponty recognized this threshold when he observed that “the body is our general medium for having a world” (Merleau-Ponty, 1945/2012, p. 147). The lived body serves as the crucial mediator between the quantitative realm that physics describes and the qualitative realm that consciousness inhabits. Through our sensorimotor engagement with the world, objective magnitudes undergo a metamorphosis into subjective meanings. The body is not merely a receiver of information but an active participant in the creation of experiential reality itself.
Mathematicians have started to prepare for a profound shift in what it means to do mathematics.

A fresh study suggests that the way a person’s pupils change while they concentrate hints at how well that mental scratchpad is working.
Working memory does more than hold stray reminders; it stitches together phone digits until they are dialed, keeps track of a spoken sentence until the meaning lands, and buffers half-finished ideas during problem-solving.
Unlike long-term memory, it works on a tight clock measured in seconds. Because the capacity is finite – typically three to seven items at once – small differences in efficiency can ripple through reading, mathematics, and decision-making.
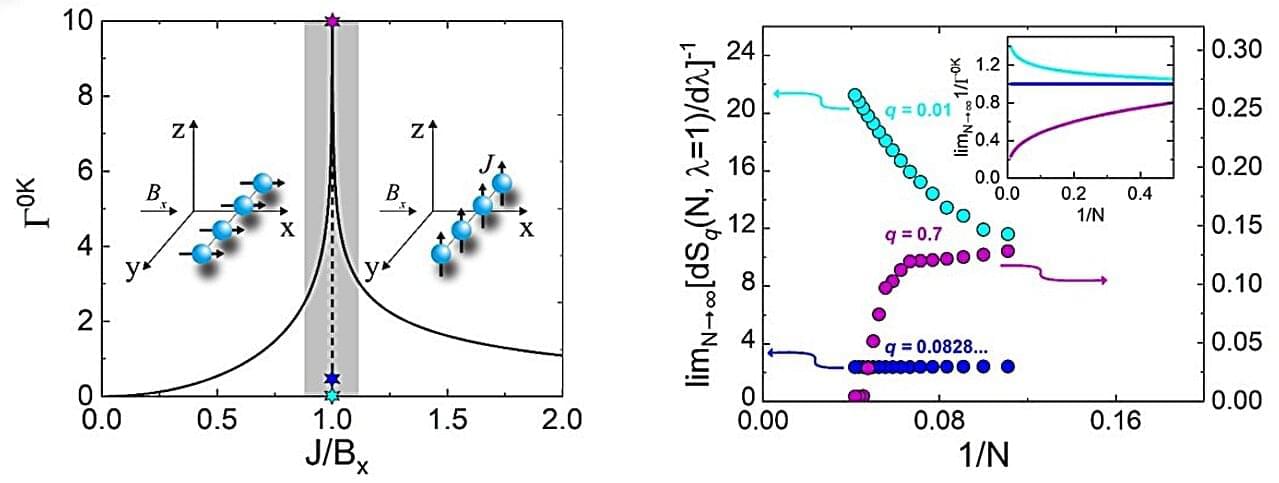
Statistical mechanics is one of the pillars of modern physics. Ludwig Boltzmann (1844–1906) and Josiah Willard Gibbs (1839–1903) were its primary formulators. They both worked to establish a bridge between macroscopic physics, which is described by thermodynamics, and microscopic physics, which is based on the behavior of atoms and molecules.
The Austrian physicist Boltzmann explained the second law of thermodynamics in statistical terms. He defined the entropy of a system based on the number of possible microstates it could assume.
Unlike Boltzmann, who focused more on the physics of gases and the distribution of particles in equilibrium, the American Gibbs developed a general mathematical formalism that could be extended to more complex systems. Together, their contributions formed the basis of a physics capable of modeling a wide variety of phenomena.
What If Math uses a relatively new concept to enhance the way math is taught so that kids are given more relevant skills for today’s digital world.
The company says that the way math — and algebra specifically — is taught today is based on a concept developed by Leonardo of Pisa in 1202 as a way to help traders. This, it says, is now redundant thanks to all the digital tools that use spreadsheets to do that part of mathematical working.
Make a donation to Closer To Truth to help us continue exploring the world’s deepest questions without the need for paywalls: https://shorturl.at/OnyRq.
For subscriber-only exclusives, register for a free membership today: https://bit.ly/3He94Ns.
Mathematics is like nothing else. The truths of math seem to be unrelated to anything else—independent of human beings, independent of the universe. The sum of 2 + 3 = 5 cannot not be true; this means that 3 + 2 = 5 would be true even if there were never any human beings, even if there were never a universe! When then, deeply, is mathematics?
Support the show with Closer To Truth merchandise: https://bit.ly/3P2ogje.
Watch more interviews on mathematics: https://bit.ly/48H9RS7
Mark Balaguer is Professor of Philosophy at California State University, Los Angeles. His major book is Platonism and Anti-Platonism in Mathematics.
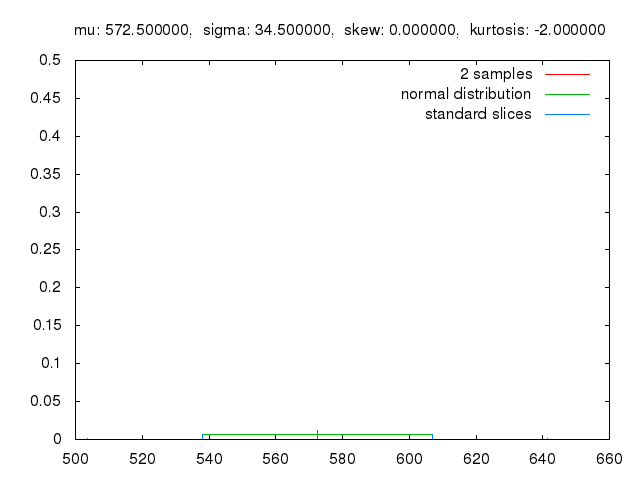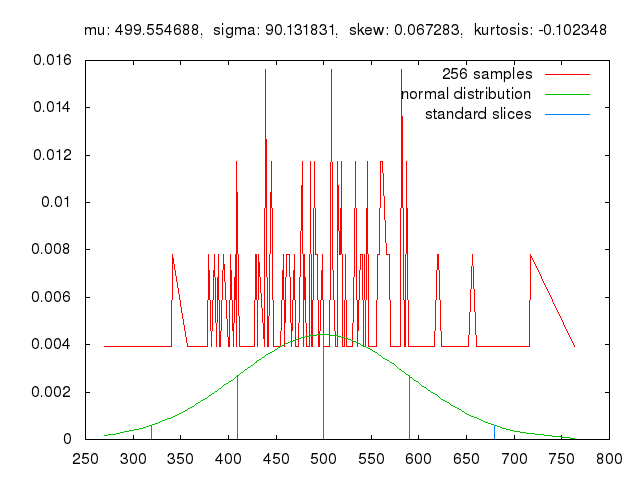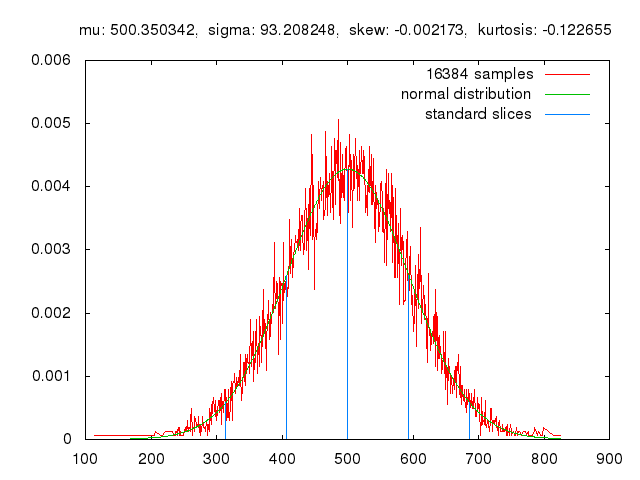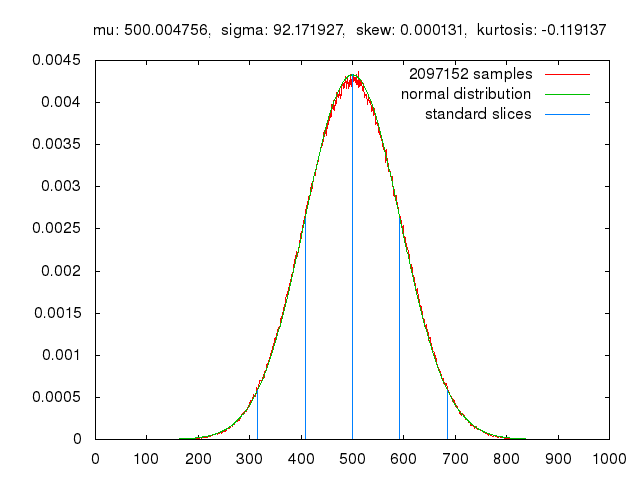
Monte Carlo methods, or Monte Carlo experiments, are a broad class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results. The underlying concept is to use randomness to solve problems that might be deterministic in principle. The name comes from the Monte Carlo Casino in Monaco, where the primary developer of the method, mathematician Stanisław Ulam, was inspired by his uncle’s gambling habits.
Monte Carlo methods are mainly used in three distinct problem classes: optimization, numerical integration, and generating draws from a probability distribution. They can also be used to model phenomena with significant uncertainty in inputs, such as calculating the risk of a nuclear power plant failure. Monte Carlo methods are often implemented using computer simulations, and they can provide approximate solutions to problems that are otherwise intractable or too complex to analyze mathematically.
Monte Carlo methods are widely used in various fields of science, engineering, and mathematics, such as physics, chemistry, biology, statistics, artificial intelligence, finance, and cryptography. They have also been applied to social sciences, such as sociology, psychology, and political science. Monte Carlo methods have been recognized as one of the most important and influential ideas of the 20th century, and they have enabled many scientific and technological breakthroughs.

What if black holes weren’t the only things slowly vanishing from existence? Scientists have now shown that all dense cosmic bodies—from neutron stars to white dwarfs—might eventually evaporate via Hawking-like radiation.
Even more shocking, the end of the universe could come far sooner than expected, “only” 1078 years from now, not the impossibly long 101100 years once predicted. In an ambitious blend of astrophysics, quantum theory, and math, this playful yet serious study also computes the eventual fates of the Moon—and even a human.
Black Holes Aren’t Alone