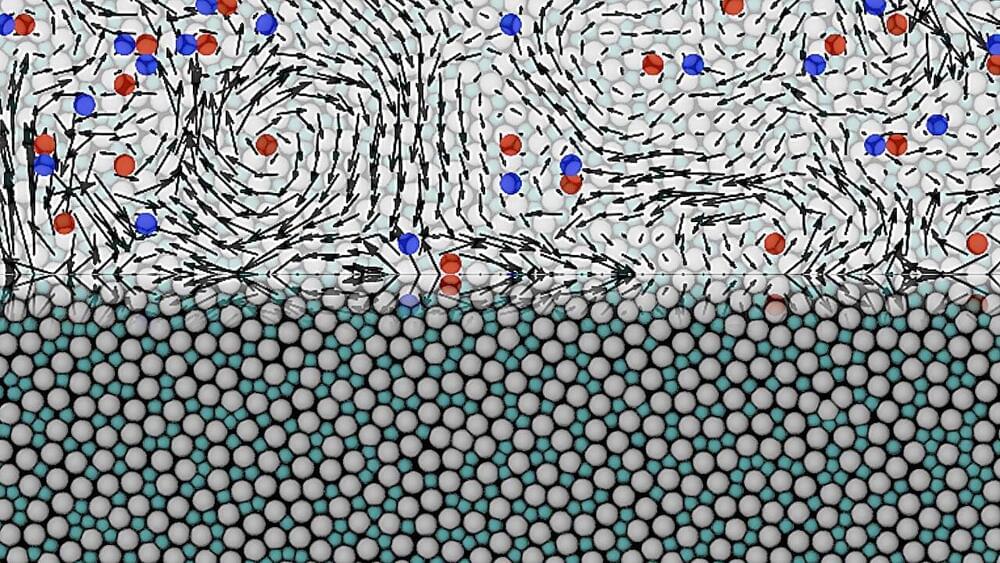
The amorphous state of matter is the most abundant form of visible matter in the universe, and includes all structurally disordered systems, such as biological cells or essential materials like glass and polymers.
An amorphous material is a solid whose molecules and atoms form disordered structures, meaning that they do not occupy regular, well-defined positions in space.
This is the opposite of what happens in crystals, whose ordered structure facilitates their mathematical description, as well as the identification of those “defects,” which practically control the physical properties of crystals, such as their plastic yielding and melting, or the way an electric current propagates through them.