Harnessing Terahertz Light for Magnetic Control
MIT physicists have discovered a way to create a new, long-lasting magnetic state in a material using only light.

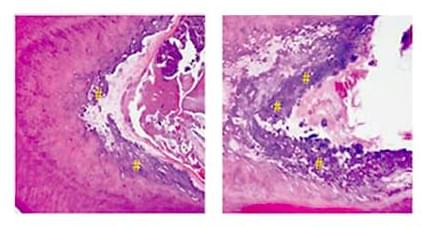
A small dose of low-power laser light activated dental stem cells in rat molars to generate dentin, one of the major components of teeth. The finding may lead to new approaches to develop low-cost, non-invasive therapies for treating dental disease and tooth damage.
Dentists currently use inert materials to repair damaged teeth. Tissue regeneration would be an attractive alternative, because inert materials can fail with time and don’t provide the full function of the tissue. Stimulating regeneration of teeth, however, is a major challenge. Teeth are composed of several parts, including the pulp at the core, dentin in the middle, and enamel on the surface.
Stem cells, found throughout the body, can give rise to specialized cells. Researchers have been able to coax stem cells to transform (differentiate) into many types of cells in the laboratory before infusing them into the body. But these techniques are time consuming and can bring unwanted side effects.

The soft metal bismuth may be a wonder material for electronics – particularly because of one surprising behaviour it displays when exposed to magnetic fields.
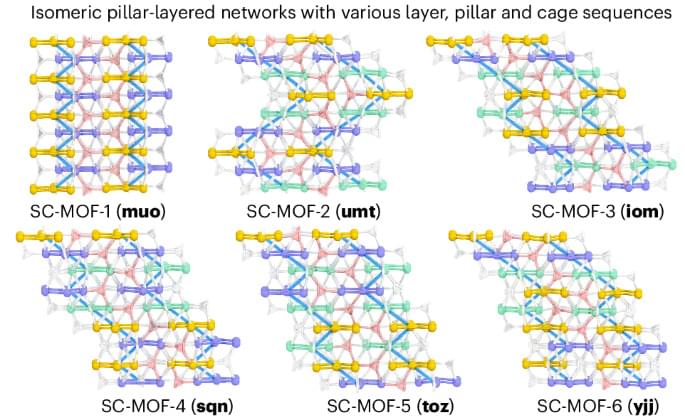
The tailoring of reticular materials is key for enhancing the complexity and diversity of their structure and function. Now, a series of isomeric pillar-layered metal–organic frameworks with tunable topologies have been prepared through altering the layer stacking, which enables variability on the backbone structure, pillar spatial arrangements and pore structure.

In the first study, a team led by Professor Jong-sung Yu at the DGIST Department of Energy Science and Engineering developed a nitrogen-doped porous carbon material to enhance the charging speed of lithium-sulfur batteries. This material, synthesized using a magnesium-assisted thermal reduction method, acts as a sulfur host in the battery cathode. The resulting battery exhibited remarkable performance, achieving a high capacity of 705 mAh g⁻¹ even when fully charged in just 12 minutes.
The carbon structure, formed by the reaction of magnesium with nitrogen in ZIF-8 at high temperatures, enabled higher sulfur loading and improved electrolyte contact. This advancement resulted in a 1.6-fold increase in capacity compared to conventional batteries under rapid charging conditions. Furthermore, the nitrogen doping effectively suppressed lithium polysulfide migration, allowing the battery to retain 82 percent of its capacity after 1,000 charge-discharge cycles.
Collaboration with Argonne National Laboratory revealed that lithium sulfide formed in a specific orientation within the carbon material’s layered structures. This finding confirmed the benefits of nitrogen doping and the porous carbon structure in boosting sulfur loading and accelerating reaction speed.

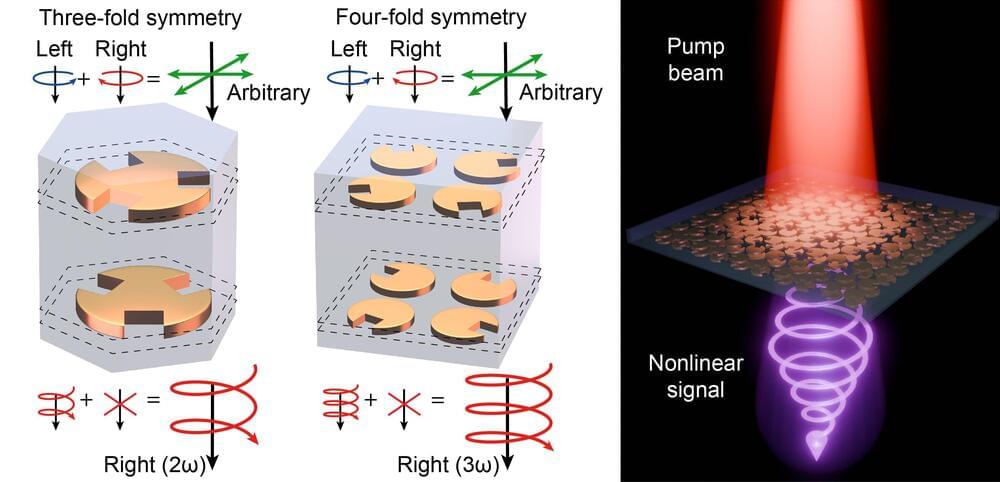
Left and right circularly polarized light, where the electromagnetic waves spiral in a clockwise and counterclockwise manner as they travel, plays a crucial role in a wide range of applications, from enhancing medical imaging techniques to enabling advanced communication technologies. However, generating circularly polarized light often requires complex and bulky optical set-ups, which hinders its use in systems with space constraints.
To address this challenge, a team of researchers from Singapore led by Associate Professor Wu Lin of Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) has put forth a new type of metasurface—an ultra-thin material with properties not found in nature—that may be able to replace traditional complex and bulky optical set-ups.
They have published their research in the Physical Review Letters paper “Enabling all-to-circular polarization up-conversion by nonlinear chiral metasurfaces with rotational symmetry.”
So-called “infinite-layer” nickelate materials, characterized by their unique crystal and electronic structures, exhibit significant potential as high-temperature superconductors. Studying these materials remains challenging for researchers; they have only been synthesized as thin films and then “capped” with a protective layer that could alter properties of the nickelate layered system.
To address this challenge, a team led by researchers at the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II)—a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science user facility at DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory—used complementary X-ray techniques at two different beamlines to gain new insights into these materials. Their results were published in Physical Review Letters.

A dry material makes a great fire starter, and a soft material lends itself to a sweater. Batteries require materials that can store lots of energy, and microchips need components that can turn the flow of electricity on and off.
Each material’s properties are a result of what’s happening internally. The structure of a material’s atomic scaffolding can take many forms and is often a complex combination of competing patterns. This atomic and electronic landscape determines how a material will interact with the rest of the world, including other materials, electric and magnetic fields, and light.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, as part of a multi-institutional team of universities and national laboratories, are investigating a material with a highly unusual structure—one that changes dramatically when exposed to an ultrafast pulse of light from a laser.