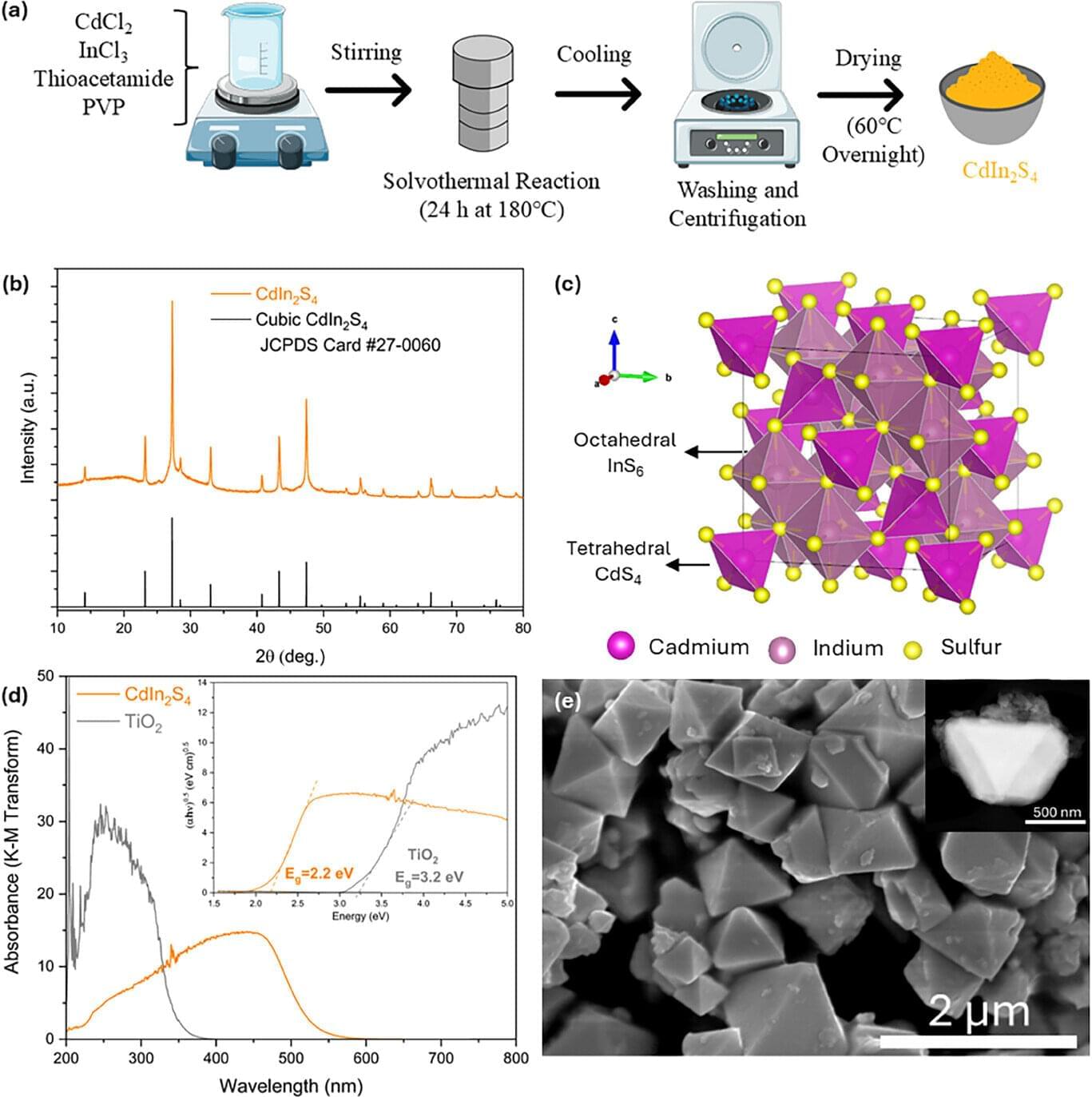
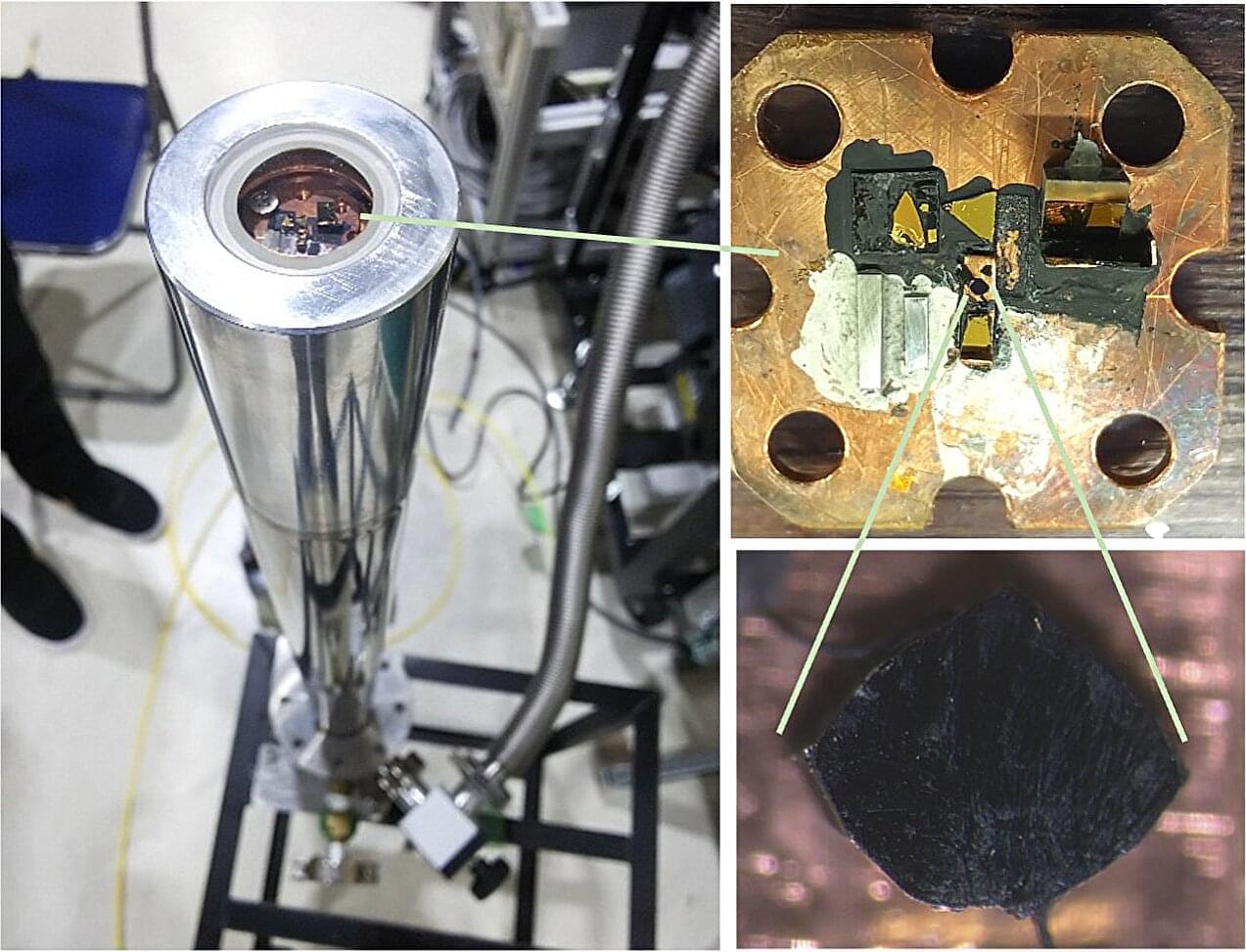
A spiking neural network consists of artificial synapses and neurons and may realize human-level intelligence. Unlike the widely reported artificial synapses, the fabrication of large-scale artificial neurons with good performance is still challenging due to the lack of a suitable material system and integration method. Here, we report an ultrathin (less than10 nm) and inch-size two-dimensional (2D) oxide-based artificial neuron system produced by a controllable assembly of solution-processed 2D monolayer TiOx nanosheets. Artificial neuron devices based on such 2D TiOx films show a high on/off ratio of 109 and a volatile resistance switching phenomenon. The devices can not only emulate the leaky integrate-and-fire activity but also self-recover without additional circuits for sensing and reset. Moreover, the artificial neuron arrays are fabricated and exhibited good uniformity, indicating their large-area integration potential. Our results offer a strategy for fabricating large-scale and ultrathin 2D material-based artificial neurons and 2D spiking neural networks.