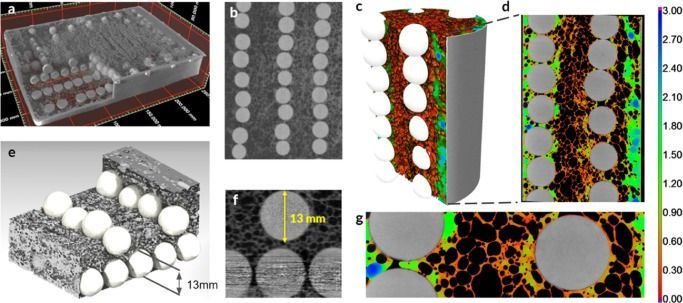
We have created a new architected material, which is both highly deformable and ultra‐resistant to dynamic point loads. The bio-inspired metallic cellular structure (with an internal grid of large ceramic segments) is non-cuttable by an angle grinder and a power drill, and it has only 15% steel density. Our architecture derives its extreme hardness from the local resonance between the embedded ceramics in a flexible cellular matrix and the attacking tool, which produces high-frequency vibrations at the interface. The incomplete consolidation of the ceramic grains during the manufacturing also promoted fragmentation of the ceramic spheres into micron-size particulate matter, which provided an abrasive interface with increasing resistance at higher loading rates. The contrast between the ceramic segments and cellular material was also effective against a waterjet cutter because the convex geometry of the ceramic spheres widened the waterjet and reduced its velocity by two orders of magnitude. Shifting the design paradigm from static resistance to dynamic interactions between the material phases and the applied load could inspire novel, metamorphic materials with pre-programmed mechanisms across different length scales.