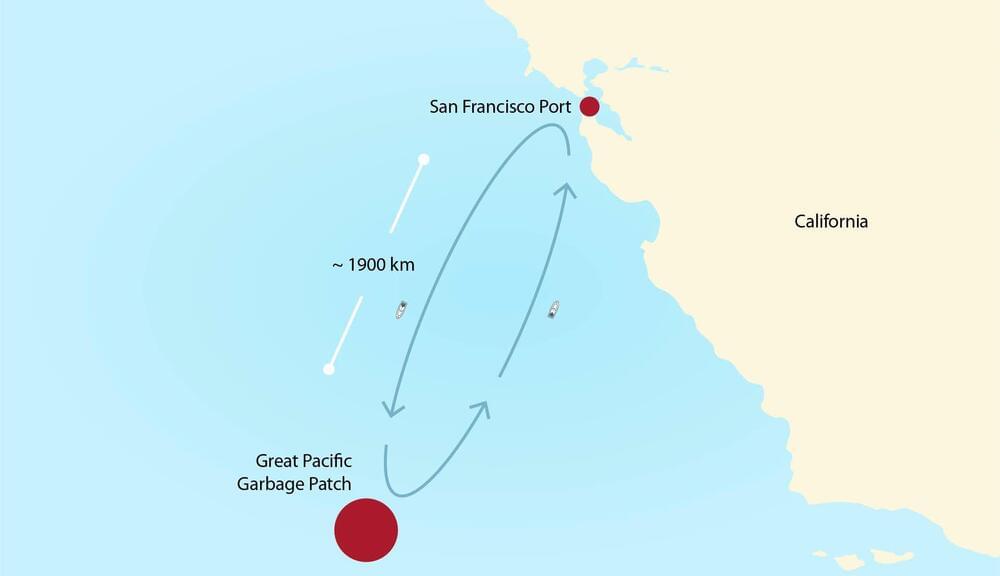
A new type of plastic can rapidly heal itself under water, even in harsh conditions. It maintains its strength after self-healing, so it may be useful in emergencies at sea.
Lili Chen at Tsinghua University in China and her colleagues developed this material, called Rapid Underwater Self-healing Stiff Elastomer (RUSSE) because most self-healing polymers don’t work very well under water. “Room temperature self-healing polymers generally have a poor underwater stability, low healing strength and a slow healing process,” says Chen.
RUSSE is made of small chunks of a type of soft polymer used in some paints connected by nanometre-sized chains of a tougher polymer. The researchers tested the material’s properties by stretching it, cutting it and bashing it with a hammer.