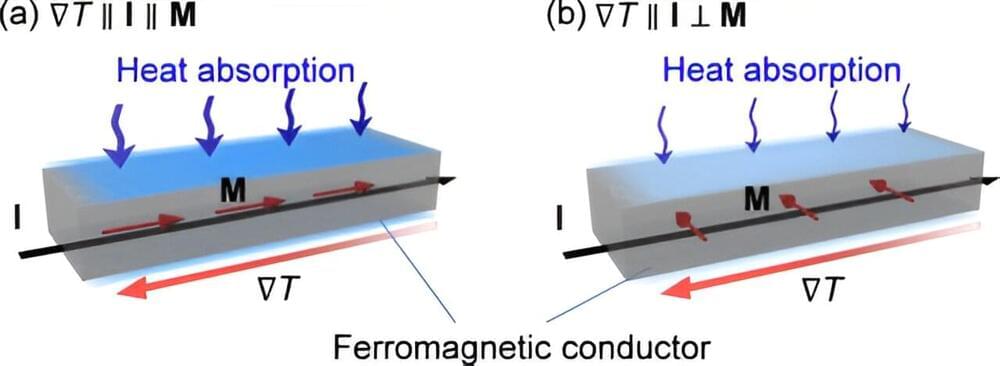
The National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) has succeeded in directly observing the “anisotropic magneto-Thomson effect,” a phenomenon in which the heat absorption/release proportional to an applied temperature difference and charge current (i.e., Thomson effect) changes anisotropically depending on the magnetization direction in magnetic materials.
This research is expected to lead to further development of basic physics and materials science related to the fusion area of thermoelectrics and spintronics, as well as to the development of new functionalities to control thermal energy with magnetism. The study is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
The Thomson effect has long been known as one of the fundamental thermoelectric effects in metals and semiconductors, along with the Seebeck and Peltier effects, which are driving principles of thermoelectric conversion technologies.