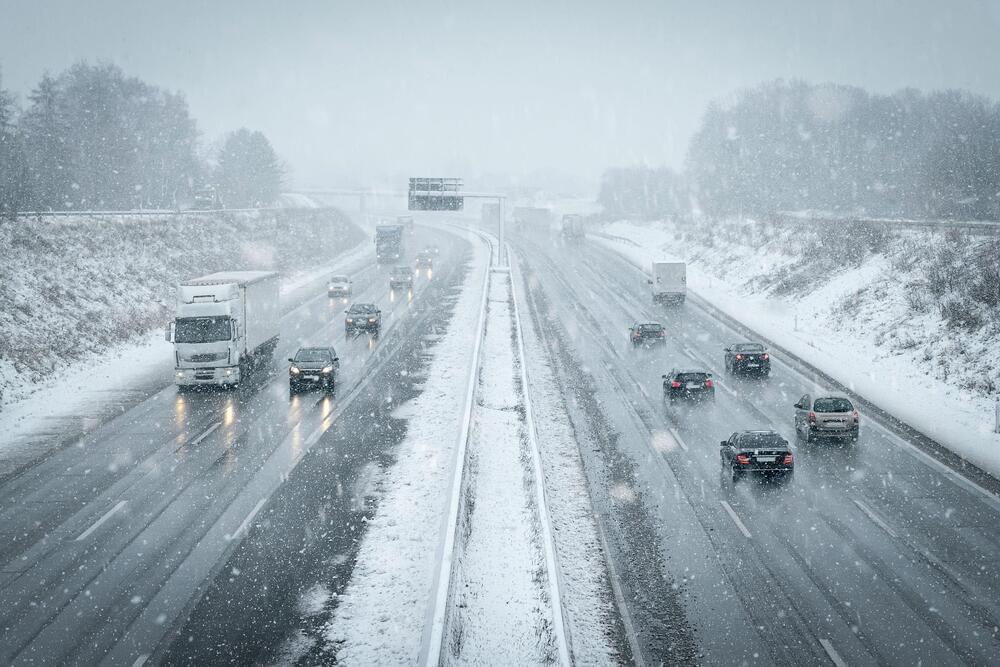
Incorporating a phase-change material into concrete, researchers have created a self-heating material that can melt snow and ice for up to 10 hours without using salt or shovels. The novel material could reduce the need for plowing and salting and help preserve the integrity of road surfaces.
According to the US Department of Transportation (DOT), more than 70% of roads are in snowy regions. Snow and ice accumulation reduces road friction and vehicle maneuverability, causing drivers to slow and increasing the risk of crashes. Snow-obstructed lanes and roads also reduce roadway capacity and increase travel time.
The DOT states that local and state agencies spend more than US$2.3 billion annually on snow and ice control operations, in addition to the millions spent repairing infrastructure damage caused by snow and ice. Salting is often used before a snow event to prevent icing, but the highly concentrated salt solution can deteriorate concrete or asphalt. In addition, when water seeps into the road and freezes, it expands, causing internal pressure and damaging the road.